Kingdoms
advertisement

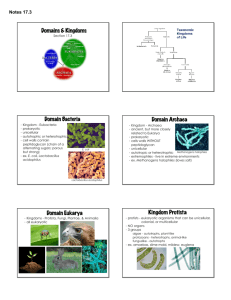
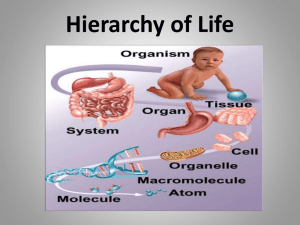
Old Categories • • • • • • • • Cattle Creeping Creatures Beasts Grasses Fowl Herbs Trees Fish Archaebacteria • • • • • Prokaryotic Different cell wall (lacks a protein) Unicellular Autotrophic Live in extreme environments (swamps, deep ocean vents) • Ex: Methanogens, halophiles Prokaryotic Eubacteria Unicellular Autotrophic or heterotrophic Live in most environments Some cause disease(strep throat, tooth decay, or pneumonia) • most are actually helpful • Examples: Rhizobium and Bacillus • • • • • Eubacteria continued • Heterotophs – Some are saprobic: • Decompose dead organisms & place nutrients back into environment. • Autotrophs – Photosynthetic: use light energy to make own food. – Chemosynthetic: use chemicals to make own food. Bacterial Reproduction • Asexual (mitosis): – Binary Fission Protista • • • • • • • Eukaryotic Have simple organ systems Have nucleus Mostly unicellular, some multicellular Autotrophic or heterotrophic Live in moist environments Ex: paramecium, algae, amoeba Basic Protist Parts • Flagella - whip like structure for movement • Cilia - hair like structures for movement & feeding • Pseudopods - “false foot” for movement & feeding (phagocytosis). Giardia Paramecium Amoeba Photosynthetic Protist Euglena Bad Protists - Red Tide Good Protists Diatoms •Used in: •Toothpaste •Reflected Road Paint •Nail polish • Eukaryotic Fungi • Unicellular or multicellular • Heterotrophic - Saprobic (Decomposers/Recyclers) • Stationary, must absorb nutrients (extra-cellular digestion), can’t ingest (eat) them • Use SPORES to reproduce Asexually • Can reproduce sexually • Ex: yeast mold mushrooms • Largest Fungi A fungus growing in the Malheur National Forest in the Blue Mountains of Eastern Oregon covers an area equivalent to around 1,220 soccer fields. The species of fungus (Armillaria ostoyae) is usually known as the honey mushroom. -Guiness World Records, 1999 http://www.giornaledibrescia.it/iniziativ e/funghi/Immagini/zoom23.jpg Plantae • • • • • • • Eukaryotic Cell wall is made of cellulose Have nucleus Multicellular Autotrophic Go through photosynthesis, have chlorophyll Ex: moss, ferns, flowers, conifers Basics on Plants • Mosses & Ferns = Use spores • Gymnosperms = (conifers), Evergreens use cones to reproduce. • Angiosperms = flowering plants Angiosperms • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Basic Flower Parts Stamen (male part) – Anther- makes pollen Pistil (female) – Stigma- place for pollen to land If pollen fits=pollination Pollen tube grows down to ovary Pollen meets ovary=fertilization Seed grows in ovary Ovary becomes fruit Seed contains complete DNA for new plant. Animalia (Our Kingdom) • • • • Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophic Cells form tissues, tissues form organs, organs form systems • Able to move around their environment • Ex: sponges, insects, mammals, birds Take out Review Sheet to be graded Fill out Bingo Sheet • • • • • • • • • • • • Species Population Taxonomy Eubacteria Archaebacteria Monera Fungi Protist Phylogenetic Tree Ameoba Grasshopper Cactus • • • • • • • • • • • • Plant Animal Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Chordata Halophiles Mold Bacillus