CHAPTER 3 LESSON 4 - WIKI-PAUL
advertisement

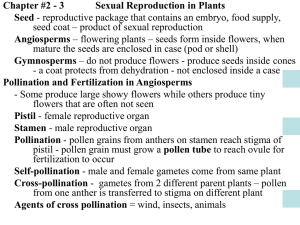
CHAPTER 3 LESSON 4 -Plants have complex life cycles that include two different stages, the sporophyte stage and the gametophyte stage -Sporophyte stage- the plant produces spores or seeds, tiny cells that can grow into new organisms -The spore develops into the plant's other stage (gametophyte) -Gametophyte stage- the plant develops two kinds of cells, sperm cells and egg cells -Angiosperms are classified based on the length of their life cycle -Annuals are flowering plants that complete a life cycle within one growing season (marigolds, petunias, wheat, cucumbers) -Biennials are angiosperms that complete their life cycle in two years (parsley, celery, foxglove) 1st year- grow roots, short stems, leaves 2nd year- lengthen their stems, grow new leaves, produce flowers and seeds -Perennials are flowering plants that live for more than two years -Most perennials flower every year -All plants undergo sexual reproduction that involves fertilization -Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell unites with an egg cell -A zygote is the fertilized egg -For algae and some plants fertilization can only happen if water is in the environment -Many plants can undergo asexual reproduction -New plants can grow from the roots, leaves, or stems of a parent plant -Asexual reproduction does not involve flowers, pollination, or seeds -Asexual reproduction can occur faster than sexual reproduction -Asexual reproduction can reproduce unfavorable traits since there is no new genetic material being passed to offspring -Scientists can take advantage of asexual reproduction- a single plant can be used to create identical plants for experiments -Scientists can copy plants with favorable characteristics -Grafting is a way to copy plants- part of a plants stem is cut and attached to another related plant species (orange and lemon). When the plant matures it can produce more than one type of fruit -Mosses, liverworts, hornworts, ferns, club mosses, and horsetails need to grow in moist environments -These plants release spores into their surroundings (they grow into gametophytes) -Gametophytes produce egg and sperm cells -Water must be available so the sperm can swim toward the eggs -Gymnosperm Reproduction: 1.Cone Production: -Most gymnosperms have reproductive cells called cones -Cones are covered in scales -Most gymnosperms (a single plant) produce male and female cones -In some gymnosperm plants, individual trees either grow male or female cones (not both) -Some gymnosperms produce no cones 2. Pollen Production and Ovule Development -Male cones produce pollen -The female gametophyte develops into structures called ovules -An ovule is a structure that contains an egg cell -Female cones contain at least one ovule at the base of each scale -Ovules develop into seeds 3. Egg Production: -Two egg cells form inside each ovule on the female cone 4. Pollination: -Transfer of pollen from male to female reproductive structure -Wind carries pollen -Pollen collects on a sticky substance made by the ovules 5. Fertilization: -After pollination, the ovule closes and seals in the pollen -Scales close -Sperm cell fertilizes egg cell inside each ovule -Zygote develops into the embryo part of the seed 6. Seed Development: -Female cones remain on tree while seed matures -Female cone gets bigger -It can take up to two years for seeds to mature -Male cones fall off the tree once they have shed their pollen 7. Seed Dispersal: -When seeds are mature the scales open -Wind shakes seed out of cone and carries them away -Angiosperm Reproduction: 1. Pollination: -Flowers are pollinated when a grain of pollen falls on the stigma -Animals and wind help the pollination process 2. Fertilization: -Pollen falls on the stigma -Sperm cell joins with egg cell inside the ovule (inside the ovary) -Zygote develops into the seed's embryo -Other parts of the ovule develop into the rest of the seed 3. Fruit Development and Seed Dispersal -Ovary turns into a fruit- The ripened ovary -One or more seeds are in the fruit -Apples, cherries, tomatoes, squash -Animals eat fruit help disperse their seeds by depositing them in new areas