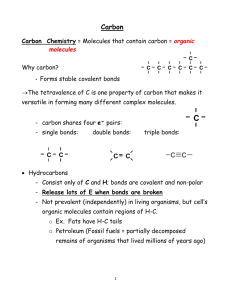
describe how hydrogen bonding occurs between water molecules
advertisement

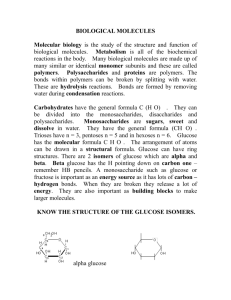
PIG describe how hydrogen bonding occurs between water molecules, and relate this, and other properties of water, to the roles of water in living organisms • Water is attracted to ions and polar molecules so is a good solvent • High specific heat capacity, so absorbs a lot of thermal energy preventing temperature changes in body • High latent heat, so lots of energy needed before evaporation meaning more heat absorbed by sweat • High cohesion between water molecules to draw water up xylem vessels • Water is reactive, so can be used in hydrolysis • Cannot be compressed so can form a hydrostatic skeleton e.g. earthworms Describe the structure of an amino acid Peptide bonds form between an amine group (NH2) and a carboxylic acid group COOH) R groups project from side of chain Properties are determined by the R group e.g. shape of active site How are peptide bonds formed and broken • Formed by condensation reaction • Peptide bond forms between the N and C • Water is produced as a result What does primary structure mean • The amino acid sequence • Determined by the gene that codes for a polypeptide What does secondary structure mean • The folding of a polypeptide into • Alpha helix or • A beta pleated sheet, a flat sheet that folds back on itself or links to adjacent polypeptides lying parallel to one another What does tertiary structure mean • Further folding of a polypeptide • Hydrogen bonds form anywhere on the polypeptide • Disulphide bonds between sulphur containing R groups (covalent bonds) • Ionic bonds between R groups (positive and negatively attracted to one another) • Hydrophobic interactions Describe haemoglobins tertiary structure • 4 polypeptides in each haemoglobin molecule called alpha and beta globin (2 of each) • In the middle is the haem group that is flat, circular and has an atom if iron in the centre • Each haem group combines loosely with one oxygen molecule • Each haemoglobin can carry four oxygen molecules Describe the structure of a collagen molecule • Fibrous protein • Three polypeptides wound tightly to form a triple helix • Glyceine every third amino acid so it can be wound tightly • Covalent bonds link the helices to make a strong fibre Compare the structure and function of a globular and fibrous protein • Globular proteins folded into 3D shapes e.g haemoglobin, enzymes • Fibrous have a linear 3D shape and are insouble e.g. collagen, keratin Describe the difference between alpha and beta glucose • Alpha glucose has H above Carbon 1 and OH below Carbon 1, • Beta has the opposite Describe a glycosidic bond • Bond between Carbon 1 and Carbon 4 of an adjacent glucose molecule, water is produced as a result Compare and contrast the structure and function of starch and cellulose • Starch: amylose and amylopectin • amylose- energy storage, single unbranched polymer forming a helix, • amylopectin is a branched chain with glycosidic bonds between carbon atoms 1 and 6 • Cellulose: strong for cell walls- polymer of beta glucose, alternate glucose molecules turned through 180 degrees, cellulose forms straight chains Diagram showing rotation Describe the structure of glycogen • Like amylopectin, Carbons 1 and 6 bond, but with more branches Describe the structure of cholesterol and steroids • Cholesterol = a lipid, polar at the OH end, 4 hydrocarbon rings and hydrocarbon tail are no polar, arranged in bilayers similar to a phospholipid • Steroids are made from cholesterol and have a four ring structure What is the chemical test for protein • Substance in test tube • Add biuret (copper sulfate and sodium hydroxide) • Positive = lilac • Negative = stays blue What is the chemical test for reducing sugars • • • • • Benedicts test Solution in test tube Add same vol of blue benedicts solution Heat to 80 degrees Positive = blue to green, then yellow then red with a precipitate • Negative = stays blue What is the chemical test for non reducing sugars • • • • • • • After negative result with benedicts Add hydrochloric acid Boil for a few minutes Add alkali to neutralise acid Carry out benedicts test Positive = blue to yellow then red Negative = stays blue What is the chemical test for starch • • • • Place substance on a tile Add yellow iodine Positive = blue/black Negative = stays yellow What is the chemical test for lipids • Crush material into ethanol • Filter and place ethanol into cold water into another test tube • Discard solid residue, ethanol will float on the water • Positive = white emulsion forms in the water Explain how concentration can be determined using colorimetry • Used to make benedicts quantitative • Colorimeter measures amount of blueness in solution • Light shines through solution and measures either absorbance (light absorbed by solution) or transmission (light that gets through solution)