Plant Reproduction: Asexual & Sexual Reproduction Worksheet
advertisement
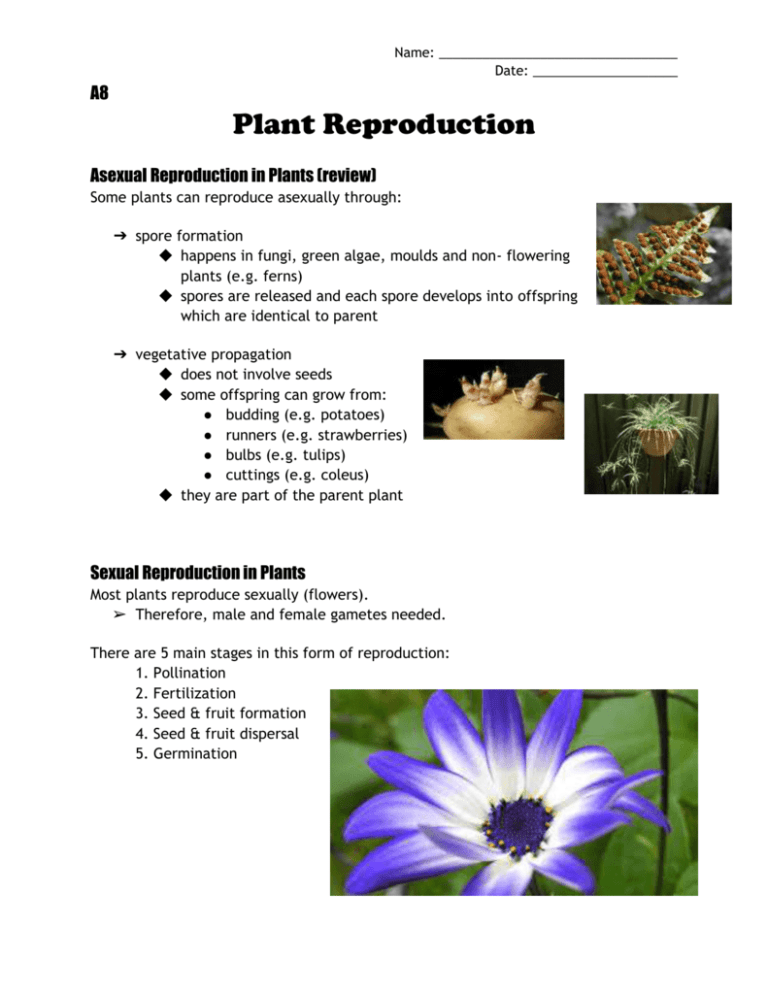
Name: _________________________________ Date: ____________________ A8 Plant Reproduction Asexual Reproduction in Plants (review) Some plants can reproduce asexually through: ➔ spore formation ◆ happens in fungi, green algae, moulds and non- flowering plants (e.g. ferns) ◆ spores are released and each spore develops into offspring which are identical to parent ➔ vegetative propagation ◆ does not involve seeds ◆ some offspring can grow from: ● budding (e.g. potatoes) ● runners (e.g. strawberries) ● bulbs (e.g. tulips) ● cuttings (e.g. coleus) ◆ they are part of the parent plant Sexual Reproduction in Plants Most plants reproduce sexually (flowers). ➢ Therefore, male and female gametes needed. There are 5 main stages in this form of reproduction: 1. Pollination 2. Fertilization 3. Seed & fruit formation 4. Seed & fruit dispersal 5. Germination Name: _________________________________ Date: ____________________ A8 Anatomy of a flower 1. Pollination - stamen is the male part and contains pollen - carpel or pistil is the female part and contains ovule (develops into seeds) Pollen grains from the anther are transferred to the stigma by the process of pollination. ● self-pollination: plant pollinates its own eggs ● cross-pollination: pollen from one plant pollinates another plant’s ovule Plants need pollinators to allow for the pollen to reach the female part of the plant: ● wind ● insects 2. Fertilization The joining of the male and female gametes to form a zygote. pollen (male) + ovule (female) ↓ single-celled zygote ↓ multi-celled embryo (contained in a seed) ↓ zygote (new individual) Name: _________________________________ Date: ____________________ A8 3. Seed & Fruit Formation Once fertilization is complete the ovule forms a seed. ● Like in humans, it begins as a zygote, and then an embryo. The ovary forms the fruit which surrounds and protects the seed. 4. Seed & Fruit Dispersal This dispersal allows for less competition for: light, food, space, and minerals. ● Dispersal is made possible by: wind, water and animals. 5. Germination The growth of a seed to form a new plant. ● water, oxygen and warmth are needed for this