Pelvis
advertisement

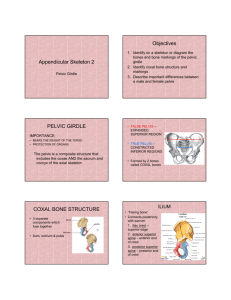
Pelvic Girdle Attaches lower extremities to the axial skeleton Provides strong support for the weight of the body Also provides support for the urinary bladder, large intestine & internal reproductive organs Pelvic Girdle Consists of two coxal bones which meet anteriorly at the pubic symphysis and posteriorly with the sacrum at the sacroiliac joints Ilium – largest component of the coxal bone Acetabulum – socket for the head of the femur; formed by the ilium, ischium and pubis Iliac crest – the superior border of the ilium Greater sciatic notch – where the sciatic nerve (the longest nerve in the body) passes Ischium – inferior, posterior portion of the hip bone Pelvic Girdle Ischial tuberosity – rough, thick area on the ischium Obturator foramen – largest foramen in the body where nerves and blood vessels pass through Pubis – anterior and inferior part of the hip bone Pubic symphysis – the joint between the two hip bones; consists of fibrocartilage Pelvic brim – boundary that divides the pelvis into superior and inferior portions Comparison of Male and Female Pelves Female - Light and thin - Large, oval pelvic brim - - Male - heavy and thick - small, heart shaped pelvic brim Small acetabulum - large acetabulum Oval obturator foramen - round obturator foramen Pubic arch >90° - pubic arch < 90° Wide greater sciatic notch - narrow greater sciatic notch Short, wide sacrum - long, narrow sacrum