Characteristics of Plants
advertisement

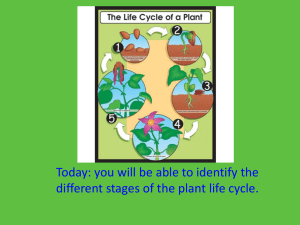
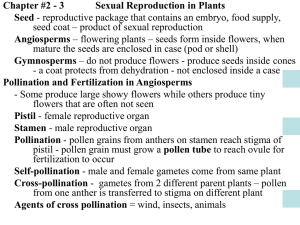
PLANTS CHARACTERISTICS OF PLANTS Cell wall containing cellulose Carry out photosynthesis using chlorophyll Most autotrophic; some are parasites or saprobes Sessile (can’t move) PLANT NEEDS: Sunlight- to carry out photosynthesis Gas Exchange- plant requires oxygen for cellular respiration & carbon dioxide to carry out photosynthesis Water & minerals- from the soil PLANT LIFE CYCLE Consists of two alternate generations : Gametophyte multi-cellular haploid organism that produces gametes by mitosis (either male or female) Fusion of gametes zygote that grows into a sporophyte Sporophyte multi-cellular diploid organism that produces spores by meiosis; spores germinate and grow into gametophytes VASCULARIZATION Tube-like elongated cells through which food and other materials are transported Xylem: transports water & minerals from the roots Phloem: transports sugar from leaves to other parts Roots: absorb water and minerals from the soil; anchors the plan to the ground Stem: provides support for growth Leaves: flat organ that traps light CHARACTERISTICS OF PLANTS Divided into 4 groups- based on embryo formation, specialized water conducting tissues, seeds and flowers Bryophytes Pteridophytes Gymnosperms Angiosperms SEEDLESS PLANTS (NON-VASCULARIZED) Bryophytes (Bryo means moss; phyte means plant) Mosses & Liverworts- attachment on a moss are not roots; they don’t absorb water and minerals like true roots Don’t contain true vascular system (can’t support tall plant) SEEDLESS PLANTS (VASCULARIZED) Pteridophytes (Pteris means fern; phyte means plant) Examples: ferns, horsetails, club mosses & whisk ferns The leaves (fronds) have a lacy appearance Found where there is a fair amount of moisture; needs moistures so spores can move for reproduction Fern Whisk Fern Horsetail SEED PLANTS Gymnosperms- bear seeds in cones (evergreens/conifers) Gymnosperm means “plant with naked seeds” Examples include: cycads, fir trees, fir, pine trees, cypress, spruce, ginkgo and redwoods SEED PLANTS Gymnosperm seeds are inside the cones: Pollen cones- male cones produce pollen grains; male gametophyte Seed cones- female cones; female gametophytes Cycle occurs in the spring male cone releases pollen; female cone captures the grains SEED PLANTS Angiosperms- bear seeds in flowers “Angio” means container; “sperm” means seed Flower contains ovaries that surround and protect the seeds After pollen reaches ovaries, ovaries develop into fruits (surround, protects & disperse the seeds)