PPT - Russian Revolution

RUSSIAN REVOLUTION
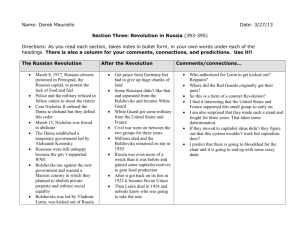
1. Why did the Czarist regime fail?
2. How did the Bolsheviks eventually come to power?
1
Who ruled Russia?
• The Romanov dynasty ruled for 300 yrs. (1613 – 1917)
• If Czar was overthrown, industrial workers could govern
Russia
Nicholas II
Alexandra
2
Why was there a lack in confidence in the Czar?
• Russia was totally unprepared for war
• Russia lacked:
– factories/supplies
– transportation system
– modern equipment
– competent military leader
– Lack of food
– Inflation went up
– Wages didn’t
3
WW I – 1914
•Czar Nicholas II hoped war would unite Russia & stop talks of revolution
•patriotism increased
Rapidly
• 1915 – Nicholas II took command of Russian military
• IF RUSSIA FAILS , SO TOO WOULD NICHOLAS II
4
WWI Conditions Worsen
•As food & goods grew scarce peasants grew desperate
•Nicholas at the front Czarina left in charge (unpopular)
•Alexandra took advice from
Rasputin (corrupt/immoral)
•A Russian peasant and selfproclaimed mystic / holy man who gained significant influence over
Tsar wife
Grigory Rasputin-
“The Mad Monk”
5
Suffered from life threatening illness
•
•Hemophilia is rare bleeding disorder in which the blood doesn’t clot normally.
• Rasputin – Stopped the bleeding
Alexis
6
Revolution Begins
• March 8, 1917 – Petrograd
•Unhappy citizens marched through the city
•Czar – ordered troop to break up demonstrations (shoot)
•Police & soldiers were sympathetic (refused)
• The Duma – (Russia’s legislature) defied Nicholas II met anyway
Russian workers striking
7
Provisional Government
The Duma – established temporary government
Urged Czar to step down
Alexander Kerensky
March 15, 1917 – Riots protesting the shortage of food forced the Czar to abdicate
Czar Nicholas II
8
Provisional Government
• mid-1917 – Kerensky’s provisional government decided to carry on the war
• Russian army was weak & collapsed
9
Bolsheviks
& V.I. Lenin
• Founder of the Bolshevik Party
• First leader of the Soviet Union.
• Spent most of the early 20 th century living in exile (primarily
Britain and Switzerland).
• Devout follower of Marxism
• Believed that once a Communist revolution took place in Russia,
Communism would spread rapidly around the world.
• He returned to Russia in April
1917 and orchestrated the
October Revolution that turned
Russia into a Communist state.
10
October Revolution
• November 1917 – Bolshevik seized The Winter
Palace
• Kerensky’s government didn’t put up much of a fight
• Lenin established radical communist program
• Promised PEACE LAND AND BREAD
– private ownership = illegal
– land redistributed to peasants
11
After the Revolution
• Lenin wanted to end involvement in war
• Leon Trotsky was sent to negotiate with Central
Powers
• Russia lost much land to Central Powers in the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
12
13
Civil War
• Some Russians disliked the negotiations & their results
• opponents of Bolsheviks = “White Army”
• France & United States supported White Army
• RED ARMY vs. WHITE ARMY
– fighting & famine cost millions of lives
• late 1920 – Bolsheviks triumph
• 1921 – New Economic Policy: plan permitting some capitalist activity
14
The Soviet Union
• 1922 – economy began to improve
• 1922 – Russia reunited with neighboring lands that had belonged to Russian Empire
• Became Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) or
Soviet Union
15