Neuromuscular Junctions Physiology of Muscle Fibers
advertisement
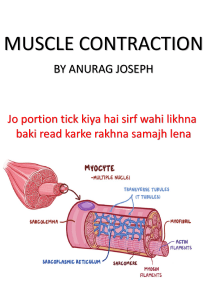
This will eventually lead to a muscle contraction if the stimulus is above the threshold. What do we have in common? Puffer fish Poison Arrow Frog Blue-ringed Octopus Neuromuscular Junction - The Real Thing! Botulinum toxin binds to pre-synaptic membranes at neuromuscular junctions, enters the neuron, and then a component of the toxin interferes with the release of neurotransmitter. Release of acetylcholine is blocked. No acetylcholine? No muscular contraction. (flaccid paralysis) The Transverse (T) Tubules work with the sarcoplasmic reticulum to rapidly concentrate and move calcium ions throughout the sarcoplasm Ca2+ binds the troponin molecules on the thin actin myofilaments. This leads to the ability of the thick myosin filaments to bind the actin. The myosin heads pull the actin molecules inward, causing the whole fiber to shorten. What is happening when ATP binds the myosin head? The cross-bridge is broken and the muscle relaxes! Body Temperature Rigor Mortis Time since death Warm Not yet stiff Dead not more than 3 hours Warm Stiffness starting in head Dead 3 to 8 hours Cold Stiff A Cold Dead 9 to 36 hours No longer stiff Dead more than 36 hours http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9FF6 UKvDgeE http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pcay ZjTKsm8&feature=related