BA 360 Review: Finance Questions & Answers
advertisement

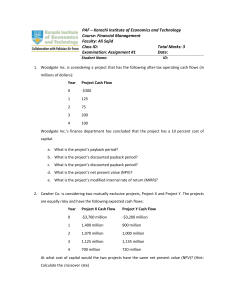
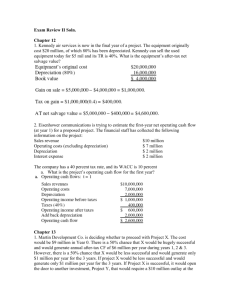
OSU SCHOOL OF BUSINESS BA 360- Review Chapter 8 1. You are considering buying a share of stock in a firm that has the following two possible payoffs with the corresponding probability of occurrence. The stock has a purchase price of $15. You forecast that there is a 30% chance that the stock will sell at $30 at the end of the year. The alternative expectation is that is a 70% chance the stock will sell for $10 at the end of one year. What is the expected percentage return on this stock, and what is the return variance. 2. George is considering an investment in Vandelay Inc. and has gathered the following information. What is the expected return for a share of the firm’s stock? State of the economy Recession Normal Boom Probability of the state 0.25 0.60 0.15 Conditional expected return vandelay inc -20% 10% 35% 3. The type of risk that can diversify away is? 4. Joel owns the following portfolio of securities: 5. What is the beta for the portfolio? Company Exxon Mobil Pacific Industries Payson Restaurants Beta 0.95 1.20 1.35 Percent of Portfolio 40% 35% 25% 6. Both Assets A and B plot on the SML. Asset A has an expected return of 15% and a beta of 1.7, and Asset B has an expected return of 12% and a beta of 1.1. What is the risk-free rate of return? Chapter 9 1. Projects are mutually exclusive if picking one project eliminates the ability to pick the other project. This mutually exclusive situation can arise for different reasons. Which of the following is not one of those reasons? 2. 3. 4. 5. One project will always have a negative NPV. There is a scarce resource that both projects would need. There is need for only one project, and both projects can fulfill that current need. By using funds for one project, there are not enough funds available for the other project. 6. Dweller Inc. is considering a four-year project that has an initial after-tax outlay or after tax cost of $80,000. The future after-tax cash inflow from its project are $40,000, $40,000, $30,000, and $30,000 for years, two, three, and four, respectively. Dweller uses the NPV method and has a discount rate of 12%. Will Dweller accept the project? 7. Flynn Inc. is considering a four-year project that has an initial after-tax outlay or after-tax cost of $80,000. The future after-tax cash inflows from its project for years one, two, three, and four are $40,000, $40,000, $30,000, and 30,000, respectively. Flynn uses the internal rate of return method to evaluate projects. What is the approximate IRR for this project? 8. The IRR model suffers from three problems. Which of the following is not one these problems? 9. Comparing mutually exclusive projects 10. Cumbersome computations not resolvable by the last technology 11. Incorporates the IRR as the reinvestment rate for the future cash flows 12. Multiple IRR’s 13. Corbett and Sullivan Enterprises use the MIRR when evualing projects. CSE’s cost of capital is 9.5%. What is the project’s MIRR if the initial costs are $10,200,000 and the project lasts seven years, with each year producing the same after-tax cash inflows of $1,900,000? 14. Corbett and Sullivan Enterprises (CSE) use the MIRR when evaluating projects. CSE’s cost of capital is 9.5%. What is the project’s MIRR if the initial costs are $10,200,000 and the project lasts seven years, with each year production the same after-tax cash inflow of $1,900,000? Chapter 10 1. The revenue is $24,000, the cost of goods sold is $12,000, other expenses (from selling and administration) are $6,000, and depreciation is $2,000. What is the EBIT? 2. _______ involves(s) a cash flow that never occurs, but we need to add it as a cost or outflow of a new project. a. Cost Recovery of divested assets b. Capital expenditures c. Sunk costs d. Opportunity costs 3. A firm is considering purchasing two assets. Asset A will have a useful life of fifteen years and cost of $3,000,000. It will have installation costs of $400,000, but no salvage or residual value. Asset B will have a useful life of six years and cost 1,300,000. It will have installation costs of $180,000 and a salvage or residual value of $300,000. Which asset will have a greater annual straight-line depreciation. 4. The advantage of MACRS over straight-line depreciation is that you can write off more of your capital costs in the _____ year(s). Chapter 11 1. Your firm has preferred stock outstanding that pays a current dividend of $3.00 per year and has a current price of $39.50. You anticipate the economy to grow steadily at a rate of 3.00% per year for the foreseeable future. What is the market required rate of return on your firm’s preferred stock? 