ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY/Dr
advertisement

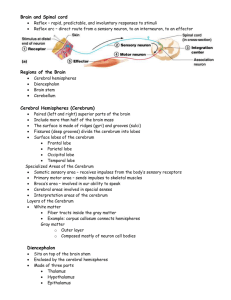
1 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CHAPTER 9 PART II NERVOUS SYSTEM (BRAIN) WORKSHEET ____1. ____ 2. ____3. ____4. ____5. ____6. ____7. ____8. ____9. ____10. ____11. ____12. ____13. ____14. ____15. ____16. NAME _____________________________ The outer membrane covering the brain is composed of fibrous connective tissues and is called the: A. dura mater B. arachnoid mater C. pia mater D. periosteum. Cerebrospinal fluid is found between: A. the arachnoid mater and the dura mater B. the vertebrae and the meninges C. the pia mater and the arachnoid mater. The spinal cord ends: A. at the sacrum C. between lumbar vertebrae 1 and 2 B. between thoracic vertebrae 11 and 12 D. at lumbar vertebra 5. Which of the following is not a major portion of the brain? A. cerebrum B. brain stem C. cerebellum D. spinal cord The hemispheres of the cerebrum are connected by nerve fibers called the: A. corpus callosum C. fissure of Rolando B. falx cerebri D. tentorium. The thalamus and hypothalamus are parts of the brain located in the: A. midbrain C. medulla oblongata B. pons D. diencephalon. The part of the brain responsible for regulation of temperature and heart rate, control of hunger, and regulation of fluid and electrolytes is the: A. thalamus C. medulla oblongata B. hypothalamus D. pons. For most of the populations the domoinant hemisphere is the: A. left B. right. Cerebrospinal fluid is produced by the: A. medulla oblongata C. choroids plexuses B. corpus callosum D. falx cerebri. The nerves that arise from the brain are known as: A. motor nerves C. cranial nerves E. mixed nerves. B. spinal nerves D. sensory nerves The spinal cord and brain are covered by three membranes called the: A. meninges C. funiculi E. peduncles. B. pia mater D. posterior horns The cranial and spinal nerves are part of the: A. central nervous system C. spinal cord E. none of these. B. brain D. peripheral nervous system The parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system: A. activates organs B. inhibits organs. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for: A. involuntary, unconscious control of heartbeat, peristalsis, etc. B. voluntary control of respiration C. coordination of voluntary muscles D. sense perception E. sight and hearing. Humans have ____pair of cranial nerves and ____ pair of spinal nerves respectively. A. 12, 31 B. 31, 12 C. 30, 6 D. 31, 10 E. 10, 12 The part of the brain that is concerned with memory, reasoning, and use of language is: A. cerebellum C. thalamus E. pons. B. cerebrum D. medulla oblongata 2 QUESTIONS 17-22 MATCHING Match the functions in the first column with the appropriate area of the brain in the second column. ____17. hearing ____18. vision ____19. recognition of printed work ____20. control of voluntary muscles ____21. pain ____22. complex problem solving a. b. c. d. frontal lobe parietal lobe temporal lobe occipital lobe QUESTIONS 23-30 MATCHING Match the descriptions on the left with the terms on the right. ____23. ____24. Cone-shaped structure attached to upper portion of thalamus Connects cerebral hemispheres ____25. Ridge on surface of cerebrum ____26. Separates frontal and parietal lobes ____27. Part of brain stem between diencephalon and pons ____28. Rounded bulge on underside of brain stem ____29. Thin layer of gray matter on surface of cerebrum ____30. Enlarged continuation of spinal cord a. central sulcus b. cerebral cortex c. convolution d. corpus callosum e. midbrain f. medulla oblongata g. pineal gland h. pons 3 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CHAPTER 9 PART II NERVOUS SYSTEM (BRAIN) LABELING NAME _____________________________ CROSS SECTION OF THE SPINAL CORD: 1 gray commissure 2 posterior median sulcus 3 posterior horn 4 white matter 5 lateral horn 6 gray matter 7 anterior horn 8 central canal 9 anterior median fissure MENINGES OF THE BRAIN AND SPINAL CORD: 1 subarachnoid space 2 dura mater 3 arachnoid mater 4 pia mater 5 cerebral cortex 4 BRAIN: 1 2 3 4 5 frontal lobe corpus callosum hypothalamus pituitary gland (hypophysis) temporal lobe 6 pons 7 medulla oblongata 8 spinal cord 9 cerebellum 10 pineal gland 11 12 13 14 15 occipital lobe thalamus parietal lobe cerebrum midbrain