t7_solidsel
advertisement

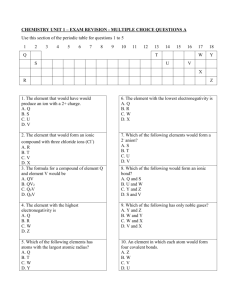
DO PHYSICS ONLINE ELECTRICAL PROPEORTIES OF SOLIDS ATOMIC STRUCTURE nucleus: protons (+) & electrons electrons (-): electron cloud h h DE BROGLIE wave model of particles p mv ELECTRONS IN ATOMS energy levels in atoms – energy quantized electron behaves as a wave calculate the probability of finding the electron within an atom or solid sodium Na Z = 11 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 overlapping bands 4d 4s 3p 3s conduction band valence band 3s empty 2p 2s 1s energy levels - sodium atom 2s filled 1s energy bands for sodium metal – good conductor electrons at the top of highest filled band can easily gain energy by moving into the conduction band and act as charge carriers electric current DO PHYSICS ONLINE 1 ELECTRONS IN SOLIDS ENERGY BANDS IN SOLIDS – energy quantized – electrons in atoms Electronic configurations (atoms) diamond C Z=6 aluminum Al Z = 13 silicon Si Z = 14 phosphorus P Z = 15 gallium Ga Z = 31 germanium Ge Z = 32 arsenic As Z = 33 1s2 2s2 2p2 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3p10 4s2 4p1 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3p10 4s2 4p2 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3p10 4s2 4p3 Energy band theory of solids Conductivity (resistance), relative abundance of free electrons (conduction electrons) A I nqv A R L insulators high resistance conductors resistance increase with temperature semiconductors resistance decrease with temperature Diamond is a very good insulator. The electronic configuration in the ground state is 1s2 2s2 2p2. It might appear that diamond is a conductor because it has only two electrons in the 2p energy level and that the 2p band is only partly filled. However, there are two distinct 2p energy bands separated from each other by an energy gap of 6 eV. The lower 2p band is completely filled. At room temperature, energy due to thermal motion is only about 0.03 eV, much small than the energy gap, so virtually no electrons will be found in the upper 2p energy band. Silicon has a much smaller band gap and therefore less energy is required for electrons to be free electrons and take part in conduction. energy bands for diamond insulator C Z=6 energy bands for silicon semiconductor Si Z = 14 1s2 2s2 2p2 forbidden band exists between two 3p bands forbidden band exists between two 2p bands 2p conduction band Egap 2p Egap valence band 3s 2p 2s 1s 3p 3p valence band 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 Egap ~ 6 eV 2s Egap ~ 1 eV 1s DO PHYSICS ONLINE 2 electron energy In a semiconductor – holes drift in the direction of the externally applied electric field and the free electrons move in the opposite direction. electron energy The greater the number of charged carriers in the conduction band, the better the conduction. insulator semiconductor conductor Intrinsic Semiconductors valence 4 Ge Si germanium Ge first used in transistors (other pure materials not available at the time) becomes conducting very easily with temperature silicon Si today, most widely used semiconductor material (at first was difficult to purify) Do problems p3.13 DO PHYSICS ONLINE p3.57 3 Extrinsic (Doped) Semiconductors see Periodic Table n type semiconductors – electrons valence 5 P, As donor levels n type semiconductor – a donor impurity atom has a 5th valence electron that does not participate in the covalent bonding and is very loosely bound. It is relatively easy for an electron to be excited from the donor level into the conduction band where it acts as a charge carrier – charge carriers are mainly negative electrons in the conduction band. p type semiconductors – holes (absence of electron) valence 3 Al, Ga, In acceptor levels p type semiconductor – acceptor impurity atom has only 3 valence electrons, so it can borrow an electron from a neighbouring atom. An electron can move from the valance band to the acceptor level creating a hole in the valance band. The resulting hole is free to move about the crystal – positive charge carriers moving in valence band. DO PHYSICS ONLINE 4 Do problems p3.55 p3.18 p3.22 p3.23 ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS np junction – diodes rectifiers – AC to DC (current single direction) p + n p n I I=0 + Transistor – switches & amplifiers invention lead to the development of integrated circuits (microchips, microprocessors) Junction transistors (npn, pnp) collector base emitter Valves thermionic devices - evacuated glass containers (gas at low pressure) electrons released from hot filament – thermionic emission large (bulky) hot – used lots of energy diodes – rectification triodes – amplifiers, switches Solid state devices - miniaturisation diodes (pn junctions) transistors (npn, pnp) IC - integrated circuits consume little power may contain millions of transistors Do problems p3.24 p3.30 p3.77 DO PHYSICS ONLINE p3.33 p.3.44 p3.52 p3.90 p3.92 5 Solar cells – photocells – photovoltaic effect - pn junction Photons are absorbed creating electron-hole pairs if the photon energy is greater than the band gap energy. The holes and electrons produce a current that when connected to an external circuit becomes a source of emf and power. conduction band conduction band energy gap Eg electrons in conduction band evalance band valance band light (photon) f > Eg / h holes in valance band p type p n n type p + n - I emf produces a current to load + load Solar cell – photovoltaic effect - current across a load (resistance) generated when light shines on the p-side of a pn junction Do problems p3.39 DO PHYSICS ONLINE p3.27 p.3.95 6