The Brain
advertisement

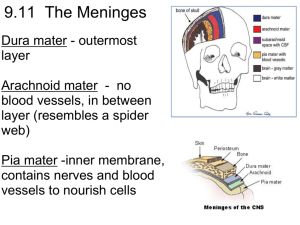
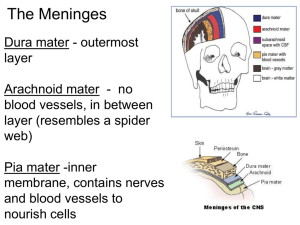
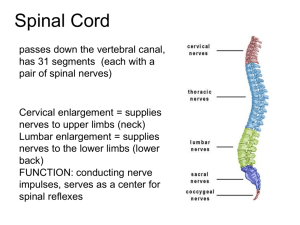
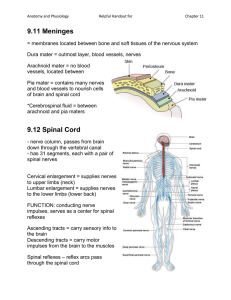
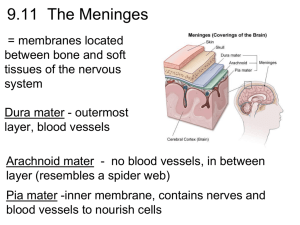
The Brain The Meninges (D.A.P.) •Dura mater - outermost layer (tough mother) •Arachnoid mater - no blood vessels, in between layer (resembles a spider web) •Pia mater -inner membrane, contains nerves and blood vessels to nourish cells (tender mother) The Meninges CSF = cerebrospinal fluid Figure 13.25a Dura mater is being peeled away in this photo. Subdural Hematoma THE BRAIN • ANATOMICAL REGIONS oCerebrum oCerebellum oBrain Stem CEREBELLUM • Balance and coordination • Could be involved in motor skill learning Cerebrum wrinkly large part of the brain, largest area in humans, higher mental function Brain Stem - regulates visceral functions (autonomic system) Figure 13.4 1. Cerebral Hemispheres - left and right side separated by the .... 2. Corpus Callosum - connects the two hemispheres - Some functions appear “lateralized” but the rightbrain, left-brain hypothesis is mostly debunked Corpus callosum 3. Convolutions of the Brain - the wrinkles and grooves of the cerebrum Fissures = deep groove Sulcus = shallow groove Gyrus = bump / ridge 4. Fissures – separate lobes Longitudinal fissure - separate right and left sides Transverse Fissure - separates cerebrum from cerebellum Lateral Fissure separates the temporal lobe from the Frontal and Parietal lobes Lissencephaly • Lack of gyri and sulci Albert Einstein’s Brain Albert Einstein’s Brain Albert Einstein’s Brain Lobes of the Brain (general functions) 5. Frontal – reasoning, thinking, language, conscious thought 6. Parietal – touch, pain, relation of body parts (somatosensory) 7. Temporal Lobe – hearing, smell 8. Occipital – vision LOBES OF THE BRAIN (CEREBRUM) Figure 13.7a Sulcus = groove Gyrus = raised bump Fissure = deep groove Cerebral Cortex - thin layer of gray matter that is the outermost portion of cerebrum (the part with all the wrinkles) Functional and Structural Areas of the Cerebral Cortex Figure 13.11a FUNCTIONAL REGIONS • A. MOTOR AREAS • B. SENSORY AREAS • C. ASSOCIATION Motor Areas • Primary Motor Cortex in Parietal Lobe • controls voluntary movements • also has Broca's Area (speech) Sensory Area • Primary Somatosensory Cortex in parietal lobe • involved in feelings and sensations = vision, hearing, smell, touch, taste Association Areas • higher levels of thinking, interpreting and analyzing information VENTRICLES OF THE BRAIN Four fluid filled cavities, contain CSF Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) - fluid that protects and supports brain Intraventricular Hemmhorage • A.k.a. “brain bleed” • Baby is so premature that capillaries are too weak to hold blood, blood escapes and fills ventricles BRAIN STEM Figure 13.4 1. Diencephalon (Interbrain – top of brainstem ) consists of two main parts: 2. Hypothalamus – hormonal regulation of heart rate, blood pressure, body temp, hunger. Connected to pituitary gland (Endocrine System) 3. Thalamus - relay station for sensory info 4. Optic Tract / Chiasma - optic nerves cross over each other BRAIN STEM • Consists of three main parts: oPONS oMIDBRAIN (Mesencephalon) oMEDULLA OBLONGATA Cerebellum balance, coordination 5. Midbrain (Mesencephalon) – visual reflexes, eye movements; motivation 6. Pons - relay sensory information; dreams 7. Medulla – heart, respiration, blood pressure Thalamus Pineal gland Hypothalamus Corpus callosum Medulla Oblongata Pons Midbrain 9. HIPPOCAMPUS • The hippocampus plays a major role in memories. • Neurogenesis – development of new neurons 10. The LIMBIC SYSTEM • Major role in emotion and memory • also includes olfactory lobes - memory, emotion, and smell are linked. • Includes hippocampus, amygdala, mammilary body, and others Spinal Cord passes down the vertebral canal, has 31 pairs of spinal nerves Cervical enlargement = supplies nerves to upper limbs (neck) Lumbar enlargement = supplies nerves to the lower limbs (lower back) FUNCTION: conducting nerve impulses, serves as a center for spinal reflexes ASCENDING impulses travel to the brain (sensory) DESCENDING impulses travel to the muscles (motor) Spinal reflexes - reflex arcs pass through the spinal cord