Foundations 30- Chapter 2 Student Notes
advertisement

Chapter 2: Borrowing Money 2.1- Analyzing Loans Define: a) Collateralb) Amortization TableFormula: Interest Paid Per Term= Balance x Interest Rate/terms per year (SEE EXAMPLE ON P. 81)- TIME CONSUMING Ex: Ricki borrowed $15000 from a bank at 4% compounded monthly to buy a new car. Ricki will pay $400 at the end of each month until the loan is paid off. a) In which month will Ricki have at least half of the loan paid off? N=? I%= 4 PV= 15000 PMT=-400 FV= -7500 (half of the borrowed amount P/Y= 12 C/Y= 12 PMT: END BEGIN b) How long will it take RIcki to pay off the loan? Leave everything from a) except FV=0. N=? c) How much interest will Ricki have paid by the time she has the loan paid off? N=______ (from b) Use some of interest on calculator: ∑(1,38)=_______________ FM 30.1- Demonstrate understanding of financial decision making including analysis of renting, leasing, and buying credit compound interest investment portfolios. Ex2: Dennis’ employer loaned him $5000 at a fixed interest rate of 6%, compounded annually. The loan is to repaid in a single payment at the end of 5 years. a) How much will Dennis need to pay at the maturity date? What is the accumulated interest? Hint: Use A=P(1+i)n b) How much will Dennis need to pay at the maturity date if interest is compounded monthly? What do you notice? Ex3: Reese wants to do home improvement. His bank will charge him 3.4% compounded quarterly. He already has a 10-year GIC that will mature in 5 years. When his GIC matures, he wants to use the money to pay his home improvement loan with one payment. He wants the payment to be less than $20000. a) How much can he borrow? b) How much interest will he pay? FM 30.1- Demonstrate understanding of financial decision making including analysis of renting, leasing, and buying credit compound interest investment portfolios. Ex4: Ameena has been told she needs to make a 10% down payment on the purchase of her $250 000 house. The bank will offer a mortgage for the balance at 3.5% compounded semiannually, with a term of 20 years with monthly payments. a) How much will each payment be? b) How much interest will Ameena end up paying after 20 years? c) How much will she pay altogether? ** DO EXAMPLE 5 on P.89 using Graphing Calculator** **Use the sum of payment method.** FM 30.1- Demonstrate understanding of financial decision making including analysis of renting, leasing, and buying credit compound interest investment portfolios. 2.2 Exploring Credit Card Use Ex: Addison is buying a used Quad for $5000 on credit. She can afford payments of $300 each month and is considering these two options: The dealership credit card at 17.2%, compounded daily, and an immediate rebate of 2% off her first purchase. A bank loan at 9.5% compounded monthly. a) How much would she pay under each option? b) How much interest would she pay in each option? c) How long would it take her to pay off each option? d) Which option should she use? Explain in detail. FM 30.1- Demonstrate understanding of financial decision making including analysis of renting, leasing, and buying credit compound interest investment portfolios. 2.3- Solving Problems Involving Credit Definitions: a)Line of Creditb)Bank of Canada Prime Rate- Ex1: Elizabeth is buying a new big screen TV work $1500 on credit. She can make monthly payments of $90 and has the following options. Which option should she choose? Explain. Option A: The TV store credit card is offering a $100 rebate off the purchase and interest rate of 19.2% compounded daily. Option B: A new bank issued credit card which has an interest rate of 15.4% compounded daily but no interest for the first year. Ex2: Sarah wants to buy a car on credit. The cost of the car is $27 350. Sarah wants to repay her loan in 4 years using monthly payments and has two credit options: She could use her line of credit at 1.7% compounded monthly, above the Bank of Canada Rate, which is currently o.5% The dealerships finance plan at 2.5% compounded daily. a) Which option should he choose? Why? FM 30.1- Demonstrate understanding of financial decision making including analysis of renting, leasing, and buying credit compound interest investment portfolios. b) Suppose the Bank of Canada rate changed to 1.1% after 2 years. How would this change the payments if he still wants to pay in 4 years? c) If the Bank of Canada rate changes as per b), does your answer to a) change? Explain. Ex3: Evan’s $730 car insurance payment is due. He is considering the following options: Borrow the money from a payday loan company for a $100 fee if paid back in 2 months. Get