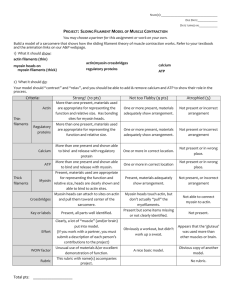
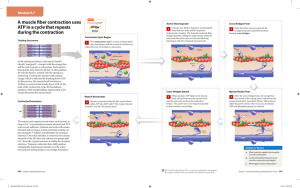
AP Bio Test Review
advertisement

AP Biology AP Test Review Jeopardy A: Cells B: Energetics C: Heredity & Genetics D: Evolution & Diversity E: Plants F: Animals G: More Animals 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 Final Jeopardy Help (1) Save a duplicate of this template. (2) Enter all answers and questions in the normal view. (view/normal) (3) Change the category headings in the normal view (view/normal) (4) View as a slideshow. (5) Use the home red button after each question. ©Norman Herr, 2003 A-100 • ANSWER: The functions of smooth ER, lysosomes and peroxisomes, respectively • QUESTION: What is – Lipid synthesis and toxin detox – Digestion of macromolecules by enzymes and an acidic environment; and – Breakdown of various substances including some toxins and H2O2? Answer Question A-200 • ANSWER: Cell junctions in plant and animal cells (respectively) that permit passage of some materials from one cell to another • QUESTION: What are plasmodesmata and gap junctions? Answer Question A-300 • ANSWER: The fluid mosaic model • QUESTION: What model describes the cell membrane as a flexible phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that can move somewhat? • Phospholipid hydrophilic heads to the outside • Hydrophobic tails inside Answer Question A-400 • ANSWER: The mechanisms for passive and active transport • QUESTION: What are diffusion down a concentration gradient (passive) and use of energy to move solutes against their gradients (active)? Answer Question A-500 • ANSWER: Parts of a signal transduction pathway • QUESTION: What are reception, transduction and response? Answer Question B-100 • ANSWER: The 3 steps in cellular respiration and the 2 parts of the last step • QUESTION: What are glycolysis, the Krebs (or citric acid) cycle and oxidative phosphorylation; and what are the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis? Answer Question B-200 • ANSWER: 2 types of fermentation, and what organisms have these processes • QUESTION: What is alcohol fermentation, done by yeasts and some bacteria, and what is lactic acid fermentation, done by animal muscles Answer Question B-300 • ANSWER: The 2 major processes of photosynthesis and the 2 reaction centers of the first process (in the order they are active) • QUESTION: What are light-dependent and the Calvin Cycle (or lightindependent) reactions, and what are photosystems II and I? Answer Question B-400 • ANSWER: The difference between C3, C4 and CAM plants • QUESTION: What are C3 plants that do the Calvin cycle during the day, (which may result in photorespiration on hot, dry days); C4 plants that fix carbon in mesophyll cells which avoids photorespiration, and CAM plants that open stomata and fix carbon at night Answer Question B-500 • ANSWER: Non-cyclic vs. cyclic electron flow • QUESTION: What is the production of ATP that uses PS II, the ETC and PSI vs. PS I, the ETC and back to PS I to generate more ATP than NADPH? Answer Question C-100 • ANSWER: Introns and exons • QUESTION: What are the noncoding and coding segments of mRNA? Answer Question C-200 • ANSWER: Stages in meiosis in which crossing over, lining up of homologues, separation of homologues, and separation of chromatids occur • QUESTION: What are prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I and anaphase II? Answer Question C-300 • ANSWER: Forms of inheritance in which – – – – • Traits blend There is equal expression of 2 alleles There is interaction of many genes Genes at one locus affect the expression of genes at another locus – An allele affects several characteristics of an organism QUESTION: What are – Incomplete dominance – Codominance – Polygenic inheritance – Epistasis – Pleitropy? Answer Question C-400 • ANSWER: Restriction enzymes, plasmids, phage, recombinant DNA • QUESTION: What are enzymes that cut DNA at a specific sequence, circular DNA of bacteria, a virus that infects bacteria, and DNA containing genetic material from more than one organism Answer Question C-500 • ANSWER: Epigenic inheritance • QUESTION: What is the transmission of traits by mechanisms that do not involve changes in DNA sequences? Answer Question D-100 • ANSWER: Phylogeny, homologous structures, and analogous structures • QUESTION: What are the terms for the study of evolutionary relationships, structures in different species that evolve from a common ancestor and structures in different species that evolve independently due to environmental conditions. Answer Question D-200 • ANSWER: Speciation that occurs when a population is divided by a geographic barrier, and speciation that occurs without a geographic barrier • QUESTION: What are allopatric and sympatric speciation (respectively)? Answer Question D-300 • ANSWER: The allele and genotype frequencies for a plant population consisting of 84% plants with red flowers and 16% white flowers (where the red allele is dominant over the white). • QUESTION: What are .6 dominant and .4 recessive allele frequencies, and 36% homozygous dominant, 48% heterozygous, and 16% homozygous recessive genotype frequencies? Answer Question D-400 • ANSWER: 4 scientific areas of study that provide evidence for evolution • QUESTION: What are (4 of) – – – – – Paleontology Biogeography Embryology Comparative anatomy Molecular biology Answer Question D-500 • ANSWER: 3 factors that cause evolution (or changes in allele frequencies) • QUESTION: What are 3 of – Natural selection – Mutations – Gene flow – Genetic drift (including founder effect and bottleneck) – Nonrandom mating Answer Question E-100 • ANSWER: The major groups of plants that include mosses, ferns, conifers and flowering