Glossary of Brain Terms

Glossary of Brain Terms
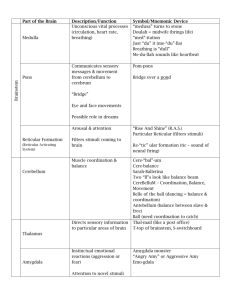
Amygdala . Located in the middle of the brain, this almond-shaped structure is an important processor of senses. It plays an important role in emotions and connects receptors sites for emotions.
Axons.
Long fibers from the brain cells that carry electrical nerve impulses.
Broca’s area . Located in the left frontal part of the cerebrum, it is the center for converting thoughts into sounds or written words and sends a message to the motor area.
Cerebellum
. The “little brain” located at the base (occipital lobe) of the brain next to the brain stem. Important for balance, posture, coordination, muscle movement, cognition, novelty, and emotions.
Cerebral cortex.
Newspaper-sized, one-fourth inch thick outer layer of the cerebrum. Six layers of wrinkled brain cells.
Cerebrum.
Right and left hemispheres of the brain which contains the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes.
Corpus collosum . White matter of millions of nerve cells that connect the left and right hemispheres of the brain.
Dendrites.
Strandlike fibers extending from the neuron that serve as receptors for axons. Each cell may have many dendrites and may grow more.
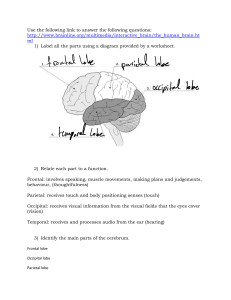
Frontal lobes . One of four parts of the cerebrum that control voluntary movement, verbal expressions, problem solving, one’s will power, and planning.
Glial.
One of two types of brain cells, often called interneurons. Their purpose is to carry nutrients, speed repair, and form their own communication network.
Hippocampus . Found deep in the temporal lobe in the middle of the brain, it is involved in learning and memory formation.
Hypothalamus . Located at the bottom center of the middle brain, it is the thermostat that influences appetite, hormones, digestion, sexuality, circulation, emotions, and sleep.
Medulla oblongata.
Part of the brain stem that controls respiration, circulation, wakefulness,, breathing, and heart rate.
Mid-brain.
Area behind the frontal lobes above the brain stem, but below the parietal lobes. It includes the thalamus, hippocampus, and amygdala.
Myelin . Fatty substance the coats the axons to make them more efficient.
Permits impulses to move about 12 times faster.
Neuron.
The second type of brain cell that connects and communicates with other neurons.
Occipital lobe.
Located at the back of the cerebrum; it processes vision.
Parietal lobe . Located on the top of the brain, it deals with receiving sensory information. Is important in reading, writing, language and calculation.
Reticular formation.
Located at the top of the brain stem and the bottom of the mid-brain, it regulates attention, arousal, sleep and wakefulness, and consciousness.
Temporal lobes.
Located on the side of the cerebrum, close to the ears, it is believed to be responsible for hearing, senses, listening, language, learning, and memory.
Thalamus.
Located in the middle of the brain, it serves as a sensory relay center and is responsible for the brain’s reward system.
Wernicke’s area.
On the upper back of the temporal lobe it converts thought processes into language.