a cash advance on his credit card at 19.95% compounded daily. He can afford to pay a $5 minimum payment at the end of the first month, and will pay the balance in full after the second month. a) Which option is the better one for Evan? b) What annual interest rate would equate to the fee charged by the payday loan company? FM 30.1- Demonstrate understanding of financial decision making including analysis of renting, leasing, and buying credit compound interest investment portfolios. Ex4: (GRAPHING CALC) Shyla wants to be debt free in 4 years. She has two credit cards that she makes payments on: Card A has a balance of $1934.62 and an interest rate of 18.3% compounded daily. Card B has a balance of $2549.43 and an interest rate of 19.2% compounded daily. Shyla has qualified for a line of credit at 8.5% compounded monthly with a credit limit of $6000. She plans to pay off both credit cards by borrowing from her credit line. How much interest will she save? Ex 5: Mr. Walker signed up for a credit offer when buying furniture. There were no payments and no interest for 12 months as long as he paid the $3211.11 balance in full by the end of the first year. Otherwise a penalty equal to 19.8% interest compounded monthly (on the full amount) will be charged starting from when he made the purchase. a)If Mr. Walker missed the deadline by one day, what would he have to pay? What would the penalty be? b)Suppose he made monthly payments of $175 during the year. What would the last payment be to avoid penalty? FM 30.1- Demonstrate understanding of financial decision making including analysis of renting, leasing, and buying credit compound interest investment portfolios. 2.4- Buy, Rent, or Lease Definition: a)Leaseb)Equityc)Assetd)Disposable Income- See: Learn About Math (p.120) and Example 1 (p.121) Ex1: A vehicle rental company depreciates the value of its vehicles each year over 5 years. At the end of the fifth year, the company writes off a vehicle for its scra value. The company uses a depreciation rate of 35% a year. a) What is the scrap value of each car below: a. Car A which is currently 2 years old at a value of $25 214 b. Car B which is currently 1 year old at a value of $33 131 b) What was the original value of each car when purchased new? FM 30.1- Demonstrate understanding of financial decision making including analysis of renting, leasing, and buying credit compound interest investment portfolios. Ex2: Brent’s water heater stopped working. He has $40 of disposable income each month and a credit card that charges 18% compounded daily. He has two options: Brent could least from a company for $12 per month. This includes parts and service. He could buy a water for $734.45 plus an installation fee of $250, using his credit card. He can only pay $40 a month. a) What costs are associated with each option? b) What do you recommend for Brent? c) Suppose you could guarantee the water heater would last 8 years. What would you recommend now? Ex3: Jon started his own construction business two years ago, but his home office needs to be replaced. His options include: He could sign a 3- year lease with monthly payments of $2100 with a $2000 damage deposit. There is also a penalty for breaking a lease. He could purchase a house for $300 000 and renovate it to make it an office. A 5% down payment would be required on a 15 year mortgage at 5% compounded semi-annually, with monthly payments. Assume appreciation of 2% yearly. a) What are the costs of leasing over 15 years? FM 30.1- Demonstrate understanding of financial decision making including analysis of renting, leasing, and buying credit compound interest investment portfolios. b) What are the costs of buying over 15 years? c) What do you recommend for Jon? Explain. Ex4: Two couples made different decisions on whether to rent or buy: David and Mandy bought a house for $275 000. They negotiated a mortgage for 95% of the purchase price, so they will need a 5% down payment. The mortgage is compounded semi-annually at 5.3% with monthly payments over 20 years. Jade and Brenden are renting a house for $1700 per month, renewed yearly. After 3 years, both couples decide to move. David and Mandy discover their house has depreciated by 10% over the three years. Compare each situation. FM 30.1- Demonstrate understanding of financial decision making including analysis of renting, leasing, and buying credit compound interest investment portfolios.




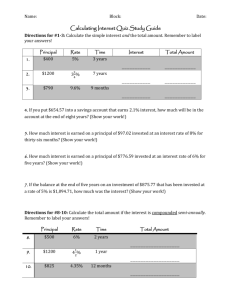

![Practice Quiz Compound Interest [with answers]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008331665_1-e5f9ad7c540d78db3115f167e25be91a-300x300.png)

