Types of Seed Plants
advertisement

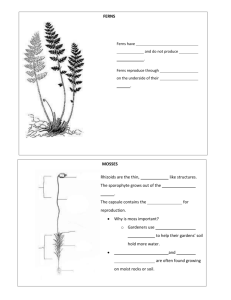
NONVASCULAR PLANTS Definition: Plants that lack a well—developed system of tubes for transporting water and other materials Examples: Mosses, Liverworts, and Hornworts Description: Low-growing, only a few centimeters tall Where They Live: Damp, shady places Obtains Water: By directly absorbing it from their surroundings, cell to cell VASCULAR PLANTS Definition: Plants that have a well—developed system of tubes for transporting water and other materials Examples: Seedless (ferns, club mosses, & horsetails) Seeds (rice, peas, squash, cotton, flax, oak, pine, maples) Description: Grow quite tall Where They Live: Drier areas Obtains Water: By absorbing it through their roots Angiosperms Gymnosperms Flowering Plants Produce seeds that are enclosed in fruits (i.e. apples and oranges) Naked seeds; do not produce flowers Reproduce with cones Needle-like leaves or scale like leaves; deep growing root systems p. 272 Types of Seed Plants Examples of Nonvascular Plants Hornworts Moss Liverworts Examples of Seedless Vascular Plants Club Mosses Ferns Horsetails Examples of Vascular Plants with Seeds Cotton Red Maple Flax Plants Rice Plants Squash Plants