Digestive System NOTES - Madison County Schools
advertisement
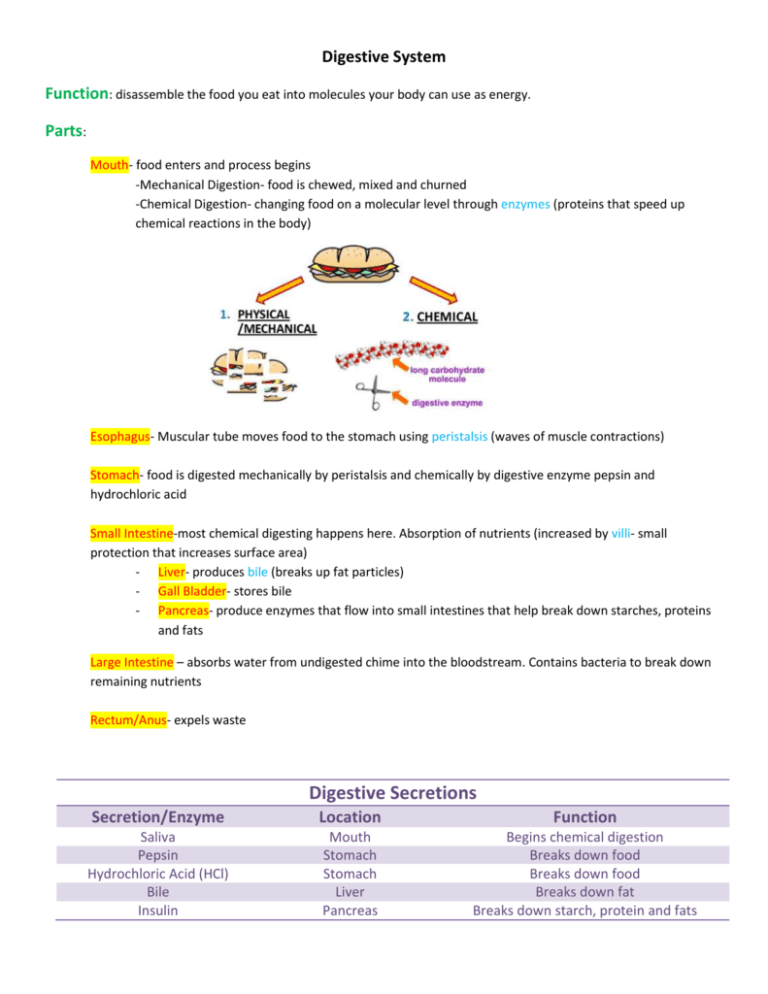
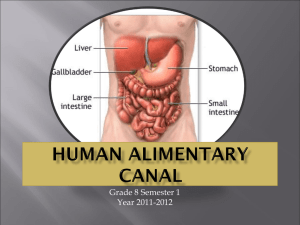
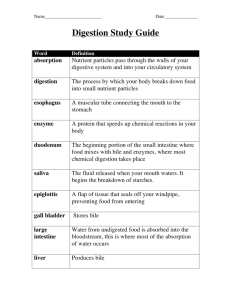
Digestive System Function: disassemble the food you eat into molecules your body can use as energy. Parts: Mouth- food enters and process begins -Mechanical Digestion- food is chewed, mixed and churned -Chemical Digestion- changing food on a molecular level through enzymes (proteins that speed up chemical reactions in the body) Esophagus- Muscular tube moves food to the stomach using peristalsis (waves of muscle contractions) Stomach- food is digested mechanically by peristalsis and chemically by digestive enzyme pepsin and hydrochloric acid Small Intestine-most chemical digesting happens here. Absorption of nutrients (increased by villi- small protection that increases surface area) - Liver- produces bile (breaks up fat particles) - Gall Bladder- stores bile - Pancreas- produce enzymes that flow into small intestines that help break down starches, proteins and fats Large Intestine – absorbs water from undigested chime into the bloodstream. Contains bacteria to break down remaining nutrients Rectum/Anus- expels waste Digestive Secretions Secretion/Enzyme Location Function Saliva Pepsin Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) Bile Insulin Mouth Stomach Stomach Liver Pancreas Begins chemical digestion Breaks down food Breaks down food Breaks down fat Breaks down starch, protein and fats