Muscle Quiz 1
advertisement

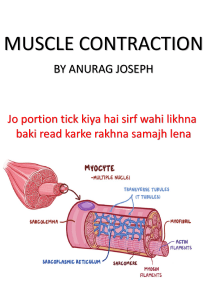
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY MUSCLE SYSTEM QUIZ 1 NAME ________________________________________________________ DATE ___________________ What does the sliding filament theory explain? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ Step 1: A muscle contraction starts in the brain, where signals are sent along the (1. CIRCLE ONE: myosin motor neuron ) where there are vesicles that contain the neurotransmitter (2. CIRCLE ONE: acetycholine cholinesterase ). This neurotransmitter reaches the receptors on the (3. CIRCLE ONE: sarcolemma sarcoplasm ) which causes an impulse. Step 2: The impulse travels down the membrane and into the transverse tubules where it causes calcium to be released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Step 3: Calcium binds to a structure on the actin that causes it to change shape. Step 4: The change in shape allows myosin heads to form cross-bridges between the actin and the myosin. Step 5: Energy from (4. CIRCLE ONE: acetycholine ATP) is used to create a "power stroke" between the two filaments. The (5. CIRCLE ONE: actin myosin ) filament then slides inward and shortens, or contracts, the whole muscle. The Neuromuscular Junction. MATCH the part with the letter indicated at right. _____6. T tubule A .. B . _____7. actin _____8. neuron _____9. myosin _____10. cross bridge C D E