ARP11handout1.
advertisement

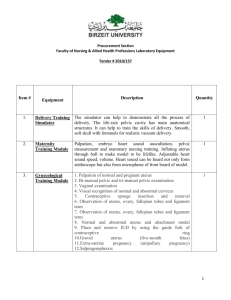
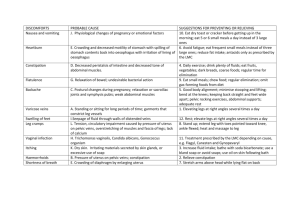
PART-I Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology of reproduction in female Lesson 1.- Female Reproductive Anatomy The genitilia of the cow consist of the pelvic cavity and the organs contained therein. Pelvic Cavity: consist of basically three bones and three ligamentous structure. The bony part comprise of : 1. Sacrum 2. The first to third coccygeal vertebrae 3. Os coxae Tuber sacral Wing of Sacrum Tuber Coxae Body of Sacrum Sacro-pubic diameter Shaft of Ilium Bis-iliac diameter Tuber Ischii Acetabulum Pubic symphysis Ischium Pubis Sacrum: Sacrum forms the roof of the pelvis and is composed of five fused vertebrae in the cow.It is somewhat triangular in shape with the base articulating crainally with the last vertebra and caudally with the first coccygeal vertebra. The dorsal side has the sacral spine and the ventral side is smooth.The wing of the sacrum articulates or fuses with the ilium laterally. In older cows the first coccygeal vertebra may be fused with the sacrum. Ilium: Is irregularly triangular in shape and form part of the lateral wall of the pelvis. The broad, flat, dorsal part of the ilium is called the wing.The medial portion of the wing is called as the Tuber sacral and its ventral medial aspects articulates with the the wings of the sacrum.The external portion of the wing of the ilium is called as tuber coxae or “.hip bone”. Dorsally the wing is cincave providing attachment for the gluteal muscles and back muscles. The narrow ventral part of the ilium is calle the Body or shaft. This shaft ventrally fuses with the Ischium and pubis at the acetabulum. Its medial pelvic surface is groved for obturator vessels and nerve. Ischium: forms the caudal part of the ventral floor of the pelvis. The caudal border slopes inward and forward to join the opposite ischium to form the ischiatic arch. The caudal lateral part of the bones ar called as the tuber ischii or “Pin bones”. The crainial border of the ischium forms the caudal margin of the obturator foramen. Dorsally ischium bears the ischial spines ,crainial and caudal to which are the greater and lesser sciatic notches respectively. The notches becomes foramina when the sacrosciatic ligament completes their boundaries. Medially the ischial and pubis fuse to form the pelvic symphysis. Pubis : is the smallest bone of the ox coxae. The dorsal pelvic surface is smooth and usually concave in female. The crainaial medial border provides attachment for the prepubic tendon and the caudal border forms the cranial border of the obturator foramen. Acetabulum : It is cotyloid cavity formed by fusion of ilium,ischium and pubis.The head of the Femur lodge into this cavity and is attached to it by the round ligament. Ligaments and tendon: Ligaments help to maintain the relationship of the pelvis to the spinal column. There are two ligaments and a tendon involved in the formation of the pelvic cavity. These are. 1. Dorsal and lateral sacro-iliac ligament. This ligamant is attached to medial wing of the ilium and the lateral portion of the sacrum and the summit of the sacral spines. 2. Sacro-shiatic ligamant. It is a quardilateral ligamantous sheet that completes the lateral wall of the pelvic cavity. It extends from the lateral border of the sacrum and the transverse process of the first coccygeal vertebra to the ischiatic spine and tuber ischii. 3. Prepubic tendon. It is the tendon of insertion of the recti abdominis muscle It is attached strongly to the cranial border of the pubic bone. The pelvic cavity is somewhat cone shaped and the inlet is roughly oval shaped with the largest diameter being sacro- pubic. Size varies between species, breed, age and size. The approximate diameter of the pelvis are: Species Mare Cow Ewe Sow Sacro-pubic 20.3-25.4 cm 19.0- 24.1 7,6-10.8 9.5-15.2 Bis-iliac 19.0-24.1 14.6 -19.0 5.7-8.9 6.3 -10.2 Bitch 3.3-6.3 2.8-5.7 Comparative anatomy of different species: Mare: Transverse or bis-iliac and sacro-pubic diameter are nearly equal, making the pelvic inlet almost spherical. The coxal tuberosities are larger and prominent. Wings of iliac are nearly perpendicular to