Plate Tectonics
advertisement

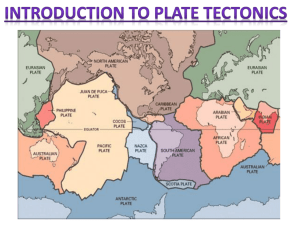
PLATE TECTONICS DO NOW SWBAT create a concept map of plate tectonics terms as a pre- assessment Enter Silently Grab Materials Begin Do Now 1. Write in your planner for the week 2. Open your notebook to the front of page 17. I DO (5 MIN) Topic: Earth Front Page 17 Title: “How to Make a Concept Map” 1. Start with the main topic at the top 2. Link concepts using words to make a sentence 3. Use arrows to show direction of linking concepts What are some terms related to Earth? Rocks, Layers, Ect… CONCEPT MAPS PRACTICE (5MIN) (WEATHERING) (YOUDOWEDO) Front Page 17 Using these terms, practice and create a concept map by connecting the concepts with a one-way arrow, and a phrase to complete a sentence Topic: Weathering 1. Mechanical 2. Chemical 3. Abrasion 4. Ice Wedging 5. Plant Root Growth 6. Pressure Release 7. Dissolving 8. Rusting CONCEPT MAP PRE-DRAFT (20MIN) Write theseterms on to your small sticky notes Topic: Plate Tectonics 1. Alfred Wegner 2. Continental Drift 3. Convection 4. Tectonic Plates 5. Plate Boundaries 6. Continental 7. Oceanic 8. Sea floor spreading 9. Fossils 10. Glacier Grooves First Create a Concept Map Individually on the small paper Second Discuss in your group similarities and differences in your map and try to fix them. Third As a group, use what you discussed, and create a concept map on the large paper. 11. Pangaea 12. Matching Rock Layers (These will be used for a gallery walk) GALLERY WALK Rotate clockwise around the room and look at each concept map Note any similarities or differences 1. Did you forget something? 2. Did they forget something? 3. Do they have something different than your group? 4. Do they have something that’s the same? DO NOW 1. Which layer of the Earth is the most dense? Explain. 2.What layer of the Earth Is divided into an upper, cooler, more rigid rock and a lower, hotter, softer rock? THE EARTH IS MADE OF LAYERS Copy Notebook BACK OF PAGE 17 Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner Core LAYERS OF THE EARTH Lithosphere -Together the crust and upper mantle are called the lithosphere and they extend about 80 km deep. Asthenosphere -The asthenosphere is flexible and can be pushed and deformed like silly putty in response to the warmth of the Earth. These rocks actually flow, moving in response to the stresses placed upon them by the churning motions of the deep interior of the Earth. (convection) BOOK CHECK OUT Changing Earth Books 1. Take a book, fill out the information on the sheet as it gets passed around the room 2. The book number is on the yellow tag. 3. Individually work on your plate tectonics concept map Keep these books in good condition, I am going to email home that you are receiving these books. They’re to be kept at home, and used for homework assignments EXIT TICKET 1. Which layer of the Earth has a upper part of cool, more rigid rock and a lower part of hotter more flexible rock? 2. What layers of the Earth is the Lithosphere comprised of? 3. What layers of the Earth is the Asthenosphere made of? 4. What part of the Earth churns, flows, and moves because of the heat coming from the core in a processes called convection? DO NOW SWBAT describe evidence of Alfred Wegener’s Theory of Continental Drift 1. Alfred Wegener, a German scientist proposed that all of the continents on Earth were once joined together in a massive supercontinent called Pangaea. Observe the map above. What evidence, or inferences could you make to support Alfred Wegener’s claim? CLASS CLOSE READ Highlight Annotate what you think as you go through it 1. What are some examples of scientific changes that you have noticed in the past few years? 2. Can new scientific ideas come from old observations or evidence? Why or why not? Scientific changes also involve developing new theories to explain observations or reinterpret old evidence.The facts may not change, but the explanation does. EVIDENCE JIGSAW This is the evidence that Alfred Wegener gathered, as well as a couple of new pieces of evidence that was later added to the theory in the mid-1900’s to further support continental drift. Individually, close read the section of article your group is assigned 1. Highlight important details and information about the section you are assigned. 