plants, respectively • QUESTION: What are nonvascular, seedless vascular, gymnosperms and angiosperms? Answer Question E-200 • ANSWER: Primary growth and where on plants it occurs, and secondary growth and where it occurs • QUESTION: What is plant growth in length that occurs at apical meristems and plant growth (in woody plants) in girth (width) that occurs in lateral meristems? Answer Question E-300 • ANSWER: The sporophyte and gametophyte in plants and the term for the type of life cycle plants undergo • QUESTION: What are the plant and the pollen/embryo sac, and alternation of generations? Answer Question E-400 • ANSWER: Photoperiodism and phytochromes • QUESTION: What is the response of plants to changes in the relative lengths of daylight and night, and pigments that are involved in plant responses to light Answer Question E-500 • ANSWER: Plant hormones that a) promote plant growth and phototropism, b) promote leaf abscission (release from the stem) and fruit ripening, c) inhibit leaf abscission and promote bud and seed dormancy • QUESTION: What are auxins, ethylene and abscisic acid? Answer Question F-100 • ANSWER: Metabolic rate, endothermic vs. exothermic • QUESTION: What is the amount of energy an animal uses in a unit of time; what are animals that generate their own body heat vs. animals that obtain body heat from the environment? Answer Question F-200 • ANSWER: The processes by which gas exchange occurs between alveoli and capillaries, between capillaries and body cells and the mechanism that permits air movement into and out of the lungs • QUESTION: What is diffusion, diffusion, and volume changes that create pressure differences? Answer Question F-300 • ANSWER: The 3 processes involved in a human nephron to produce urine from blood, and where they occur • QUESTION: What are filtration (in the glomerulus), secretion (in the proximal convoluted tubules) and reabsorption (in the loop of Henle and distal convoluted tubules)? Answer Question F-400 • ANSWER: Steps that lead to transmission of a nerve impulse across a synapse once the action potential reaches the axon terminal • QUESTION: What are – Release of Ca2+ into the axon terminal – Vesicles containing a neurotransmitter travel to the axon membrane – The neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft between the pre-synaptic and post-synaptic cells – Receptors on the post-synaptic cell bind to the neurotransmitter and the post-synaptic membrane is excited or inhibited (depending on the type of signal from the neurotransmitter) – The neurotransmitter is reabsorbed by the pre-synaptic cell or broken down and recycled Answer Question F-500 • ANSWER: Steps to muscle contraction in a sarcomere • QUESTION: What are – ATP binds to myosin heads on the thick filaments and forms ADP + P – An action potential causes Ca2+ to be released and Ca2+ binds to proteins on the thin actin filaments, exposing binding sites for myosin – Myosin heads attach to binding sites on actin, forming cross bridges between the thick and thin filaments – ADP + P are released and the myosin head swivels, pulling the actin inward, causing the sarcomere to contract (this is done many times causing the whole muscle to contract) – New ATP attaches to the myosin, causing the cross bridges to unbind, and the process is ready to repeat – When the action potential stops, the Ca2+ is reabsorbed and the myosin binding sites on the actin are not exposed, so cross bridges cannot form Answer Question G-100 • ANSWER: 3 Stages in embryonic development after fertilization • QUESTION: What are cleavage, (morula), blastula, and gastrula Answer Question G-200 • ANSWER: Coelom, gastrovascular cavity and alimentary canal • QUESTION: What is a fluid-filled body cavity that separates the digestive tract from the outer body wall; and what is a single opening that functions in both digestion and excretion; and what is a one-way digestive tract with 2 openings? Answer Question G-300 • ANSWER: Agonistic behavior, taxis, kinesis, and imprinting • QUESTION: What is aggression or submission resulting from competition, undirected change in speed of an animal’s response to a stimulus, a directed movement in response to a stimulus, and a process for acquiring specific behavior only if an appropriate stimulus is experienced during a critical period? Answer Question G-400 • ANSWER: The functions and source organ/gland for antidiuretic hormone, insulin, epinephrine and aldosterone • QUESTION: What are regulation of water balance (posterior pituitary), decreases blood sugar levels (pancreas), fight or flight response [increase blood sugar and heart rate] (adrenal medulla), and sodium and potassium homeostasis (adrenal cortex)? Answer Question G-500 • ANSWER: In the immune response, 2 functions of macrophages, functions of the 2 types of B cells, and functions of each of the 4 types of T cells • QUESTION: What are – Phagocytosis and antigen presentation; – Plasma cells that produce antibodies and memory Bs which remember the antigen the next time it attacks ; and – Helper Ts which activate B and other T cells, cytotoxic Ts which destroy infected body cells, suppressor Ts which turn off the immune response when it has done enough, and memory Ts which remember the antigen the next time it attacks so the antigen can be destroyed before you realize you’ve been infected Answer Question FINAL JEOPARDY • ANSWER: The energy-carrying molecules used in cellular respiration vs. those used in photosynthesis (include what they begin as and what they are reduced to, if applicable) • QUESTION: – In cellular respiration, what are NAD+ to NADH, FAD to FADH2 and ATP – In photosynthesis, what are NADP+ to NADPH and ATP Answer Question