Digestive and Excretory Systems Finz 2014
advertisement

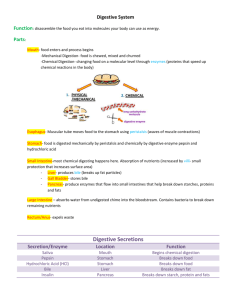
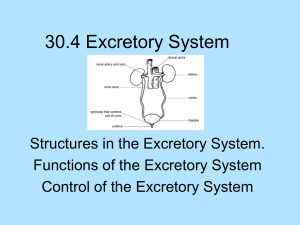
Digestive and Excretory Systems Finz 2014 Function: To physically and chemically ingest, digest, and absorb food and nutrients. The path of food... 1) Mouth ingests and digests using teeth, tongue (physical) and saliva (chemical). 2) Esophagus transports food to stomach through peristalsis muscle contractions. 3) Stomach stores and digests food by contracting (physical) and with acid (chemical) 4) Small intestine digests (chemical) and absorbs food. 5) Large intestine absorbs water and vitamins and minerals. (chemical) 6) Anus eliminates unused wastes. Other organs of the digestive system • Food does NOT pass through these: • Liver: produces bile for breaking down fats. • Gall bladder: stores the bile. • Pancreas: produces enzymes for breaking down starches. Nutrition • proteins: – growth and repair, breaks down into amino acids, examples are meats, nuts and fish. • carbohydrates: – main source of quick energy, breaks down into sugars, examples are starchy foods like breads, pastas, grains. • fats: – stored energy, breaks down into fatty acids and glycerol, saturated (butter) and unsaturated (oils) types. Nutrition • water: – needed for chemical reactions to take place in the cells. • vitamins: – organic molecules to regulate processes. • minerals: – inorganic molecules to regulate processes. Food guide pyramid Quiz 1. What is the “food tube?” Esophagus 2. What substance breaks down fats? Bile 3. Name 1 part of the Digestive System that does “Physical” digestion. Mouth or stomach contractions 4. Name 1 part of the Digestive System that does “Chemical” digestion. Saliva or stomach acid or small intestines Excretory System Functions of the Excretory System • Every cell produces metabolic wastes. • The process by which these wastes are eliminated is called excretion. Organs that can excrete • The skin excretes excess water and salts in the form of sweat. • The lungs excrete carbon dioxide. • The kidneys also play a major role in excretion. The Kidney: • remove waste products – mostly urea- from the blood. • maintain blood pH. • regulate the water content of the blood and, therefore, blood volume. The Kidney: • Blood enters the kidney through the renal artery. • The kidney removes urea, excess water, and other waste products and passes them to the ureter to the urinary bladder. • The clean, filtered blood leaves the kidney through the renal vein and returns to circulation. The Kidney The Kidney • The mechanism of blood purification involves two distinct processes: filtration and reabsorption. – Filter out wastes – Reabsorb water