2. Make annotations about things that come to mind when reading CREATE A POSTER TO PRESENT With your group, and using the article Create a poster about your section of evidence to present to the class, using this framework Evidence Details Picture (what is the evidence) (What are the details of the evidence?) Draw a picture of the Evidence PRESENTATION NORMS Listener: Be Respectful Listen Actively Be Supportive Fill in your chart for your notes Presenter: Speak at a 5 Speak Clearly Use scholarly vocabulary Address the topic completely MY CHART FRONT OF PAGE 18 Make sure your chart looks like this and has this information on it EXIT TICKET 1. Who is credited with the theory of continental drift? 2. According to the theory of continental drift, a) Earth’s surface is made up of 7 different land masses b) Continents don’t move c) Earth was once joined with the moon to make a super planet d) The continents were once joined together in a single landmass called Pangaea 3. What 6 pieces of evidence is there that proves that tectonic plates have drifted apart? DO NOW SWBAT identify and describe evidence for continental drift 1. Who is credited with the theory of continental drift? 2. According to the theory of continental drift, a) Earth’s surface is made up of 7 different land masses b) Continents don’t move c) Earth was once joined with the moon to make a super planet d) The continents were once joined together in a single landmass called Pangaea https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nbU809Cyrao PRESENTATION NORMS Listener: Be Respectful Listen Actively Be Supportive Fill in your chart for your notes Presenter: Speak at a 5 Speak Clearly Use scholarly vocabulary Address the topic completely MY CHART FRONT OF PAGE 18 Make sure your chart looks like this and has this information on it LITHOSPHERIC PLATES NOTES BACK OF PAGE 18 TECTONIC PLATE VS. CONTINENT Notice that the African plate extends out of the continent and into the ocean. The continent itself only makes about half of the plate. PREDICT Make a prediction Predict the names of each of the plates on your map. Write the name down for each of the plates LABEL AND COLOR EACH PLATE Use the Earth’s Lithospheric Plates Map and Page 19 of the book to color and label some of the Earth’s most important tectonic plates Label Color EXIT TICKET 1. What 6 pieces of evidence is there that proves that tectonic plates have drifted apart? 2. What is the name of the plate that is pushing to the right (light blue) into the South American Plate. DO NOW 1. What 6 pieces of evidence is there that proves that tectonic plates have drifted apart? 2. What is the name of the plate that is pushing to the right (light blue) into the South American Plate. CONCEPT MAP PRE-DRAFT (10MIN) Write these terms to create your concept maps Topic: Plate Tectonics 1. Alfred Wegner 2. Continental Drift 3. Convection 4. Tectonic Plates 5. Plate Boundaries 6. Continental 7. Oceanic 8. Sea floor spreading 9. Fossils 10. Glacier Grooves First Create a Concept Map Individually on the small paper Second Discuss in your group similarities and differences in your map and try to fix them. Third As a group, use what you discussed, and create a concept map on the large paper. 11. Pangaea 12. Matching Rock Layers (These will be used for a gallery walk) GALLERY WALK 1. What concepts do you need to study? EXIT TICKET 1. How do fossils support Wegener Continental Drift Theory? 2. How do glacier grooves support Wegener’s Continental Drift Theory? 3. Which type of lithospheric plate is more dense, oceanic or continental? (MINI QUIZ MON) SWBAT demonstrate their understanding of continental drift theory. Enter Silently Grab Materials Begin Do Now 1. Explain continental drift theory as if you were explaining it to a 1st grader Continents drift apart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HhkyXrWNoVA NUMBERED HEADS Numbered heads together 1,2,3 A,B,C 1. What is Pangaea, and what happened to it? 2. What evidence is there for continental drift? PANGAEA PUZZLE (5 MIN) Puzzle contest Groups of 3 (put the books up as barriers in between) Look at the World map as it is today Put the puzzle together by using the evidence from page 17 of your notebook “Cover it up-” or “no-” NAMES OF PLATES (EACH OF YOU GET 3 MINUTES) Sage and scribe study With your partner across from you: 1. Person with longest hair goes first. 