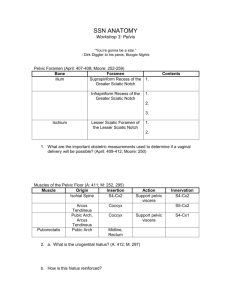
LQB389_390 PracGuide – PRAC WEEK 5: Use the following models to identify the major features/structures listed (tick off as you find each one) and answer the relevant questions using the resources listed. Pelvic Cavity and its contents 1. Median Section of Male and Female Pelves 11.11x and 11.12x rectum rectal ampulla rectovesicular pouch rectouterine pouch uterovesicular pouch prostatic urethra ejaculatory ducts ductus deferens seminal vesicles retropubic space round ligament of uterus fundus, body and cervix of uterus vagina Explain the position of the uterus in model 11.12x by defining the terms anteflexed, anteverted and retroverted. __________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ How are these uterine positions related to the function of the urinary bladder? ____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Nervous system model 8.31x sacral plexus lumbosacral trunk The sacral plexus lies on the pelvic surface of what muscle? ___________________________________ The ventral rami of which spinal nerves form the sacral plexus? ________________________________ 3. Bony pelvis model and articulated skeletons superior pelvic aperture inferior pelvic aperture sacrotuberous ligament true pelvis false pelvis 4. Muscles of the pelvic walls and floor model 1.42x obturator internus piriformis levator ani coccygeus greater sciatic foramen urethra anal canal vagina sacral plexus sciatic nerve lesser sciatic foramen internal pudendal artery Which of the above muscles contribute to the formation of the pelvic diaphragm? ____________________________________________________________________________________ Name the artery that passes through the greater sciatic foramen and then enters the perineum through the lesser sciatic foramen?______________________________________________________________ 5. Urinary system model 14.61x, female reproductive system model 11.12x and male reproductive system model 11.11x abdominal ureter pelvic ureter ureteric orifices superior, inferolateral and posterior surfaces, apex and neck of the urinary bladder prostate gland (and its seminal colliculus) sigmoid colon rectum rectosigmoid junction perineal/anorectal flexure Perineum 1. Muscles of perineum model 1.42x, reproductive inserts from torsos (male and female 11.13x), model 11.131 (female) and model 5.811/1.431 (with blood vessels of perineum) pelvic diaphragm anal canal urogenital diaphragm/deep perineal pouch vagina muscles of superficial perineal pouch labia majora labia minora genital vestibule clitoris perineal body anococcygeal body gluteus maximus internal pudendal artery pudendal canal obturator internus levator ani anterior and posterior recesses of right and left ischiorectal fossae inferior rectal artery 2. Female reproductive system models 11.12x and 11.021 and male reproductive system models 11.11x, 11.011 and 1.041 (also look at torso reproductive inserts 11.13x for both male and female) pelvic diaphragm urogenital diaphragm/deep perineal pouch bulbourethral gland bulb of penis vagina external & internal anal sphincters rectum anal canal perineal/anorectal flexure Contrast the location of the internal and external anal sphincters: ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________