nervous system outline PPT
advertisement
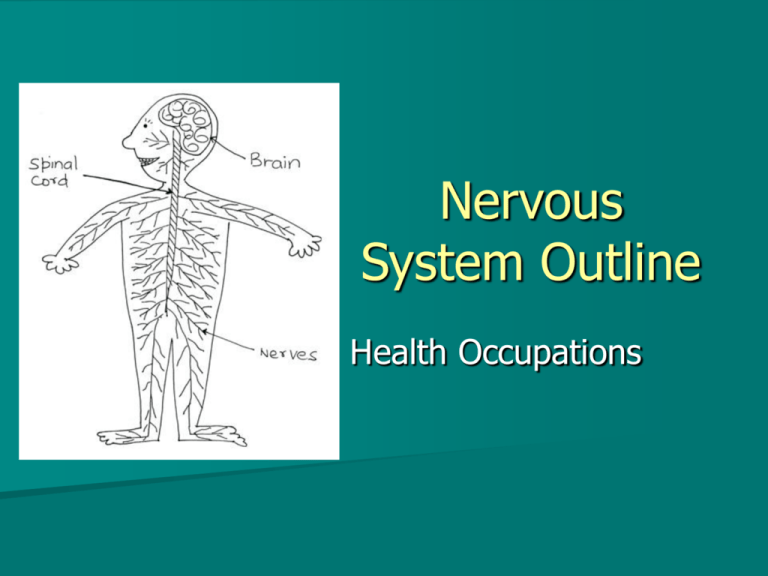
Nervous System Outline Health Occupations Nervous System Functions Directs the functions of all human body systems – 100 Billion Nerve cells Carry messages from brain to rest of body Neurons The basic element of nervous system Highly specialized Vary in function, shape, and size Separated by synapses – Gaps in between each neuron Neurotransmitters – Stimulates impulse to jump to next nerve Neurons 3 Parts – Cell Body Have fibers to reach out to send or receive impulses – Dendrites Thin branching extensions of cell body Conduct nerve impulses to cell body – Axon Conducts nerve impulses away from cell body Covered by a myelin sheath – Fatty tissue that makes impulse travel faster End of axon has fibers that let the impulse leave the nerve Neurons 2 Basic Properties – Excitability Ability to respond to a stimulus – Conductivity Ability to transmit a signal Neurons 3 Types – Efferent (motor) Carry information to muscles and glands from CNS – Afferent (sensory) Carry information from sensory system to CNS – Interneurons Carry and process sensory information Neuron bundles = Nerves Stimulus Receptor Nerve Receptor Impulse Neuroglias Support, connect, protect, and remove debris Do not transmit impulses Form blood-brain barrier – Permits some chemical substances to reach the brain’s neurons but blocks most others Central Nervous System (CNS) Consists of: – Brain – Spinal cord Center of Control CNS Functions Receives and interprets all stimuli Sends nerve impulses to instruct muscles and glands to take over or respond to certain actions Causes Voluntary and Involuntary actions Brain Divisions Brainstem Cerebellum Cerebrum Diencephalon Midbrain Brain Stem – Visual reflexes Pons – Controls certain respiratory functions Medulla Oblongata – Regulates heart & lung functions – Swallowing – Vomiting – Coughing – sneezing Cerebellum Coordinates musculoskeletal movement – Maintains balance – Posture – Muscle tone Cerebrum 2 hemispheres – Left and Right Cerebral Cortex – Conscious decision making Four Lobes – Frontal Moral Behavior, voluntary motor movements – Parietal Controls and interprets senses and taste – Temporal Memory, equilibrium, emotion, hearing – Occipital vision Diencephalon Deep portion of brain Contains: – Thalamus – Hypothalamus Relay center for sensations Controls: – Heart rate – Blood pressure – Temperature regulation – Water and electrolyte balance – Digestive functions – Glandular activities Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Fills the area between the brain and cranium Watery fluid that contains various compound Cradles and cushions brain Spinal Cord Extends from base of brain to first lumbar vertebrae in back Protected by: – Cerebrospinal fluid – Vertebral column – Meninges 3 layers of membranes that cover brain and spinal cord Meninges Dura Mater (outer layer) – Tough, fibrous – Contains channels for blood to enter brain tissue Arachnoid Mater (middle layer) – Web-like structure Pia Mater (innermost layer) – Contains blood vessels that nourish spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System 12 Cranial Nerves – Carry impulses to and from the brain 31 pairs of spinal nerves – Carry messages to and from the spinal cord and the torso and extremities of the body Peripheral Nervous System 2 Subsystems according to function – Somatic Nervous System – Autonomic Nervous System Somatic Nervous System Receive and process sensory input from the skin, muscles, tendons, joints, eyes, tongue, nose and ears Excite voluntary contraction of skeletal muscles Autonomic Nervous System Carry impulses from the central nervous system to glands, various involuntary muscles, cardiac muscle, and membranes Stimulates organs, glands and senses by stimulating secretions of substances Divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic – Operates when the body is under stress – Activates responses necessary to react in dangerous or abnormal situations – Fight or Flight response Parasympathetic – Operates to keep the body in homeostasis under normal conditions The End