Cost Management—Basic Principles - Seneca
advertisement
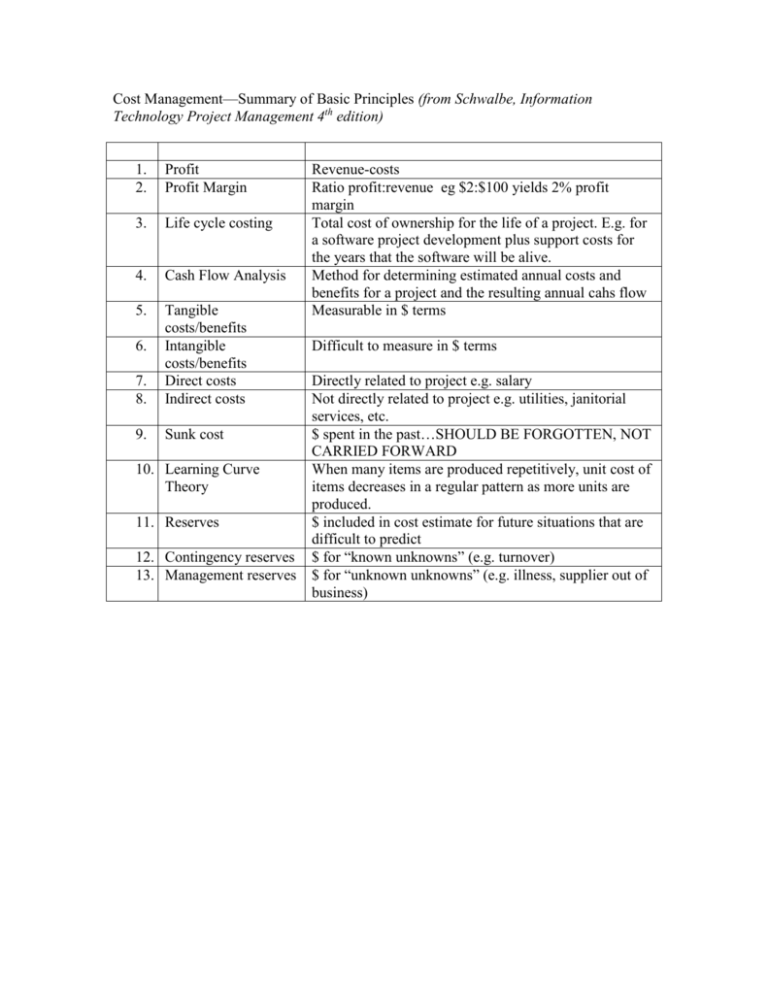
Cost Management—Summary of Basic Principles (from Schwalbe, Information Technology Project Management 4th edition) 1. 2. Profit Profit Margin 3. Life cycle costing 4. Cash Flow Analysis 5. 7. 8. Tangible costs/benefits Intangible costs/benefits Direct costs Indirect costs 9. Sunk cost 6. 10. Learning Curve Theory 11. Reserves 12. Contingency reserves 13. Management reserves Revenue-costs Ratio profit:revenue eg $2:$100 yields 2% profit margin Total cost of ownership for the life of a project. E.g. for a software project development plus support costs for the years that the software will be alive. Method for determining estimated annual costs and benefits for a project and the resulting annual cahs flow Measurable in $ terms Difficult to measure in $ terms Directly related to project e.g. salary Not directly related to project e.g. utilities, janitorial services, etc. $ spent in the past…SHOULD BE FORGOTTEN, NOT CARRIED FORWARD When many items are produced repetitively, unit cost of items decreases in a regular pattern as more units are produced. $ included in cost estimate for future situations that are difficult to predict $ for “known unknowns” (e.g. turnover) $ for “unknown unknowns” (e.g. illness, supplier out of business)