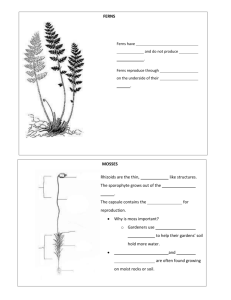
Plants Without Seeds
advertisement

PLANTS WITHOUT SEEDS CHAPTER 8 SECTION 2 NONVASCULAR PLANTS • Three major groups of nonvascular plants • Mosses • Liverworts • Hornworts CHARACTERISTICS OF NONVASCULAR PLANTS • Low-growing • Live in moist environments • Absorb water and other nutrients directly • Watery surroundings enable sperm cells to swim to egg cells MOSSES 10,000 species • Green, fuzzy moss is the gametophyte generation of the plant • Rhizoids: thin, rootlike structures that anchor the moss and absorb water and nutrients from the soil • The sporophyte generation grows out of the gametophyte • The sporophyte consists of a slender stalk with a capsule at the end • The capsule contains spores A MOSS PLANT LIVERWORTS 8,000 species • Often found growing as a thick crust on moist rocks or soil along the sides of a stream HORNWORTS • Fewer than 100 species • Live in moist soil, often mixed in with grass plants SEEDLESS VASCULAR PLANTS • Characteristics • Ferns, club mosses and horsetails have true vascular tissue • Do not produce seeds, these plants reproduce by releasing spores • Can grow tall because vascular tissues effectively transport materials • Provide strength and stability • Grow in moist environments • There must be enough water for the sperm to swim to the eggs FERNS • Stems of most ferns grow underground • Fronds • Fern leaves, divided into many smaller parts that look like small leaves • The cuticle is found on the upper surface of each frond, helps retain plant water • Tiny spore cases are found on the underside of the fronds HORSETAILS • Seedless, vascular plant • Stems are jointed • Long, coarse, needle-like branches • Resemble a horse’s tail • Silica • Stem contains a gritty substance also found in sand CLUB MOSSES • Seedless, vascular plant • Not to be confused with moss • Grow in moist woodlands and near streams