Characteristics of living things
advertisement

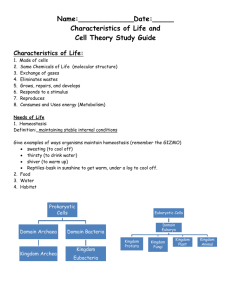
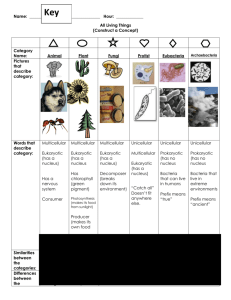
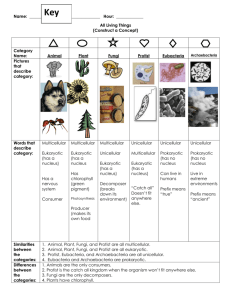
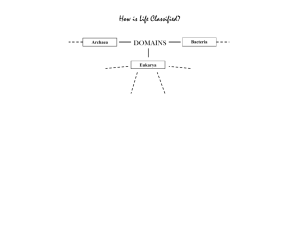
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS The 8 Characteristics of Life All Living Things… are made up of cells (one cell = unicellular / many cells = multicellular) reproduce (on their own = asexual / with another parent = sexual) have a genetic code (DNA) with instructions for growing and reproducing grow and develop use energy and materials respond to their environment control the conditions inside their bodies (maintain homeostasis) Groups of living things adapt/evolve/change over time. Objectives for Class: • List 6 of 8 characteristics that all living things share Two Main Cell Types Eukaryotic (eu = true; karyote = kernel/nucleus) Cells that have a nucleus in which their DNA/ chromosomes are stored Cells that are larger and more complex Prokaryotic (pro = before; karyote = kernel/nucleus) Cells that don’t have a nucleus (DNA just floats around in the cell) Cells that are smaller and simpler Class Objective: Distinguish between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Two main cell types: PROKARYOTES and EUKARYOTES White Blood Cell w/ Cocci (bacteria) Class Objective: Distinguish between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Epithelial Cells w/ Bacilli (bacteria) Two main cell types: PROKARYOTES and EUKARYOTES Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Class Objective: Distinguish between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells DOMAINS & KINGDOMS OF LIFE Domain Bacteria unicellular/microscopic prokaryotic (tiny cells with no nucleus) very diverse – live and eat in many different ways Objectives for Class: 1. Identify and explain two defining characteristics of each kingdom and domain. Domain Archaea unicellular/microscopic Prokaryotic (no nucleus) live in extreme environments (very hot, salty, or acidic places) Objectives for Class: 1. Identify and explain two defining characteristics of each kingdom and domain. Domain Eukarya unicellular OR multicellular all have nucleus eukaryotic (bigger cells w/ nucleus and organelles) includes 4 Kingdoms: Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia Objectives for Class: 1. Identify and explain two defining characteristics of each kingdom and domain. Kingdom Protista all are eukaryotic; most are unicellular most live in water “miscellaneous” category – some are like plant cells, some are like animal cells Objectives for Class: 1. Identify and explain two defining characteristics of each kingdom and domain. Kingdom Fungi mostly multicellular decomposers (feed on dead/decaying things) ex: mushrooms, mold, yeast Objectives for Class: 1. Identify and explain two defining characteristics of each kingdom and domain. Kingdom Plantae multicellular use photosynthesis to make food from sunlight, CO2, and water Objectives for Class: 1. Identify and explain two defining characteristics of each kingdom and domain. Kingdom Animalia multicellular eat other living things for food most can move Objectives for Class: 1. Identify and explain two defining characteristics of each kingdom and domain. BIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM Hierarchical Classification System: Largest category Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Smallest & most Species specific category DOMAIN Eukarya Species Definition and Examples Species – a specific group of living things that have similar characteristics, similar DNA, and can reproduce with each other to make fertile offspring (this means their babies can also have babies) Example: tiger + tiger = baby tiger (which grows up to reproduce) lion + tiger = liger (a hybrid which can’t reproduce) Every species has a 2-part Latin name: Ex: Canis lupus (wolf) Genus name Specific name Genus species