Digestive System PPT
advertisement

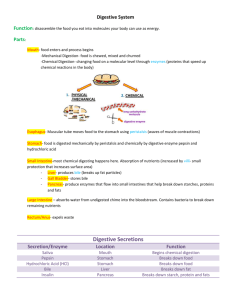
Biology 2 http://www.youtube.com /watch?v=Wu2iJseYlOQ The mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods and the absorption of the resulting nutrients by cells ◦ Mechanical digestion- breaks large pieces into smaller ones without altering their chemical composition ◦ Chemical digestion- breaks food into simpler chemicals Explain how both types of digestion occur in the mouth… Alimentary canal: ◦ Extends from the mouth to the anus ◦ 8-9 meters long (or about 30 feet) Accessory organs: ◦ Secrete substances used in the process of digestion into the canal 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Rectum Anus 1. 2. 3. 4. Salivary Glands Liver Pancreas Gallbladder Mucosa: innermost layer, bordering lumen ◦ Mostly epithelial with tiny projections extending into the lumen to increase surface area to enhance absorption ◦ Glandular epithelium that secrete digestive enzymes Submucosa: ◦ Connective tissue ◦ Nervous tissue ◦ Blood vessels Muscular Layer - smooth muscle ◦ Contracts resulting in peristalsis ◦ Circular fibers and longitudinal fibers Serosa – outermost layer ◦ Connective tissue and epithelium ◦ Protection ◦ Secretes serous fluid which moistens and lubricates tube so organs within abdominal cavity freely slide against eachother Mixing movements ◦ Smooth muscles in small segments contract rhythmically ◦ Such as a wave of contractions from one end of the stomach to another to mix digestive juices and food Propelling movements ◦ Peristalsis- wavelike motion when a ring of contraction appears in the wall of the tube but a section of the tube ahead is relaxed ◦ Pushes food along the tube from one end to the other such as in the esophagus https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_QYwscALNng Take about 30 minutes to complete the jot chart for all the parts of the digestive system. ◦ Be sure to use details (write small) ◦ We will discuss the anatomy & physiology of each part and potentially add to your jot chart Lips, tongue, cheek, and palate surround the oral cavity Tongue- skeletal muscle with raised papillae and taste buds found in pores Palate- bony roof of oral cavity Teeth- 20 primary teeth; 32 secondary teeth ◦ Composed of outer enamel, hard dentin, & root with canal of nerves and blood vessels Receives food, beginning mechanical digestion with reducing solid particles and mixing them with saliva in a process called mastication Tongue- moves and mixes food, while rough papillae create friction, further breaking down food Teeth- increase the surface area of the food by breaking it down for further chemical digestion Has lymphatic structures, such as tonsils and adenoids ◦ These are common sites of infection and can interfere with breathing and swallowing when infected ◦ Tonsillectomy- removal of tonsils due to repeated infection Dental caries- when acid forming bacteria decay tooth enamel ◦ Arises when sticky, sweet food is not brushed off the teeth 3 pairs of salivary glands: 1. Parotid glands- large amylase secreting glands b/w skin of cheek and masseter muscle, slightly below ears 2. Submandibular glands- located on floor of mouth on lower jaw & consists of serous and mucous cells 3. Sublingual glands- small on floor of mouth below tongue, consisting of mucous cells Secrete saliva that moistens food particles and begins chemical digestion of carbohydrates (sugar) Cleanses mouth and teeth Dissolves food so it can be tasted Contains two types of cells: ◦ Serous cells- make salivary amylase enzyme that breaks down complex carbs into simpler disaccharides ◦ Mucous cells- make mucus to bind and lubricate food for swallowing Cavity posterior to mouth from where the esophagus leads to the stomach Connects the nasal and oral cavities Muscular passageway that functions in swallowing 3 stages of swallowing: 1. Voluntary stage in which food is chewed and mixed with saliva, tongue rolls food into ball (bolus) and forces it into the pharynx 2. Food stimulates sensory receptors, triggering swallowing reflex 3. Peristalsis transports food through esophagus to stomach Straight muscular food tube from pharynx to stomach Lies posterior to trachea Penetrates the diaphragm Lower esophageal sphincter remains contracted until peristalsis waves open it Simply a muscle to pass food through peristalsis Reflux of gastric juices from the stomach through the esophageal sphincter causes heartburn ◦ Can even lead to esophageal cancer if continuous J-shaped pouch-like organ in upper left portion of abdominal cavity Can hold 1L or more Regions of stomach: ◦ Cardiac region- near esophageal opening ◦ Fundic region- balloons superior to cardiac region for temporary storage ◦ Body- main part of the stomach ◦ Pyloric region – narrows into the pyloric canal, which ends at a muscular pyloric sphincter valve that empties into the small intestine Mixes food with gastric juice, initiates protein digestion, carries on limited absorption, & moves food to the small intestines ◦ Pepsinogen from chief cells mixes with HCl to form pepsin and break down protein ◦ Intrinsic factor is released to help absorb