Module 25- Banking and the Multiplier

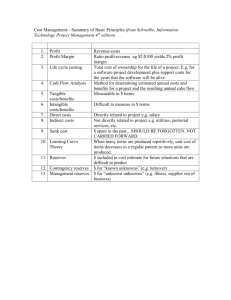
Module 25- Fractional Reserve Banking and the Money Multiplier
J.A.SACCO
Fractional Reserve Banking
Depository institutions are required by the Fed to maintain a specific percentage (reserve requirement) of their customers deposits as reserves
Three types of reserves!
Fractional Reserve Banking
Legal (Total) Reserves-
reserves that depository institutions are allowed by law to claims as reserves (deposits held at Federal Reserve District Bank and/or commercial bank vault cash.
Required Reserves-
the value of reserves that a depository institution must hold in vault cash or with the
Federal District Bank. These reserves are required to back its checkable deposits.
Fractional Reserve Banking
Excess Reserves-
the difference between legal reserves and required reserves. These reserves can be used as new loans and/or purchase government bonds & securities.
Excess Reserves = Legal Reserves- Required Reserves
Fractional Reserve Banking
Example: Total (Legal) Reserves is $20 B. and the
Reserve Requirement is 10%.
What is the required reserves? Excess reserves?
RR is $2B in deposits to be held in Fed District Bank or vault cash.
ER is $18 B. in new loans or to buy gov’t securities.
Reserves and Total Deposits
SACCO KEY POINT- New reserves are not created when checks written on one bank are deposited in another bank.
The bank writing the check will lose reserves, and the bank receiving the check will gain reserves.
Only when the Fed buys/sells securities from banks or the public, or when you put available cash in the bank are reserves increased/decreased and in turn the money supply.
Money Expansion by the Banking System
Why is the reserve requirement and excess reserves important?
How much will the money supply increase after you deposit
$100,000 cash into a commercial bank.
7
How Money is Created?
“Multiple Expansion of Checkable Deposits”
Assume a 10% Reserve Requirement
Bank
1
2
3
New Deposits
(new reserves)
$100,000
90,000
81,000
New Required
Reserves
$10,000
9,000
8,100
Maximum
New Loans plus Investments
(excess reserves)
$90,000
81,000
72,900
.
.
.
4 72,900
.
.
.
All other banks 656,100
Totals $1,000,000
7,290
.
.
.
65,610
$100,000
65,610
.
.
.
590,490
$900,000
The Money Multiplier
Money Multiplier
Gives the maximum potential change in the money supply due to a change in reserves
Potential money multiplier
1 required reserve ratio
Initial change in excess reserves x
Actual money multiplier
=
Actual change in the money supply
9
Forces that Reduce the Money Multiplier
Leakages
Currency DrainsPeople hold money in wallet. Don’t put money in bank to allow deposit expansion.
Excess ReservesBanks keep more as excess reserves.
How the Fed Controls the Money Supply
Fed Tools
Reserve Requirement
Increase
Macro. Effects
Contractionary
Money Supply
Interest rate
Investment
Decrease Expansionary
Money Supply
Interest rate
Investment
How the Fed Controls the Money Supply
Fed Tools
Discount/Federal Fund Rate
Increase
Macro. Effects
Contractionary
Money Supply
Interest rate
Investment
Decrease Expansionary
Money Supply
Interest rate
Investment
How the Fed Controls the Money Supply
Fed Tools
Open Market Operations
Sell Securities
“Sell Bonds, Small Bucks”
Macro. Effects
Contractionary
Money Supply
Interest rate
Investment
Buy Securities
“Buy Bonds, Big Bucks”
Most used by the Fed to expand the money supply. Why?
Expansionary
Money Supply
Interest rate
Investment
The Fed and the Money Supply
A.
B.
What has a greater affect on the expansion of the money supply:
$100 deposit of an individual into a commercial bank?
A Fed purchase of a government bond/security from a commercial bank for a $100?
Assume a 20% Reserve Requirement
The Fed and the Money Supply
A.
B.
C.
Money Multiplier?
Individual- RR= $20, ER= $80--- Expansion of Money
Supply is $400.
Fed- RR= $0, ER=$100--- Expansion of Money Supply is
$500.