Unit 5 Cellular & Organismal Reproduction
advertisement
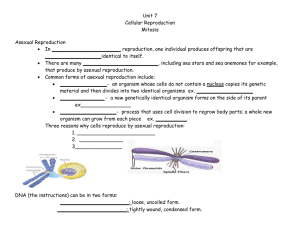
Unit 5: Cellular & Organismal Reproduction Topic 1: The Cell Cycle Cell reproduction • How do cells reproduce? They divide into two cells! First they copy all their parts (DNA, organelles, ribosomes) • When does a cell reproduce? When a multicellular organism is growing or needs to replace dead or damaged cells (mitosis) To make gametes for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes (meiosis) When a single-celled organism reproduces asexually (mitosis or binary fission) Some Definitions • Parent Cell • Daughter Cell • Sexual Reproduction – Variation • Asexual Reproduction 3 Asexual reproduction in bacteria (binary fission) Figure 8.3A, p127 Binary Fission 4 Other forms of asexual reproduction • • • • Budding Fragmentation Regeneration Advantages: – Don’t need to search for a mate – Can reproduce if damaged • Disadvantage: – No recombination of genetic material Chromatin 6 7 Fun facts: number of chromosomes in a variety of organisms Species Humans Kangaroo Cat Cow Dog Turkey Algae Shrimp Ophioglossum reticulatum (fern) # chromosomes 46 12 38 60 78 82 148 254 ~1200! (highest UNreplicated Chromosome Replicated Chromosome Sister Chromatids UNreplicated Chromosomes Figure 8.4, p128 10 Chromosome Anatomy 11 Homologous chromosomes • Each chromosome has a homologue, or a chromosome that carries the same type of information as another chromosome • The chromosomes may have different versions of the genes but the genes code for the same type of information 12 Cell cycle Figure 8.5, p129 13 Mitosis inquiry Cell cycle Figure 8.5, p129 15 The stages of mitotic cell division in an animal cell: G2 phase; prophase; prometaphase Figure 8.6, p130 16 The stages of mitotic cell division in an animal cell: metaphase; anaphase; telophase and cytokinesis. Figure 8.6, p131 17 Mitosis 18 Mitosis in an onion root 19 Cytokinesis in animal and plant cells Figure 8.7, p132 20 Cell turnover • The length of a cell cycle depends on the type of cell and its function in the body. • Some cells never divide after the first few months of life: brain, nerves • Some cells never divide at all: red blood cells • Some divide every 20 hours or so: cells of organ linings and skin cells Chromosomes 23