The Nervous System

The Nervous System
Vocabulary Review
Peripheral nervous system
Cranial and spinal nerves outside the central nervous system
Central nervous system
Consists of the brain and spinal cord
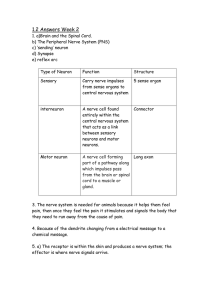
Neuron
A nerve cell
Nerve impulse
Electrochemical process that communicates within the nervous system
Dendrite
Part of the neuron that receives input from other neurons
Axon
Carries nerve impulses away from the cell body of a neuron
Nerve
Bundle of axons or nerve cell fibers
Sensory receptor
Specialized structure associated with the peripheral end of a sensory neuron specific to detecting a particular sensation and triggering a nerve impulse in response
Somatic nervous system
Motor pathways of the PNS that lead to skin and skeletal muscle
Autonomic nervous system
Portion of the PNS that controls organs (viscera), smooth, and cardiac muscle
Myelin
Fatty covering that protects and insulates an axon
Sensory neurons
Nerve composed of sensory nerve fibers
Interneurons
Link motor and sensory neurons in the CNS
Motor neurons
Transmits impulses from the CNS to effector muscles or glands
Nerve pathway
Route a nerve impulse travels
Synapse
Functional connection between an axon and a dendrite; wireless connection between neurons
Neurotransmitter
Chemical secreted at the end of an axon on to another neuron or effector muscle or gland
Reflex arc
Nerve pathway that forms the structural and functional basis for a reflex
Reflex
An automatic response to a stimulus
Meninges
3 membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord
Spinal nerves
Nerves that branch from the spinal cord; part of the PNS
Cerebrum
Larger portion of the brain that provides higher level mental functions
Diencephalon
Region of the brain containing the thalamus and hypothalamus; acts as a relay station for sensory input, as well as to maintain homeostasis
Brain stem
Includes the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the midbrain; connects brain to spinal cord
Cerebellum
Coordinates skeletal muscle movements