the long axis of the body. Cow: Ischial tuberosities are high and prominent. The pelvic inlet is more elliptical. Ewe: Similar to cow except that the ischial tuberosities are relatively smaller. Sow: Pelvic inlet is log and narrow wing of the ilium are not prominent The pubic symphysis is not completely fused The tuber ischii are largerly cartilagenous. Bitch: Wing of iliac are smaller and nearly parallel to the medial plane the ilium has a twisted appearance. The reproductive tract consist of the following organs. Ovaries Oviduct Uterus Cervix Vagina Vestibule Valva Uterine Horn Ovary Uterine body Oviduct Ovarian Bursa Cervix Vagina Genital tract of cow Ovaries: The main function of the Ovaries is to produce ova and ovarian hormones. In cow the ovary are oval in shape and about 1.3-5cm in length ; 1.3-3.2 cm in width; and 0.6 - 1.9 cm in thickness. In mare, it is bean shaped.The ovaries consist of a stroma of connective tissue and blood vessel surrounded by covering of peritoneum except at the attached border or hilus where blood vessels and nerves entres. Within the ovary are interstitial cells,primitive ova, developing or secondary ova or follicles, maturing graffain follicles, atretic follicles or developing or maturing Corpus luteum. The ovaries are attached by the broad ligament called as Mesovarian dorsally and laterally ; by the utero-ovarian ligament medially. Blood suppy is by the Ovarian artery. Ovary and its associated structures Oviduct: Oviducts are the site of fertilization.In cow, the oviduct is 20-30 cm long and 1.5-3 mm in diameter. They are torturous,wiry and hard and are difficult to palpate. The oviduct is divide into three parts. Infundibulum : The part nearest to the ovary is the infundibulum which is funnel shaped. It has finger like projection called as frimbrae which aids in the collection of the ovum into the oviduct. Ampulla : Is the middle part which joins the isthmus at the isthmus- ampullary junction which is believed to be the real site of fertilization. Isthmus : Isthmus joins the tip of the uterine horns at the utero-tubal junction. The oviduct is lined by hair like projection called as cilia the wave like movement of which helps in the transportation of the ovum through the oviduct and into the uterus. Uterus: Uterus is the site of carrying the foetus during gestation.Is a muscular structure. The endometrium is the layer of mucous membrane while the mesometrium is made of circular and longitudinal muscle. In cow, the uterus is cornuate in shape with two horns. The body of the uterus is about 2.5-5 cm in length; 1.25-5cm in diameter while the horms measure about 2-040 cm in length. The horns are joined by a intercornual ligament for about 1/3 of its length. Normally uterus lies on the floor of the pelvic cavity but sometimes especially in matured cows it the horns may be found over the pelvic brim. Uterus is attached dorsolaterally by the broad ligament. Cervix: The main function of the cervix is to form a barrier between the uterus and the vagina. Is a powerful tubular sphincter like muscular structure between the uterus and the vagina about 5-10 cm in length; 1.5-7cm in diameter. The wall is thick and hard and composed of 3-5 muscular fibrous transverse annular folds. The opening into vagina is called external os. Vagina: Vagina is the copulatory organ and also serves as the passage of the foetus. It is capable of great dilation. It is a muscular membranous structure lying in the pelvic cavity. The slight cricular constriction between vagina and valva is the hymen. The vagina is surrounded by connective tissues and fats. In cow it is about 25-30 cm in length. Vestibule: The vestibule is located between the vulva and the vagina and extends for 10-12 cm.It has several circular muscles that closes the genital tract to the outside. The urethra opens into the cranial- ventral portion of the vestibule. Below the urethral opening is the suburethral diverticulum. Vulva: The vulva comprise of two labia- the inner lip is called the labia major and the outer lip the labia minor. Clitoris: It is the homologue of the penis.The clitoris which is about 5-10 cm in length is located in the caudal portion of the vestibule at the ventral commissure.