Cell Cycle
advertisement
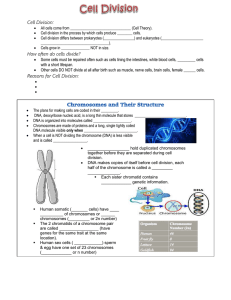
Cell Cycle Asexual Reproduction ALL substances must pass through a cell membrane to enter and exit a cell smaller cells higher surface-area-tovolume ratio can exchange materials faster cell division occurs when a cell reaches a certain size Asexual Reproduction purpose: in simpler organisms: reproduction of offspring in complex organisms: increase number and size of cells; repair damaged cells only 1 parent is required parent DNA is passed onto offspring, therefore, offspring are IDENTICAL to Types of Asexual Reproduction Prokaryotes (bacteria): binary fission: 1 bacteria cell divides into 2 bacteria cells of the same size Types of Asexual Reproduction Hydra Eukaryotes (protis budding: part of t) the parent organism pinches off and forms a new organism. Yeast (fungu Types of Asexual Reproduction Eukaryotes mitosis: division of the nucleus into 2 nuclei chromosomes: carry the DNA chromosome # varies between species humans46 chromosomes (23 pairs) Cell cycle: repeating sequence of cellular growth and division during the life of an organism; check points trigger the next stage of the cycle growth, preparation to divide Loss of Control of the Cell Cycle if checkpoints are not working properly, the cell cycle can cause the cell to grow uncontrollably leads to cancer http://outrea ch.mcb.harv ard.edu/anim ations_S03.ht m Cell Cycle http://www.cellsalive.com/cell_cycle_js.htm 1. Interphase (G1, S, G2) – cell grows, prepares to divide and DNA replicates 2. Mitosis: nucleus divides; each nuclei winds up with the same # and kind of chromosomes as the parent 3. Cytokinesis: division of cytoplasm http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm DNA replicates in interphase nucleus disappears chromosome s line up on equator chromosome s separate http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072437316/student_view0/chapter11/animations.html# no cell wall cell wall Mitosis parent cell 46 chromosomes 92 chromosomes 46 chromoso mes daughter cells 46 chromoso mes Results of Mitosis offspring (daughter) cells are about equal in size each daughter cell receives ½ the cytoplasm and organelles of the parent cell each daughter receives an IDENTICAL copy of the parent cell’s chromosomes (DNA)