File
advertisement

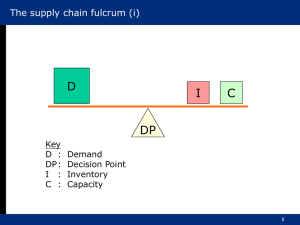
Chapter 2 1 Supply Chain Strategy and Performance Measures Content……. Customer service and cost trade offs Supply chain performance measures Linking supply chain and business performance Enhancing supply chain performance Cost Versus Service A firm must ensure a smooth fit between its business strategy and supply chain strategy Business strategy: the firm decides the market segment in which it wants to operate and the level of customer services it wants to offer Supply chain strategy: issues of costs that the firm has to incur to provide the targeted level of customer service Cost of service Supply Chain Performance Measures Low High Service Level Managing Supply Chains Efficiently Inefficient Practices . Cost Existing Position Low High Service Level Impact of Service Level on Revenue Costs and Profits Supply Chain Performance Measures: Cost Versus Service Cost Service Order delivery lead time Responsiveness Delivery reliability Product variety Order delivery lead time It is the time taken by the supply chain to complete all the activities from order to delivery Order penetration point/ decoupling point Customer order Order delivery lead time Supply chain lead time Supply Chain Typology Order Penetration Point/ Decoupling Point Make to Stock Make to Order Configure to Order Supply Chain Focus Efficiency Responsiveness Supply Chain Typology: Order Penetration Point/ Decoupling Point Push-Pull Boundary of Supply Chains Supply Chains responsiveness Responsiveness captures the firm’s ability to handle the uncertainty of market demand Functional products are those that satisfy the basic needs of a customer and therefore have low variety, stable and predictable demand, long life cycles and low profit margins Innovative products are those that try to satisfy a broad rand of customers’ wants and have the high variety, unstable, very hard to predict demand, short life cycles, high profit margins and frequent stock outs and markdowns Physical function is the process of converting materials into parts, then to finished products and then transporting them across the various stages of the chain Market mediation function ensures that the variety of products reaching the market matches the needs of the customers Functional Versus Innovative Products: Differences in Demand Aspects of demand Functional (predictable Demand) Innovative (Unpredictable Demand) Product Life cycle More than 2 years 3 months to 1 year Contribution margin ( % of 5% to 20% sales price) 20% to 60% Product variety Low ( 10 to 20 variants per High ( often thousands of category) variants per category) Likely forecast error 5% to 20% 40% to 100% Average stock-out rate 1% to 2% 10% to 40% End-of-season mark markdown 0% 10% to 30% Match Supply Chain Design with Product Category Delivery reliability It is the degree to which a firm is able to service its customers within the promised delivery time Product variety The quantum of variety offered by a firm Variety explosion Supply Chain Performance Measures: SCOR Model Internal Facing Cost Total logistics management cost, Value-added productivity , Warranty cost Assets Cash-to-cash cycle time, Inventory days of supply, Asset turns Customer facing Reliability Order fulfilment performance ,Perfect order fulfilment Flexibility Supply-chain response time, Production flexibility Benchmarking Supply Chain Performance Using Financial Data Total length of the chain: = DRM + DWIP + DFG DRM = RM * 365/ CRM, DWIP = SFG*365/ CP, DFG = FG * 365 / CS DRM , DWIP , DFG = Days of RM, WIP and FG Inventory Supply chain inefficiency ratio: SCC = DC + INV * ICC & SCI = SCC / NS SCC = SC mgnt. costs , ICC= Inv. Car. cost SCI = SC inefficiency ratio Supply chain working capital productivity: SWC = SC working capital, SWCP = SC working capital productivity SWC = INV +AR–AP SWCP = NS / ISWC The Strategic Profit Model Impact of supply Chain Intiative on Business Performance Cost reduction achieved by: Reducing Inventory, Reducing logistics expenses, Reducing direct material expenses, Reducing indirect material expenses Improved revenue and profitability by: Selling higher margin products, Achieving higher market share, Reducing backorder and lost sales, Attacking new markets, Decreasing supply time to market Improved Operational efficiency by: Reducing procurement expenses, Increasing assets utilization, Delaying capital expenditure Reducing working capital by Reducing inventory, Reducing accounts receivables Enhancing Supply Chain Performance Enhancing Supply Chain Performance Supply Chain Integration Toyota, Ford Motor Company (1910-1920), The Dubbawallas of Mumbai Supply Chain Optimisation Use of Quantitative models in supply chain design and operations Supply Chain Reconfiguration Dell, TVS Scooty