L.15.6 Taxonomy
advertisement

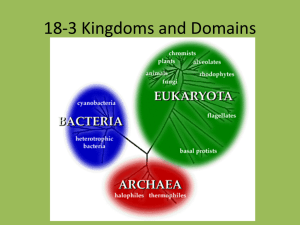
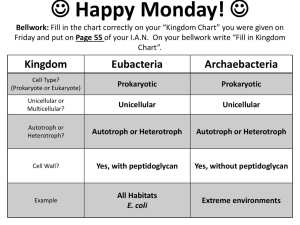
Taxonomy SC.912.L.15.6 Discuss distinguishing characteristics of the domains and kingdoms of living organisms. Source:http://higheredbcs.wiley.com/legacy/college/levin/04716974 35/chap_tut/chaps/chapter06-02.html What do I need to know? the distinguishing characteristics of the domains and kingdoms of living organisms. how organisms are classified based on evolutionary relationships and explain the reasons for changes in how organisms are classified. Domains and Kingdoms The 3 domains (archaea, bacteria, & eukarya) and the 6 kingdoms (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae & animalia) are separated from one another by characteristics such as cell type, number of cells, mode of nutrition, and cell structures like cell walls and chloroplast. Domains and Kingdoms Guiding Questions: What are the cell type, number of cells, cell structures and mode of nutrition for each of the 6 kingdoms of life? Videos: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q9-Ks474dxA Domains and Kingdoms DOMAIN Bacteria Archaea KINGDOM Eubacteria Archaebacteria CELL TYPE Eukarya Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Cell walls with peptidoglycan Cell walls without peptidoglycan Cell walls of cellulose in some; some have chloroplasts Cell walls of chitin Cell walls of cellulose; chloroplasts No cell walls or chloroplasts Unicellular Unicellular Most unicellular; some colonial; some multicellular Most multicellular; some unicellular Multicellular Multicellular MODE OF NUTRITION Autotroph or heterotroph Autotroph or heterotroph Autotroph or heterotroph Heterotroph Autotroph Heterotroph EXAMPLES Streptococcus, Escherichia coli Methanogens, halophiles Amoeba, Paramecium, slime molds, giant kelp Mushrooms, yeasts Mosses, ferns, flowering plants Sponges, worms, insects, fishes, mammals CELL STRUCTURES NUMBER OF CELLS Evolutionary Relationships Living things are classified according to their evolutionary relationship or how long ago they shared a common ancestor. Evolutionary relationships can be shown using a cladogram. Cladograms can be built using physical characteristics or DNA sequencing. Source: http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/evo_03 Evolutionary Relationships Guiding Questions: 1) How do scientists determine the evolutionary relationships between living things? 2)What is a phylogenic tree/cladogram? How are they created and used to show how living things are related? Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DUF1TTcy-m8 Show What You Know Organisms classified as fungi have unique characteristics. Which of the following characteristics is found only in organisms classified in the kingdom Fungi? A. single cells without a nucleus B. multicellular with chloroplasts C. multicellular filaments that absorb nutrients D. colonies of single, photosynthetic cells that reproduce asexually Show What You Know It was recently determined that giant pandas are much closely related to bears, than to raccoons. Before this, many scientists believed that giant pandas were members of the raccoon family. What is the best piece of evidence that was probably used to re-classify giant pandas as a bear and not a racoon? A. More behavioral similarities to bears than to raccoons B. More similarities in appearance to bears than to raccoons C. More similarities in bear DNA and giant panda DNA than in racoons DNA and giant panda DNA D. A more similar habitat to bears than to raccoons Show What You Know Many protists are single-celled organisms, as are all bacteria. However, protists and bacteria are in different biological kingdoms. Which of the following comparisons of protists and bacteria is NOT true? A. Both protists and bacteria can be motile. B. Both protists and bacteria are microorganisms. C. Protists are eukaryotes, while bacteria are prokaryotes. D. Protists may be photosynthetic, but bacteria cannot be photosynthetic. Show What You Know Fungi were once classified as a member of the plant kingdom. Over time scientists recognized a defining characteristic that forced the reclassification of fungi as their own kingdom. What is this defining characteristic? A. Fungi lacked a cell wall and plants have a cell wall B. Fungi are heterotrophs and plants are autotrophs C. Fungi are prokaryotic and plants are eukaryotic D. Fungi are onlu unicellular and plants are only multicellular