Mitosis Meiosis notes
advertisement
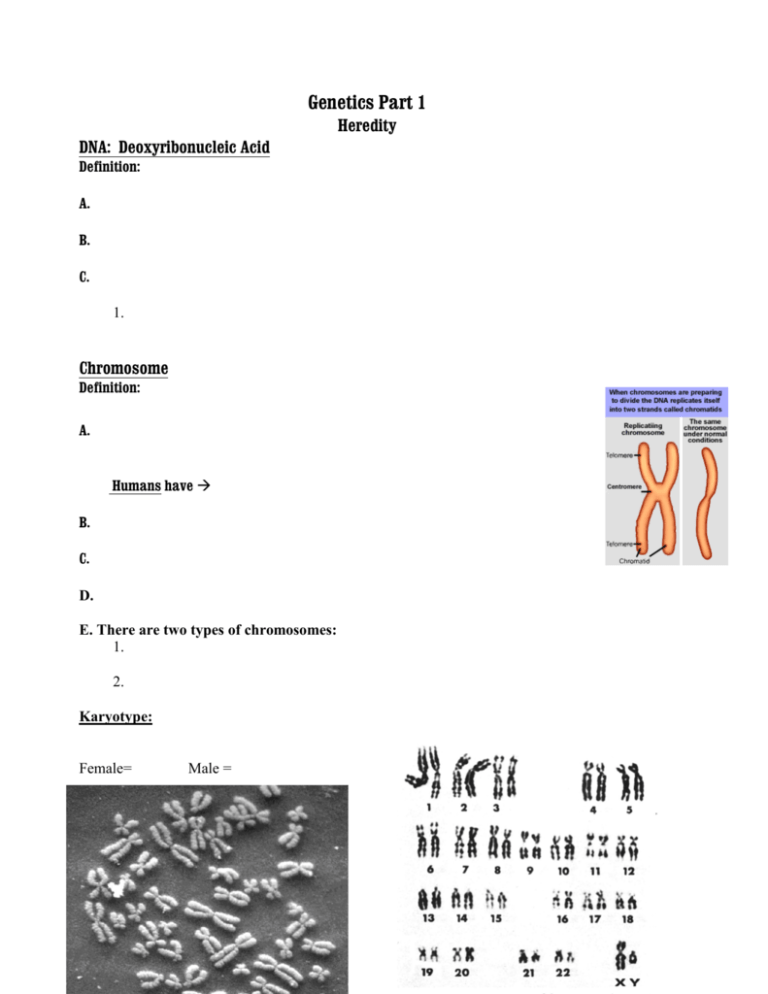
Genetics Part 1 Heredity DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid Definition: A. B. C. 1. Chromosome Definition: A. Humans have B. C. D. E. There are two types of chromosomes: 1. 2. Karyotype: Female= Male = Genes Definition: A. 1. 2. 3 4. Vocabulary terms Diploid: a. b. Haploid: a. b. c. Reproduction of Cells: Reproduction of cells occurs in one of 2 ways •Mitosis- •Meiosis- a. The Cell Cycle: There are five phases that make up the cell cycle 1. G-1 Phase: The growth phase of the cell. The cells grows rapidly and carries out it’s normal functions. This phase occupies most of the cells time. 2. S Phase: DNA replication (copying) occurs, all chromosomes have been copied, so there are double the number. 3. G-2 Phase: Preparations made for cell division (organelles are duplicated). 4. M-Phase: Mitosis occurs, the nucleus divides in two. 5. C-Phase: “Cytokenisis”….the cell splits into two individual, identical cells. An Overview of the Process of Mitosis The reproduction of regular body cells (somatic cells). This occurs in 98% of the cells that make us and virtually all living organisms. 1. 2. 3. Stages of Mitosis Mitosis is divided into 4 Stages. 1. Prophase: 2. Metaphase: 3. Anaphase: 4. Telophase: 5. 6. The chromosome, as we recognize it, is made up of two sister chromatids held together by a button called a centromere. A. B. Meiosis Definition: 1. Has two phases: 2. 3. 4. Gametes: Sperm and eggs Definition: a. b. Overview of Meiosis: Production of egg or sperm cells (reproductive cells) These four cells are called _____________, And examples of them are ___________ and ______________. Because of ____________ and ___________ _____________________, these four daughter Even more Variation: Crossover: Independent Assortment: When the homologous pairs of chromosomes separate, there is no predictable pattern of which will end up in a given egg or a given sperm cell. Mistakes in Meiosis Trisomy: Definition: A. B. Monosomy: Definition: A. B. Summary 1. 2. 3. 4.