Manufacturing Processes
advertisement

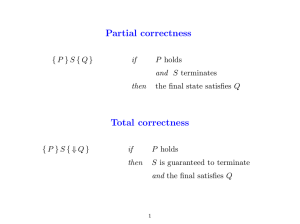
Operations Management Dr. Ron Lembke PRODUCTION PROCESSES RESPONSIVENESS – SUPPLY CHAIN DESIGN Price / Quality / Speed? Decoupling Point Make to Stock – ready on the shelf – Breyer’s Assemble to Order – parts waiting for an order – DQ Make to Order – Raw Materials waiting – Cold Stone Engineer to Order – Anything you want – Home made Design MTS ATO MTO ETO Produce Assemble Deliver LITTLE’S LAW Assume things are in “steady state,” not startup Production level = average demand Inventory = Throughput rate * Flow Time Flow Time = Inv / Throughput rate TH rate = Inv / Flow Time Single workstation, a line, or whole supply chain TH = 5 units/day TH Rate = 100 units/ hr Inv = 24 units Flow Time = 24 /100 = 0.24 hrs Flow Time = 15 days Inv = 5/day * 15 days = 75 units WIP PROCESS STRATEGY Variety High Process Focus (job shops) Repetitive (cars, motorcycles) Medium Product Focus (steel, glass) Low Low Medium High Volume PROCESS FOCUS (JOB SHOP) Low volume, high variety, “do it all” “Job shop” environment (e.g. Kinko’s) High amount of flexibility Each job is different Relatively high cost per unit Very high flexibility PROCESS SELECTION / EVOLUTION Products tend to move through the four stages over life cycle. Unit costs decrease as standardization increases, and production increases. Flexibility decreases as volume, standardization increase PROCESS STRATEGY Variety High Medium project Workcenter Manufacturing Cell Assembly Line Continuous Process Low Low Medium High Volume PROCESS FLOW STRUCTURES Job Shop - low standardization, every order is a different product, new design Batch Shop - Stable line of products, produced in batches Assembly Line - Discrete parts moving from workstation to workstation Continuous Flow - Undifferentiated flow of product (beer, paper, etc.) DESIGN FOR MANUFACTURING -BEFORE DESIGN FOR MANUFACTURING-AFTER SUMMARY Production Process selection very important Strategic considerations – decoupling Volume / Variety tradeoffs Maturation of processes over life cycle Little’s Law: FT = TH * INV