2. Look at the map of the tectonic plates and name as many as you can. 3. Other partner, you can help coach- but do not tell answers 4. Celebrate your partner Switch sage and scribe at the buzzer. QUIZ (15 MIN) Turn in quiz in the back basket DO NOW (TUES) SWBAT describe the difference between divergent, convergent, and transform plate boundaries Enter Silently Grab Materials Begin Do Now Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift was rejected because he didn’t have evidence to explain how the continents drifted apart from each other. 1. Describe how do tectonic plates move as if you were telling a first grader. HOW DO THE PLATES MOVE? The lithosphere is made up of these giant slabs of rock called tectonic plates that “float” on top of the asthenosphere. Convection is the transfer of energy by the movement of fluids Convection occurs in the Asthenosphere Heated rock rises, then cools and starts to sink https://youtu.be/ryrXAGY1dmE 1. If convection is a way for heat to transfer, where is the heat coming from to make the asthenosphere rise and fall? DO NOW 1. This is a picture of San Francisco after an Earthquake in 1906. How do you think Earthquakes like this one happen? NUMBERED HEADS TOGETHER What direction do the convection currents move to create a ridge? In what direction do the plates move as a result? PLATE BOUNDARIES TYPES OF LITHOSPHERIC PLATE BOUNDARIES Boundary Type Divergent – plates move away (separate) Results Rift Valleys (Africa) Ocean Ridges – Sea floor spreading (Mid-Atlantic Ridge) New Crust Convergent – plates Volcanoes (Ring of Fire) move together Builds mountains (Himalayas) (collide) Plates shrink Creates trenches Subduction - one plate is pushed into the mantle where it melts. Transform – plates move side by side Earthquakes (California) Epicenter – beginning above ground Focus – beginning underground Faults (San Andreas) Picture BOUNDARY DANCE 3 types of boundaries Divergent- spread apart Convergent- come together Transform- slide Convection review- motion, what types of boundaries occur (how convection currents create these boundaries) (hand dance) PLATE BOUNDARIES WORKSHEET (EXTREME 8?) Books EXIT TICKET 1. What process causes tectonic plates to move? 2. What are the three types of plate boundaries? 3. How are the plate boundaries which collide, slide, and separate related to the motion of convection currents? DO NOW ( FRI DIVERGENT BOUNDARIES RESULTS) SWBAT describe the results of a divergent boundary What type of boundary is shown in the diagram above. VIDEO OF ICELAND DIVERGENT BOUNDARY https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sgDM6m0lUGY DIVERGENT BOUNDARY Definition Place where 2 plates are being forced apart by convection Creates new crust Convection Direction Plate Direction EAST AFRICAN RIFT VALLEY (RESULTING LAND FORMS) 2 continental plates Land is pulling apart Lakes are filled by rain water and run-off Volcanoes caused by thinning crust East African Rift Valley will split MID-OCEANIC RIDGES (RESULTING LAND FORMS ) 2 oceanic plates Large chain of volcanoes Plates are separating Iceland is the only place on land page 18. Mid-Atlantic Ridge Add the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the East African Rift Valley as shown below East African Rift Valley BOARDS UP Kagan strategy Numbered heads together? WHICH LETTER IS THE DIVERGENT BOUNDARY WHAT LANDFORM IS THE RESULT OF THE DIVERGENT BOUNDARY IN THE DIAGRAM WHAT IS THE PROCESS CALLED AT THE MID-OCEANIC RIDGE THAT IS CAUSING NEW CRUST TO BE MADE SPREADING THE OCEANIC PLATE APART? WHAT IS HAPPENING AT LETTER E? EXIT TICKET Fill in the “ACTUAL BOUNDARY” portion for Djibouti (E. African Rift Valley) and the Mid-Atlantic Ridge with this information. 1. type of boundary, 2. resulting landforms, 3. plate movement, 4. types of plates involved 5. how convection currents are moving DO NOW (MON) SEA FLOOR SPREADING CLOSE READ AND MAG REVERSALS 1. What is a plate boundary? 