Study Guide
advertisement

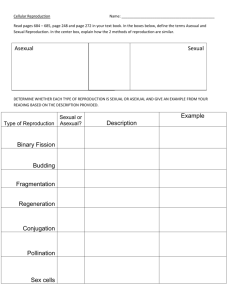
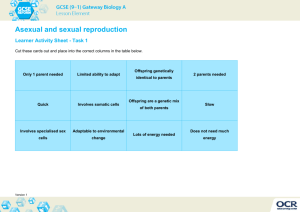
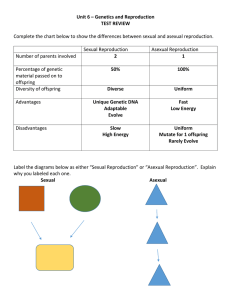
Asexual & Sexual Reproduction Study Guide Cytokinesis – division of the cytoplasm Asexual Reproduction One parent Offspring is genetically identical to the parent Clone is genetically identical to the parent. Disadvantage – no variety Advantage - quick Types of Asexual Reproduction: 1. Vegetative reproduction - plants use stems, leaves, or roots 2. Budding – Yeast use budding to reproduce 3. Fission – Bacteria 4. Regeneration – re-growing a body part Mitosis: (asexual) Body cell (mi- TOE – sis) Division of the nucleus Chromosomes replicate (copy) before mitosis begins Phases: Interphase – cell spends most time in this phase growing Prophase – Chromosomes pair up Metaphase – Chromosome line up in middle Anaphase – pull apart Telophase – Two new daughter cells Sexual Reproduction Two parents Chromosomes contain DNA which is passed onto offspring Offspring of sexual reproduction are different from their parents Fertilization – egg and sperm combine Zygote – fertilized egg Meiosis (sexual) Two divisions of the nucleus Half the chromosomes in the daughter cell Produces sex cells