File
advertisement

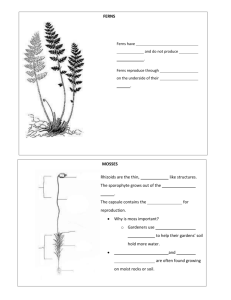
Chapter 3 Questions True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. Figure 9-1 ____ 1. Plant A in Figure 9-1 is a monocot. ____ 2. Plant B in Figure 9-1 is a monocot. ____ 3. Plant C in Figure 9-1 is a nonvascular plant. ____ 4. Plant D in Figure 9-1 is a dicot. ____ 5. Plant E in Figure 9-1 is a monocot. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 6. Of the following, which is NOT a vascular plant? a. moss c. fern b. pine tree d. horsetail 7. Ancient seedless plants compacted and eventually turned into the ____ we use today. a. coal c. minerals b. oil d. rubber 8. Of following, which is NOT an adaptation plants made to life on land? a. cell walls c. more complex reproduction b. a cuticle d. cell membrane 9. Of the following, which is NOT a characteristics of plants? a. have cell walls c. range in height b. have roots d. live only on land 10. Scientists think that plants evolved directly from ____. a. animals c. bacteria b. mosses d. green algae 11. Nonvascular plants include ____. a. ferns and horsetails c. liverworts and ferns b. horsetails and mosses d. mosses and liverworts 12. Nonvascular plants have all of the following EXCEPT ____. a. flowers c. spores ____ 13. ____ 14. ____ 15. ____ 16. ____ 17. ____ 18. ____ 19. ____ 20. ____ 21. ____ 22. ____ 23. ____ 24. ____ 25. b. rhizoids d. cell walls Moss plants are held in place by threadlike structures called ____. a. dicots c. guard cells b. rhizoids d. vascular tissue The first plants to grow in new environments are usually ____. a. ferns and horsetails c. liverworts and mosses b. grasses d. mosses and ferns Ferns are the most abundant of the ____ plants. a. gymnosperm c. nonvascular b. seedless vascular d. vascular ____ have unique, jointed stem structures. a. Club mosses c. Horsetails b. Ferns d. Spike mosses Peat is actually the earliest stage of ____. a. coal c. petroleum b. natural gas d. petrified wood The oldest trees alive are the ____. a. angiosperms c. monocots b. gymnosperms d. dicots ____ is a chemical compound that forms tangled fibers in the cell walls of plants. a. Stomata c. Cellulose b. Cambium d. Cuticle Of the following, which is NOT an example of a seed plant? a. peanuts c. oranges b. peat moss d. wheat The most common type of plants on Earth is ____. a. angiosperms c. nonvascular plants b. gymnosperms d. seedless vascular plants Roots have all of the following functions EXCEPT to ____. a. anchor the plant c. store food b. absorb water d. make food Stems have all of these functions EXCEPT ____. a. storing food and water b. absorbing soil nutrients c. supporting the plant d. moving materials between leaves and roots The major function of leaves is to ____. a. make food c. transport b. store food d. absorb nutrients Of the following, which is NOT a gymnosperm? a. gingoes c. flowering plants b. cycads d. conifers Yes/No Indicate whether you agree with the statement. Indicate which of the following are characteristics of seed plants by writing Y for yes and N for no. ____ 26. root systems ____ 27. leaves with stomata ____ 28. stems of various sizes ____ 29. produce spores ____ 30. produce seeds ____ 31. vascular tissue of phloem and xylem ____ 32. produce rhizoids Matching Match each term with the correct definition below. a. rhizoids e. moss b. liverworts f. cuticle c. pioneer species g. bogs d. cellulose ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. rootlike filaments made up of a few long cells are first to grow in new or disturbed areas means "herb for the liver" a waxy, protective layer on leaves of plants an organic compound found in plant cell walls a seedless, rootless plant with leaflike growths poorly drained areas with spongy, wet ground that is comprised mainly of dead and decaying plants Match each term with the correct definition below. a. vascular plants e. b. stomata f. c. phloem g. d. spongy layer h. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. palisade layer xylem guard cells cambium small pores on leaf surfaces allowing carbon dioxide in vessels that move food from leaves to other plant parts tissue that produces new xylem and phloem cells vessels that transport substances from the roots to other parts of the plant open and close stomata loosely arranged cell layer in the leaf closely packed cells under the epidermis of leaves plants that have tubelike structures for transporting substances Completion Complete each statement. 48. Mosses and liverworts that are among the first plants to inhabit a new environment are called ____________________ species. 49. Plants with vessels to transport water and nutrients are called ____________________ plants. 50. The primary difference between seedless vascular and nonvascular plants is that seedless vascular plants have ____________________ tissue. 51. All plants are many-celled, and most contain green pigment called ____________________. Seedless Vascular Plants Types Nonvascular Plants Characteristics Types Characteristics A C mosses H club mosses roots F stalks that look like stems B D G leaflike green growths E I Table 9-1 52. In Table 9-1, ____________________ are the missing data represented by A and B. 53. In Table 9-1, ______________________________ are the missing data represented by C, D, and E. 54. In Table 9-1, _________________________ are the missing data represented by F and G. 55. In Table 9-1, ______________________________ are the missing data represented by H and I.