2. Use the dividend growth model to determine the required rate of return for equity. Your firm intends to issue new common stock. Your investment bankers have determined that you should offer the stock at a price of $45 per share and you should anticipate paying a dividend of 3.50% per year and the investment banking firm will take 7.00% per share as flotation costs, what is the required rate of return for this issue of new common stock? 3. Elway Electronics has debt with a market value of $350,000, preferred stock with a market value of $150,000, and common stock with a market value of $450,000. If debt has a cost of 8%, preferred stock a cost of 10%, common stock a cost of 12%, and the firm has a tax rate of 30%, what is the WACC? 4. Your firm has an average-risk project under consideration. You choose to find the project in the same manner as if the firm’s existing capital structure. If cost of debt is 9.50%, the cost of preferred stock is 10%, the cost of common stock is 12.00%, and the WACC adjusted for taxes is 11.50%, what is the project’s NPV given the expected cash flows listed here? Category Investment Net working Capital Operating Cash Flow Salvage Total incremental cash flow T0 T1 T2 T3 -$800,000 -$50,000 $50,000 $350,000 $350,000 $350,000 $20,000 -$850,000 $350,000 $350,000 $420,000 5. Takelmer Industries has a different WACC for each of three types of projects. Low-risk projects have an 8% WACC, average-risk projects a 10% WACC, and high-risk projects a 12% WACC. Which of the following projects do you recommend that the firm accept? Project A B C D E F G Level of Risk Low Average Average Low High High Average IRR 9.50% 8.50% 7.50% 9.50% 14.50% 17.50% 11.50% 6. International Geographica is adding a new magazine project to the company portfolio and has the following information: the expected market return is 12%, the risk-free is 4%, and the expected return on the new project is 20%. What is the project’s bet? 7. Your firm has $2,000,000 available for investment in capital projects. Which combination of projects is the best, given this budget constraints. Project A B C D Initial investment $750,000 $1,500,000 $500,000 $500,000 NPV $100,000 $125,000 $75,000 $35,00 8. Runway Fashions Inc. is considering the following potential projects for the company but has only $1,000,000 in the capital budget. Which projects should it consider? Project Cost NPV IRR Winter Costs $750,000 $95,000 13% Spring Dresses $500,000 $45,000 9% Fall Suits $500,000 $55,000 11% Summer Sandals $400,000 $60,000 14% Chapter 12 1. The sales for October, November, and December are $10,000, $12,000 and $18,000, respectively. For any particular sales month, the company receives the following percentages over time in cash: 20% in cash from that same sales month, 50% in cash from the previous month’s sales, and 30% in cash from the sales from two months ago, What amount of cash will the company receive during December? 2. A company estimates the following expenditures: preferred dividends payout of $22,200, wages to workers of $49,600, overhead costs of $24,300, raw material costs of $45,000, and shipping costs of $12,100. What are the total production costs? 3. The following information is for auxiliary Inc. for the month of May: cash sales of $200,000, accounts receivable payments of $200,000, accounts payable of $200,000, wages and salaries of $100,00, and interest payments of $50,000. There are no other cash inflows or outflows for the month of May, and its beginning monthly cash balance is $50,000. What is Auxiliary’s ending cash balance of May? Chapter 13 1. Use the following information, the inventory turnover for the company is? Cash Sales $1,500,000 Credit Sales $7,500,000 Total Sales $9,000,000 COGS $6,000,000 Current Year Accounts Receivable $270,000 Inventory $125,000 Accounts payable $110,000 Last Year $240,000 $100,000 $90,000 Change $30,000 $25,000 $20,000 2. The optimal order quantity as determined by the EOQ occurs when __________. a. Ordering costs equal carrying costs b. Ordering costs are exactly one-half carrying costs c. Ordering costs are exactly twice as much carrying costs d. None of answers (a) through (c) is accurate Chapter 14 1. Everything else being equal, which firm is placing the most burdens on its borrowing? Debt-to-equity Earnings per share Firm 1 0.2 $4.00 Firm 2 0.3 $3.00 Firm 3 0.35 $2.50 Firm 4 0.4 $2.00