Acc_Bio_Plants_Reproduction_kl_12
advertisement

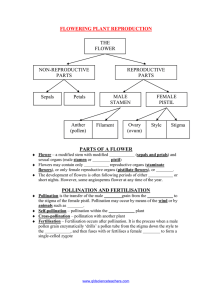
Plant Reproduction Asexual and Sexual (yes, sexual!) Asexual Reproduction Most plants reproduce asexually Does not require fertilization faster and requires less energy Results in clones of the parent plant genetically identical Vegetative propagation – a type of asexual reproduction in which new plants grow from nonreproductive plant parts Vegetative Propagation Stolons – runners from the stems of parent plant produce buds which grow into new plants crabgrass, aspen trees, strawberries Vegetative Propagation Rhizomes – specialized stems that grow underground bamboo and sumac trees Sexual Reproduction Usually requires two parent plants Generates diversity in offspring Flowers – reproductive structures in angiosperms Flower Anatomy Flower parts are arranged in 4 concentric whorls 1. Sepals – protect flower from damage when it is a bud 2. Petals – attract pollinators often very colorful Flower Anatomy 3. Stamens – male structure that produces pollen Anther – tip of stamen meiosis produces spores develop into pollen grains (contain sperm cells) Filament – supports anther Flower Anatomy 4. Pistil – female structure that produces ovules Stigma – sticky tip that receives pollen Style – narrow structure that leads pollen to ovary Ovary – develops into fruit and produces eggs in ovules ovules develop into seeds Flower Anatomy Flowers may or may not have all four of the basic flower parts Complete – has all four flower parts Incomplete – lacks any one of the four parts “Perfect” flowers – has both stamens (male) and pistils (female) “Imperfect” flowers – lack either stamens or pistils Sexual Reproduction Steps in Sexual Reproduction 1. Maturation of ovules 2. Pollination 3. Fertilization 4. Seed germination Pollination Pollen is transferred from an anther to a stigma Pollination Pollen can be carried by: Wind Water Insects Birds Bats Fertilization Fertilization – When the sperm and egg unite. Occurs inside the ovule. The zygote develops into the embryo. Another sperm fertilizes polar nuclei to form endosperm (food storage) Germination Germination – A plant emerges from the seed and begins to grow Germination Conditions necessary for seed germination Proper temperature Water Steps in Seed Germination 1. Seed absorbs water and swells 2. Primary root develops 3. Shoot begins to grow 4. Cotyledons begin to shrivel Review 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Pollen develops Pollination occurs Upon pollination, stigma sends out pollen tube that grows through the style to the ovary Sperm enters ovule (contains egg) – site of fertilization One sperm fertilizes egg and forms zygote Another sperm fertilizes polar nuclei to form endosperm (food storage) Zygote becomes plant embryo Ovule becomes seed Ovary develops into fruit that surrounds seed Click here for BrainPop Pollination Animation