2. What is the first type of plate boundary we learned about? 3. Describe the plate movement and what two types of landforms it creates. THINK-WRITE-PAIR-SHARE Sea floor spreading video 1. How did Harry Hess map the sea floor? 2. How did scientists discover the Mid-Atlantic ridge? 3. What kind of boundary is a mid-oceanic ridge, and what types of tectonic plates are involved? 4. How is the age of the sea floor related to how far or close it is to the midoceanic ridge? 5. If new rock is being created at the mid-oceanic ridge, why does the Earth not get larger? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t-ctk4KR-KU SEA FLOOR SPREADING CLOSE READ (choice options to read) 1. Highlight definitions (4-5) 2. Highlight important facts in a different color (5) 3. Answer questions on back- cite where you found the evidence in the article by writing the question number next to the sentence where you found the answer MAGNETIC REVERSALS AND AGES OF ROCKS New oceanic crust at midoceanic ridge Old oceanic crust is in a subduction zone under the continental plate Magnetic reversals show that rocks on each side of the ridge are created at the same time because the magnetic poles in the rocks match. EXIT TICKET 1. What type of plate boundary would you find at a mid-oceanic ridge? 2. Draw the direction of the convection currents in the asthenosphere at a mid-oceanic ridge (circles- which way are they going?) 3. The process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor is called what? 4. How do magnetic reversals in rocks along mid-oceanic ridges provide evidence for sea-floor spreading? DO NOW (TUES- CONVERGENT BOUNDARIES) Make a prediction: Fossils deposited in a deep sea 400 million years ago are now found on top of Mount Everest, the highest mountain in the world. Why are marine fossils at the top of the tallest mountain in the world? (subduction= TRENCH) "The Summit of Mt. Everest is Marine Limestone" The great nature writer John McPhee wrote about Mount Everest in his book Basin and Range: "When the climbers in 1953 planted their flags on the highest mountain, they set them in snow over the skeletons of creatures that had lived in the warm clear ocean that India, moving north, blanked out. Possibly as much as twenty thousand feet below the seafloor, the skeletal remains had turned into rock.This one fact is a perfect example for the movements of the surface of the Earth. If I had to limit all this writing to one sentence, this is the one I would choose: The summit CONVERGENT BOUNDARY Definition Place where 2 plates are colliding because of convection Convection Direction Plate Direction OCEAN VS. OCEAN Ocean to Ocean Collision https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bYv6V5EJAKc The older oceanic plate subducts (sinks because it is more dense) and creates a subduction zone Results 1. Trench 2. Islands Examples Marianas Trench MARIANAS TRENCH I JUST ABSOLUTELY LOVE IT WHEN TWO OCEANIC PLATES MEET AT A CONVERGENT BOUNDARY AND THE OLDER OCEAN PLATE SUBDUCTS UNDER THE NEWER OCEAN PLATE TO MAKE A TRENCH OCEANIC VS. CONTINENTAL Ocean to Continent Collision https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UgPy_bXNA-Y Ocean V. Continent Oceanic plate subducts under the continental plate Results 1. Trench 2. Coastal Mountains Examples: Andes Mountians CONTINENTAL VS. CONTINENTAL Continent to Continent Collision Both plates collide and begin to rise Results 1. Folded Mountains Example: Himalayas https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M0lTfJDiZsw http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/plate-tectonics Exit Ticket T-W-P-S A B C H G F D 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. E In the Diagram above, which letters represent the convergent boundaries? Draw the direction of the convection currents at a convergent boundary. In the Diagram above, which letters represent a subduction zone? What two types of plates converge to create a volcanic island? What two types of plates converge to create a Trench? What two types of plates converge to create a coastal mountain? What two types of plates converge to create folded mountains like the Himalayas? EXIT TICKET Fill in the “ACTUAL BOUNDARY” portion for Himalayas and the Marianas Trench with this information. 