vitamin B12 ◦ Chyme, mixed gastric juices and food, get pushed to pyloric region of stomach Inner lining of the stomach has 3 cell types: 1. Mucous cells- secrete mucus, coating walls to protect them from strong stomach acid 2. Chief cells- secrete digestive enzymes 3. Parietal cells- release hydrochloric acid (HCl) Lining has many gastric pits (grooves) and is very thick Extends horizontally across the posterior abdominal wall in C-shaped curve of duodenum C cells produce pancreatic juice that empties into the pancreatic duct The pancreatic duct connects to the duodenum Exocrine function is to secrete pancreatic digestive juices ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Amylase- digest carbs Lipase- breaks down lipids (fats) Nucleases- break down nucleic acids Trypsin- main enzyme that breaks down protein In cystic fibrosis, defective chloride channels in cells draws in water, drying out the lungs and pancreas specifically ◦ Causes sticky mucus that can make breathing difficult and blocks secretions of the pancreas ◦ Can cause malnutrition Upper right quadrant of abdominal cavity Heaviest organ in the body at 3 pounds Reddish brown and surrounded by blood vessels Separated into 2 lobes Hepatic duct releases bile into duodenum Aids in carbohydrate metabolism by breaking down glycogen into glucose when blood sugar is low Functions in lipid metabolism, where fats made in the liver get transported away to adipose tissue for storage Protein metabolism & makes clotting proteins found in blood plasma Stores substances, detoxifies body, destroys damaged RBCs & WBCs Livers digestive function is the secretion of bile, which is contain bile salts that emulsify fats, breaking them down into smaller droplets Hepatitis- inflammation of the liver and can be caused by virus, alcoholism, or various drugs Muscular pear-shaped sac in a depression on the liver’s interior surface Connects to cystic duct that joins to hepatic duct Stores bile between meals, reabsorbs water to concentrate bile, and contracts to release bile into the small intestine Gallstones- caused by cholesterol precipitating out of bile, forming crystals ◦ Can block bile flow into the small intestine, causing pain ◦ Cholescystectomy can surgically remove the gallbladder when gallstones are obstructive Long tubular, looping organ extending from pyloric sphincter of stomach to large intestine 3 portions 1. Duodenum- follows a C shaped path and is fixed in place 2. Jejunum- mobile portion of the s.i. with thicker wall more active in absorption 3. Ileum- last stretch of s.i. that joins the large intestine Mesentery- double layered fold of membrane that suspends s.i. from abdomen walls w/ blood vessels & lymph tissue Intestinal villi cover the inner wall of s.i. that increase surface area for absorption Goblet cells secrete mucus to further dissolve chyme Peptidases- enzymes that break down ______ Sucrase, maltase, and lactase- enzymes that break down ______ Intestinal lipase- enzyme that breaks down ___ Mixing and peristalsis ◦ Peristalsis is much slower in s.i., taking about 3-10 hours to go from one end to the other In malabsorption, the s.i. digests but doesn’t absorb all nutrients ◦ Symptoms- weight loss, vitamin deficiency, anemia, diarrhea ◦ Causes could be obstructions, reaction to gluten (protein in grains), microvilli are damaged Ileoceccal sphincter joins the ileum of the s.i. to the cecum of the large intestine Much larger in diameter than s.i. Parts of Large Intestine: ◦ Cecum- beginning pouch that hangs below the ileoceccal sphincter Appendix projects down from it ◦ Colon- ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colons Lacks villi Little or no digestive function Goblet cells that function in mucus secretion, protecting the intestinal walls from abrasion Absorbs water and electrolytes Intestinal flora- many bacteria species that break down some of the molecules that humans cannot digest, such as cellulose from plants ◦ This creates gas as a by-product Mixing and peristalsis movements ◦ Usually peristalsis only occurs 2-3 times a day in l.i. Why can antibiotics often times cause digestive problems, such as diarrhea and/or stomach cramping? What can be done to prevent or help circumvent this? Attaches to the sigmoid colon and ends about 5 cm below the tip of the coccyx Simply a canal to rid the body of waste Colorectal cancer screenings are recommended for those over 50 ◦ Polyps and tumors are recognized and removed ◦ Fiberoptic colonoscopyinvasive and requires a sedative ◦ Virtual/tomographic colonoscopy- much less invasive but if a polyp is found, then the fiberoptic procedure must take place An opening at the inferior end of the alimentary canal to expel wastes Internal anal sphincter muscle under involuntary control External anal sphincter muscle under voluntary control Expels feces Feces includes materials that were not digested or absorbed, plus water, electrolytes, mucus, shed intestinal cells, and bacteria ◦ 75% water ◦ Color is due to bile pigments altered by bacterial action ◦ Odor due to bacterial breakdown of nutrients and their byproducts ◦ Diversity of gut bacteria is linked to good health