Ch 4 Reading Questions
advertisement

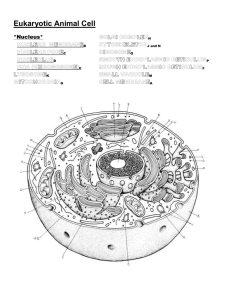
Honors Textbook Guided Reading Questions Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell Section. 4.2-4.3 1. 2. 3. 4. Explain how a cell’s functions limits its size. Why do small cells have a greater surface area relative to their volume? Describe the commonalities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Explain the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Section 4.4-4.12 4.4: Define the terms cytoplasm and organelles. Explain where the activities of cellular metabolism occur. Where do these processes occur? Describe the structures that are unique to plant cells. Explain the role of ribosomes and where they can be found in a eukaryotic cell. 4.5: Define and explain the terms: nucleus, chromatin, chromosome, nuclear envelope, & nucleolus. Explain the difference between chromatin and chromosomes. Explain the function of the nucleolus and nuclear envelope. 4.6: Explain what organelles compose the endomembrane. With what organelles are the endomembrane system continuous? 4.7: Explain the difference in structure and function between the smooth and rough ER. Explain why liver cells contain large amounts of smooth ER. Explain why complications can occur when liver cells respond to drugs. Why do muscle cells require a large amount of smooth ER? 4.8: Explain the functions of the rough ER. Describe the process the rough ER undergoes to synthesis and package a protein. 4.9: What does the number of golgi bodies correlate to? Explain the functions of a golgi apparatus. What is the relationship of the Golgi apparatus to the ER in a protein secreting cell? 4.10: Explain where the term lysosome comes from. How are lysosomes created? Why are lysosomes necessary for the cell? What are their functions? 4.11: What are some examples of diseases caused by damaged lysosomes? 4.12: What is the difference in function between a plant’s central vacuole and a food vacuole? How does a contractile vacuole maintain the cells’ internal environment in the Paramecium?