1. What type of boundary? 2. What is the resulting landform? 3. How are the plates moving? 4. What types of plates are involved? 5. How are convection currents in the asthenosphere moving? DO NOW A C B H G F D E 1. In the Diagram above, which letters represent the divergent boundary? 2. In the Diagram above, which letters represent the convergent boundaries? 3. Pick one of the Following to answer: a. How is a Rift Valley Formed? b. How is a island formed? c. How are the Himalayas currently forming? d. How did the Marianas Trench Form? TRANSFORM BOUNDARIES NUMBERED HEADS TOGETHER https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AhPpp7As8k8 1. Earthquakes shake and crumble buildings, but what else were the residents of San Francisco unprepared for that caused a lot of damage? 2. What type of plate boundary is the San Andreas fault line? 3. What type of fault is the San Andreas Fault? 4. Why is it important to understand tectonic plate boundaries like the one that occurs at the San Andreas Fault? TRANSFORM BOUNDARY Definition Place where 2 plates slip past each other in opposite directions Convection Direction Plate Direction RESULTS Transform Faults and Earthquakes are the results of Transform Boundaries WHAT TYPE OF BOUNDARY CREATED THE EARTHQUAKE? The 2011 Japan Tsunami Was Caused By Largest Fault Slip Ever Recorded Experts calculate the fault—or the boundary between two tectonic plates—in the Japan trench slipped by as much as 164 feet (50 meters). Other similarly large magnitude earthquakes, including the 9.1 Sumatra event in 2004, resulted in a 66-to-82 foot (20-to-25 meter) slip in the fault. "We've never seen 50-meter [slips]," said Kelin Wang, a geophysicist with the Geological Survey of Canada in British Columbia. INDIVIDUAL ASSIGNMENT Due at the end of class today EXIT TICKET Fill in the “ACTUAL BOUNDARY” portion for the remainder of the Extreme 7. (if you do not have room, complete this on a separate sheet of paper and tape it into your notebook on the back of page 19) 1. What type of boundary? 2. What is the resulting landform? 3. How are the plates moving? 4. What types of plates are involved? 5. How are convection currents in the asthenosphere moving? DO NOW A B C H G F D E 1. In the Diagram above, which letter represents the transform boundary? 2. What is the resulting feature of the transform boundary in the diagram? 3. If the two plates at the transform boundary were to slip past each other what event would occur? E D C T-P-S 1. Which letter is a rift valley? B A BOUNDARIES WORD SORT (T-W-P-S) Match each concept or vocabulary term with the type of boundary it is associated with 1. Think/ Write- Individual 2. Pair- With person across from you 3. Share- Class (cold call) CHOICE CLOSURE (INDIVIDUAL) 1. Draw and label a plate boundary of your choice (POSTER) OR 2. Write a paragraph about one type of plate boundary What type of boundary is it? (di/con/tran) Landforms that form at the boundary Types of plates (continental / oceanic) Plate movement Convection movement in the asthenosphere Explain why your boundary happens and how the landforms are forming. DIAGRAM POSTER (ACC THREES) Create a poster by making a Diagram and labeling the following information on it: A Divergent Boundary Definition, convection direction, and plate direction Mid-oceanic ridge Rift valley Label the types of plates involved (oceanic/continental) Name an example of each landform An explanation of Sea-Floor Spreading and Magnetic reversals Convergent Boundary Definition, convection direction, and plate direction Subduction zone Volcanic islands Trench Coastal Mountains Label the types of plates involved in each (oceanic/continental) Name an example of each landform Transform Boundary Definition, convection direction, and plate direction Transform Fault Label the types of plates involved (oceanic/continental) Name an example DO NOW (QUIZ DAY) What causes the motion of the lithosphere, and how does it work? TEST Chance to reach class goal Try your best Turn the test into the back basket when you finish PLATE BOUNDARIES LAB? Demonstrate different plate boundaries What do you think each type makes?