Ch07 - Muscles
advertisement

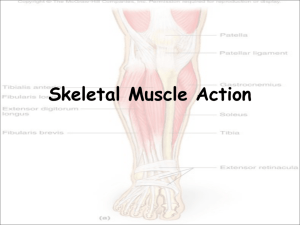
Muscles What you Need to Know • Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle • Naming, Identification, Functions You are only responsible for the identification of ALL muscles which are on your Lab Packet In general: Generates force to move your bones Propel body fluids & ingested food Generate and distribute heat Muscle Specialized for contraction movement of skeleton or internal organs c) smooth a) skeletal b) cardiac Skeletal Muscle -generally attaches to bone causes movement of skeleton Characteristics: -long & unbranched, tightly packed, parallel cells -multinucleated -striated (striped) -voluntary (conscious control) Cardiac Muscle -muscle of the heart Characteristics: -1 nucleus per cell -branched cells with mild striations -involuntary (not consciously controlled) Smooth Muscle -movement within internal organs other than the heart (e.g. digestive tract, bladder, arteries, etc.) Characteristics: -tapered cells -single nucleus/cell -no striations -involuntary Observe muscle slides! Use these pictures to quiz yourself! Dense Regular Connective Tissue -forms tendons (attach muscle to bone) and ligaments (attach bone to bone) -fibroblasts in collagen matrix Collagen fibers Fibroblasts Facial Muscles Frontalis: raises eyebrows; wrinkles forehead Orbicularis oculi: closes eye Buccinator: compresses cheek Masseter: elevates mandible (closes jaw) p. 84 Temporalis: elevates mandible Orbicularis oris: closes and purses lips Facial Muscles Temporalis: elevates mandible Frontalis: raises eyebrows; wrinkles forehead Orbicularis oculi: closes eye Buccinator: compresses cheek Masseter: elevates mandible (closes jaw) No equivalent picture in lab manual Orbicularis oris: closes and purses lips Sternocleidomastoid -If both contracted flexion of head when both (nod down) -If one contracted rotates head to opposite shoulder Muscles Many muscles form antagonistic muscle pairs Agonist: muscle that’s causing movement Antagonist: muscle that opposes the agonist An example… During arm flexion: Agonist: Biceps brachii Antagonist: Triceps brachii During arm extension: Agonist: Triceps brachii Antagonist: Biceps brachii Muscles that Move Shoulder Trapezius: elevates (i.e. raises shoulders) & retracts scapula (i.e. pulls shoulders back) Elevates scapula Retracts scapula Muscles that Move Shoulder No pic in lab manual Pectoralis minor: draws scapula forward & downward (i.e. pulls shoulders down and forward) Draws scapula forward Draws scapula downward p. 82, 85 Muscles that Move Shoulder Serratus anterior: draws scapula forward (i.e. pulls shoulder forward) Serratus anterior Draws scapula forward Muscles that Move the Upper Arm Pectoralis major: flexes (moves arm up and forward) & adducts upper arm (moves arm toward the body) Flexes upper arm Adducts upper arm Muscles that Move the Upper Arm Latissimus dorsi: extends (i.e. moves arm down to the rear) & adducts arm (moves arm toward body) Extends upper arm Adducts upper arm Muscles that Move Upper Arm Deltoid: abducts arm (raises arm up away from the side) Abducts arm Deltoid Biceps brachii: flexes forearm Brachialis: flexes forearm Biceps brachii Brachialis Moving the Forearm Biceps brachii Brachialis Flexion of forearm Muscles that Move the Forearm p. 83, 85 Triceps brachii: extends the forearm extension Flexors & Extensors of Hand Hand flexor group: flex the hand p. 82. 84, 85 Hand extensor group: extend the hand p. 83. 85 p. 82 Muscles of Abdominal Wall – Movement of Spine Rectus abdominus: flexes vertebral column Muscles of Abdominal –Moving the spine Lateral flexion External oblique: compresses abdomen; rotates trunk; lateral flexion Trunk Rotation Internal oblique: compresses abdomen; trunk rotation; lateral flexion No pic Transversus abdominis: compresses abdomen No pic Compressing abdomen Muscles of Chest Wall –Movement of Ribs Internal intercostals: depresses rib cage during forced expiration External intercostals: elevates rib cage during inspiration No pics Diaphragm: prime mover during inspiration; increases vertical dimension of thorax Muscles of Chest Wall –Movement of Ribs Internal intercostal External intercostal Muscles that Move the Thigh Gluteus maximus: extends thigh p. 83, 86 Muscles that Move the Thigh iliopsoas: flexion of thigh Flexion of thigh Muscles that Move the Thigh Flexion of thigh Abducts of thigh Tensor fascia latae: flexes & abducts thigh Muscles that Move the Thigh Adducts of thigh Flexion of thigh Adductor group: adducts and flexes thigh Muscles that Move the Thigh Lateral rotation & flexion of thigh sartorius: flexes & laterally rotates thigh; helps you sit cross-legged Muscles that Move the Thigh Knee extension Quadriceps femoris group: extends knee Flexion of thigh Rectus femoris: extends knees and flexes thigh Muscles that Move the Lower Leg Extension of thigh Hamstring group: extends thigh & flexes knee Knee flexion Muscles that Move the Foot Tibialis anterior: dorisflexes foot Gastrocnemius: plantar flexes foot, flexes knee Soleus: plantar flexes foot Today’s Activities Muscles: Tissue & Histology Examine the following slides using the microscope: 1) Skeletal muscle 3) Cardiac muscle 4) Dense regular connective tissue 2) Smooth muscle Muscles: Gross Anatomy Use the models and diagrams in you textbook & lab manual to study locations & actions of the muscles listed on pp. 76-79 Diagrams in textbook = right side; most models = left side Don’t worry about extra muscles described in textbook Don’t worry about extra actions described in textbook Answer questions, fill out diagrams on pp. 80-86 If you get done early, you can go back to the bones, etc. DO NOT leave until you have been excused, or you will be marked absent!!! Medial View Radial view Medial View-Deep flexors Lateral View Lateral View-Deep extensors Lateral View-Deep shoulder extensors Anterior View Lateral View Medial View Posterior View Plantar surface Search “MuscleandMotion” on YouTube