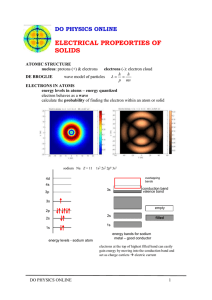
Examples
advertisement
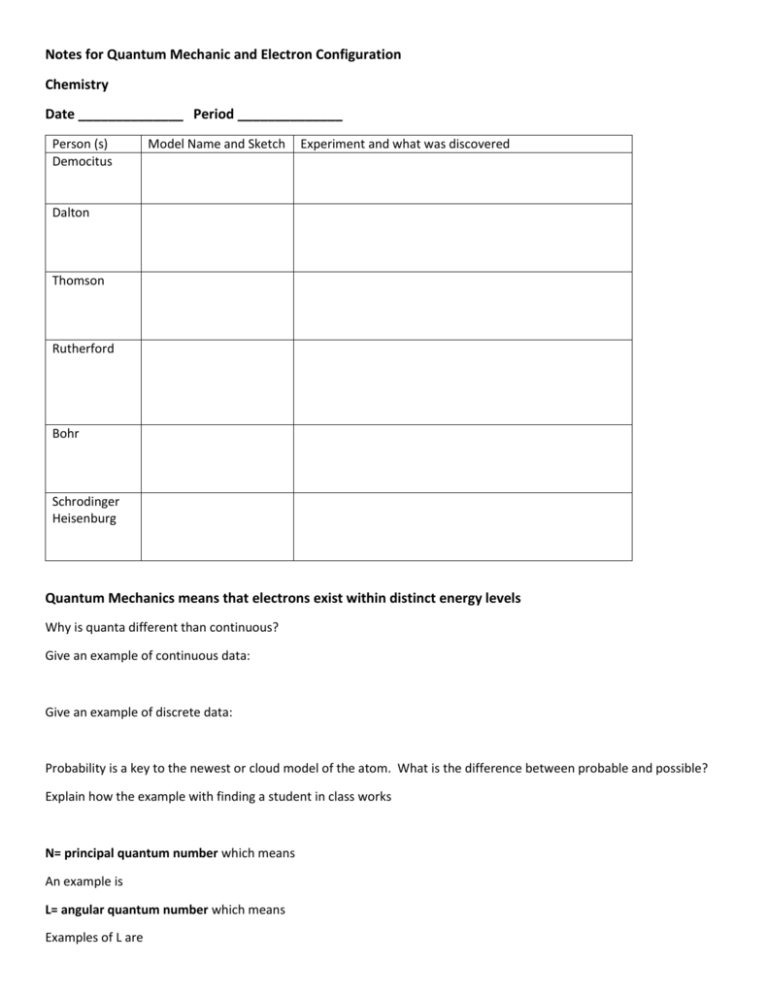
Notes for Quantum Mechanic and Electron Configuration Chemistry Date ______________ Period ______________ Person (s) Democitus Model Name and Sketch Experiment and what was discovered Dalton Thomson Rutherford Bohr Schrodinger Heisenburg Quantum Mechanics means that electrons exist within distinct energy levels Why is quanta different than continuous? Give an example of continuous data: Give an example of discrete data: Probability is a key to the newest or cloud model of the atom. What is the difference between probable and possible? Explain how the example with finding a student in class works N= principal quantum number which means An example is L= angular quantum number which means Examples of L are orbital (L) s sketch where on p. table? p d f g How many electrons can each orbital hold? Ml = magnetic quantum number which shows the orientation (x, y, z etc) of the orbital s orientation number of orientations p p p d d d d d f g Ms = spin quantum number There are _____ electrons in every orbital. They have ___________ spins. By agreement, we give the first electron a designation as ________________ and the second as _________________. Electron Configuration We use the _____________ method to fill the orbitals. This just means : “House Model” 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 N s p ___rooms Means d _____ rooms means f ______ rooms =L = Ml = Ms Why does 1s fill first? Why are the d levels “dropped”? Why are the f levels “fallen” out? Where is g? Periodic Table Blocks: Put the N (energy level), and L (orbital of s, p, d, f), Each element has a ___________________ atomic number and _______________. If two elements, like H and He, share the N, M and Ml quantum numbers then the __________ will be different. The location of an element on the periodic table tell us the electron configuration and the electron configuration tell us _____________________________________________________. Examples: put the element name 1s2 2s2 2p2 valence is ___________ total electrons ___________ 1s2 2s2 2p6 valence is ___________ total electrons _____________ 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 valence is ___________ total electrons _________________ 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3 valence is ___________ total electrons _________ shorthand [ 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 valence is ____ total electrons ________ shorthand [ Examples: put the superscript and cross out the orbitals with no electrons H 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p valence is __________ He 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p valence is __________ Li 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p valence is __________ Na 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p valence is __________ Shorthand [ ] Al 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p valence is __________ Shorthand [ ] Ar 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p valence is __________ Shorthand [ ] Why is the atom a “fuzzy blob of uncertainty”? What does electron configuration tell us that is useful? ] ]