Chapter 16: Thermochemistry Review
advertisement
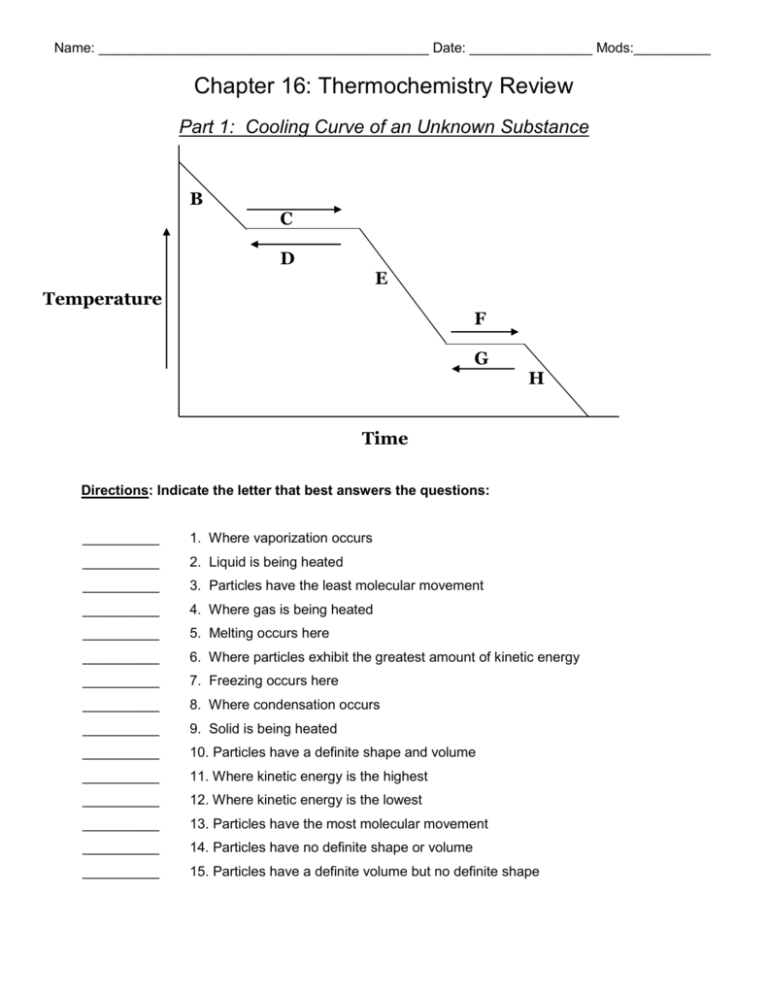
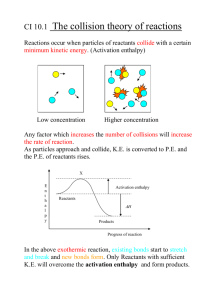
Name: ___________________________________________ Date: ________________ Mods:__________ Chapter 16: Thermochemistry Review Part 1: Cooling Curve of an Unknown Substance B C D E Temperature F G H Time Directions: Indicate the letter that best answers the questions: __________ 1. Where vaporization occurs __________ 2. Liquid is being heated __________ 3. Particles have the least molecular movement __________ 4. Where gas is being heated __________ 5. Melting occurs here __________ 6. Where particles exhibit the greatest amount of kinetic energy __________ 7. Freezing occurs here __________ 8. Where condensation occurs __________ 9. Solid is being heated __________ 10. Particles have a definite shape and volume __________ 11. Where kinetic energy is the highest __________ 12. Where kinetic energy is the lowest __________ 13. Particles have the most molecular movement __________ 14. Particles have no definite shape or volume __________ 15. Particles have a definite volume but no definite shape Part 2: Calculating Specific Heat Worksheet q = mCp∆T, where q = heat energy, m = mass, and ∆T = change in temp. Remember, ∆T = (Tfinal – Tinitial). Show all work and proper units. 1. A 15.75-g piece of iron absorbs 1086.75 joules of heat energy, and its temperature changes from 25°C to 175°C. Calculate the specific heat capacity of iron. 2. How many joules of heat are needed to raise the temperature of 10.0 g of aluminum from 22.8°C to 53.9°C, if the specific heat of aluminum is 0.90 J/g°C? 3. What mass of water will change its temperature by 3.5°C when 525 J of heat is added to it? The specific heat of water is 4.18 J/g 0C 4. A 0.3 g piece of copper is heated and fashioned into a bracelet. The amount of energy transferred by heat to the copper is 66,300 J. If the specific heat of copper is 390 J/g 0C, what is the change of the copper's temperature? 5. Calculate the specific heat capacity of a piece of wood if 1500.0 g of the wood absorbs 67,500 joules of heat, and its temperature changes from 32°C to 57°C. Part 3: Thermochemical Equations & Enthalpy Diagrams 1. Determine if the following reactions are endothermic or exothermic: a) CaO (s) + H2O (l) Ca(OH)2 (s) ∆H = - 65.2 kJ Circle One: Do the reactants or products have a HIGHER enthalpy? b) 2 NaHCO3 (s) + 129 kJ Na2CO3 (s) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g) _________________________ Circle One: Do the reactants or products have a HIGHER enthalpy? c) NaOH (s) + H2O (l) Na+ (aq) + OH-- (aq) + 445.1 kJ ________________________ _______________________ Circle One: Do the reactants or products have a HIGHER enthalpy? d) PbCl2 (s) + Cl2 (g) PbCl4 (l) ∆H = 30.1 kJ _________________________ Circle One: Do the reactants or products have a HIGHER enthalpy? Draw and label an Enthalpy Diagram for this reaction below: e) RbOH (aq) + HBr (aq) RbBr (aq) + H2O + 55.9 kJ _________________________ Circle One: Do the reactants or products have a HIGHER enthalpy? Draw and label an Enthalpy Diagram for this reaction below: Part 4: Calorimetry q(gained) = - q(lost) mCp∆T(gained) = - mCp∆T(lost) 1. A room temperature (27°C) glass statue with a mass of 11.4 g is heated to dropped into 175 g of hot water at 100.0°C. The final temperature of the water is 97.6°C. What is the specific heat capacity of the glass statue? (Cp of water is 4.184 J/g°C). a) Which substance – glass or water- is losing heat (aka: getting cooler)? _________________ Calculate the quantity of heat lost by this substance: b) Which substance - glass or water- is gaining heat (aka: getting warmer)? __________________ Determine the quantity of heat gained by this substance: c) Determine the specific heat of the glass statue: 2. A 500.0 g piece of iron is heated in a flame and dropped into 400.0 g of water at 10.0°C. The temperature of the water rises to 90.0°C. What temperature was the iron initially when it was first removed from the flame? (Cp of iron is 0.473 J/g°C; Cp of water is 4.184 J/g°C). a) Which substance - iron or water- is gaining heat (aka: getting warmer)? __________________ Calculate the quantity of heat absorbed by this substance: b) Which substance - iron or water- is losing heat (aka: getting cooler)? __________________ Determine the quantity of heat lost by this substance: c) Determine the initial temperature of the iron when it was first removed from the flame: