Chap9-10 Review Exer..
advertisement

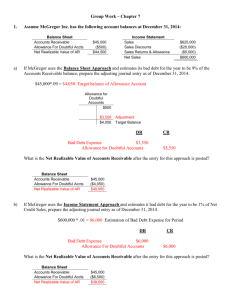
Chapter Review Exercise 9-10 McGraw-Hill/Irwin1 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2006 Exercise 1: Bad Debt Expense, Allowance Method, Percent of Sales Method (Chap 9) Alvare Company Dec.31, estimate 0.5% bad debt of annual credit sales of $875,000 Feb.1, decide that $420 account of P. Coble is uncollectible and write it off as a Bad Debt June 5, Coble unexpectedly pays the amount previously written off McGraw-Hill/Irwin2 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2006 Exercise 1: Bad Debt Expense, Allowance Method, Percent of Sales Method (Chap 9) Alvare Company Dec.31, estimate 0.5% bad debt of annual credit sales of $875,000 Feb.1, decide that $420 account of P. Coble is uncollectible and write it off June 5, Coble unexpectedly pays the amount previously written off Annual Credit Sales Bad Debt Ratio Bad Debt Expense Dec.31 Bad Debt Expense Allowance for Doudtful Accounts 875,000 0.50% 4,375 4,375 4,375 Bad Debt Adjustment at year end Feb.1 Allowance for Doudtful Accounts Account Receivable - P.Coble 420 420 Write off bad debt of P.Coble June.5 Account Receivable - P.Coble Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 420 Cash 420 Account Receivable - P.Coble 420 420 P.Coble paid the account fomerly written off McGraw-Hill/Irwin3 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2006 Exercise 2: Bad Debt Expense, Allowance Method, Percent of Account Receivable Method (Chap 9) Cabool Supply Co. Dec.31, 2005, outstanding account receivable $53,000, estimate 4% uncollectible (a) Allowance for Doubtful Accounts has $915 credit balance (b) Allowance for Doubtful Accounts has $1,332 debit balance McGraw-Hill/Irwin4 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2006 Cabool Supply Co. Dec.31, 2205, outstanding account receivable $53,000, estimate 4% uncollectible (a) Allowance for Doubtful Accounts has $915 credit balance (b) Allowance for Doubtful Accounts has $1,332 debit balance Year-end outstanding Account Receivable Uncollectible ratio Adjusted Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 53,000 4% 2,120 a) Allowance for Doubtful Accounts unadjuted Bal. Bad Debt Expense Adjuted Bal. De.31 Bad Debt Expense Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 915 1,205 2,120 1,205 1,205 Bad Debt Adjustement at year end b) unadjuted Bal. Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 1,332 Bad Debt Expense Adjuted Bal. De.31 Bad Debt Expense Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 3,452 2,120 3,452 3,452 Bad Debt Adjustement at year end McGraw-Hill/Irwin5 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2006 Exercise 3: Note Receivable, Interest Revenue (Chap 9) Deshawn Company 2004 Dec.13, accept $10,000, 60-day,8% note dated Dec.13 in granting Clark a time extension on her past-due account receivable. Dec.31, Prepare adjusting entry for accrued interest of Clark note. 2005 Feb.11, Receive Clark’s payment for principle and interest on note of Dec.13 Mar.3, accept $4,000, 90-day,10% note dated Mar.3 in granting Shandi Company a time extension on her past-due account receivable. Mar.17, accept $2,000, 30-day,9% note dated Mar.17 in granting Torres a time extension on her past-due account receivable. Apr.16, Torres dishonor his note when presented for payment. May.1, Wrote off Torres account against allowance for Doubtful Accounts June.1 Receive Shandi payment for principle and interest on note of Mar.17 McGraw-Hill/Irwin6 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2006 2004 Dec.13 Note Receivable - Clark Account Receivable -Clark 10,000 10,000 Accept Note receivable for past-due Account receivable of Clark Dec.31 Interest Receivable Interest Revenue 40 40 Record Accrued Interest revenue 2005 Feb.11 Cash 10,133 Note receivable - Clark Interest Receivale Interest Revenue 10,000 40 93 Clark pay the Note Receivable and Interest Mar.3 Note Receivable - Shandi Account Receivable -Shandi 4,000 4,000 Accept Note receivable for past-due Account receivable of Shandi Mar.17 Note Receivable - Torres Account Receivable Torres 2,000 2,000 Accept Note receivable for past-due Account receivable of Torris Apr.16 Account Receivable - Torres Note Receivable -Torres Interest Revenue 2,015 2,000 15 Torris dishonor Note receivable May.1 Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Account Receivable - Torres 2,015 2,015 Write off Torris' Account receivable June.1 Cash 4,100 Note Receivable -Shandi Interesr Revenue Shandi pay the Note Receivable and Interest McGraw-Hill/Irwin7 4,000 100 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2006 Exercise 4: Extraordinary Repairs, Plant Asset Depreciation (Chap 10) Passat Company has a building with original cost $561,000, and Accumulate Depreciation $420,750 The building has 20-year life and no salvage value, and depreciate with straight-line method Major structural repair costing $67,200 completed during first week of January. The repair will extend useful life of building for 7 years. What’s the age of building? Journal entry for structural repair Book value of building immediately after repair? Journal entry for current year’s depreciation? McGraw-Hill/Irwin8 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2006 Exercise 4: Extraordinary Repairs, Plant Asset Depreciation (Chap 10) Passat Company has a building with original cost $561,000, and Accumulate Depreciation $420,750 The building has 20-year life and no salvage value, and depreciate with straight-line method Major structural repair costing $67,200 completed during first week of January. The repair will extend useful life of building for 7 years. What’s the age of building? Journal entry for structural repair Book value of building immediately after repair? Journal entry for current year’s depreciation? McGraw-Hill/Irwin9 Divide Multiple Jan.1 Building Original Cost Salvage Value useful life Annual Depriciation Service years Accumulate Depriciation 561,000 0 20 28,050 15 420,750 Building Cash 67,200 67,200 Record Extraordinary Repair Less Add Dec.31 Building Original Cost Accumulate Depriciation Building Book Value Extraordinary Repair Cost Building Book Value after Extra. Repair Useful life Annual Depriciation after Extra. Repair Depriciation Expense Accumulated Depriciation - Building 561,000 420,750 140,250 67,200 207,450 12 17,288 17,288 17,288 Record Depreciation Expense © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2006 Exercise 5: Plant asset disposal, exchange similar assets (Chap 10) Jan.2, Atlantic Co. dispose a machine costing $42,000 with accumulated depreciation $22,625. Prepare journal entry for, (a) Machine is sold for $16,250 (b) Machine is traded in on a similar machine with $58,500 cash price. A $20,000 trade-in allowance is received, and balance is paid in cash. (c) Machine is traded in on a similar machine with $58,500 cash price. A $15,000 trade-in allowance is received, and balance is paid in cash. McGraw-Hill/Irwin10 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2006 Less Less Machine Cost Accumulated Depriciation Book Value of Machine Disposal Value of Machine Loss on Disposal of Machine 42,000 22,625 19,375 16,250 3,125 Cash Loss on Disposal of Machinery Accumulated Depriciation - Machinery Machinery 16,250 3,125 22,625 42,000 (b) Less Market Value of New Machine Old Machine Cost Accumulated Depriciation Book Value of Old Machine Cash Book Value of Assets given up Gain on Exchange New Machinery Accumulated Depriciation - Old Machinery Cash Old Machinery 58,500 42,000 22,625 19,375 38,500 57,875 625 57,875 22,625 38,500 42,000 ( c) Less Market Value of New Machine Old Machine Cost Accumulated Depriciation Book Value of Old Machine Cash Book Value of Assets given up Loss on Exchange New Machinery Loss on Exchange of Machinery Accumulated Depriciation - Old Machinery Cash Old Machinery McGraw-Hill/Irwin11 58,500 42,000 22,625 19,375 43,500 62,875 4,375 58,500 4,375 22,625 43,500 42,000 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2006