5.-Plant-Life-Cycle - Walama Restoration Project
advertisement

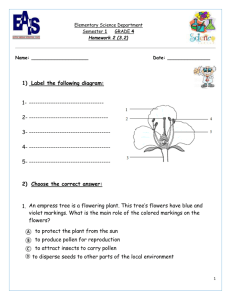
Lesson 5. Plant Life Cycle Class Discussion: What does the life cycle of a plant look like? Annuals: Plants with a life cycle of one year that die after the seeds are made. Perennials: Plants that survive for many growing seasons. Class Discussion: How do the seasons affect plant life cycles? The plant life cycle is influenced by temperature and the photoperiod: the period of daylight in a day. As days lengthen, warmth and light trigger plants and seeds to come out of dormancy and begin growing. Class Discussion: How are seeds formed? 1. Flowers: Flowering plants are called angiosperms. The flower’s purpose is reproduction. Flowers bud, bloom and wilt. 2. Pollination: Many flowers have male and female parts. The Pistil is the female part. At the top of the pistil is a sticky pad called the Stigma that catches the pollen. Pollination happens as a result of pollinators moving from flower to flower, by wind or water. 3. Fertilization: When the genetic material from pollen unites with the egg to form a new seed, fertilization happens. Fertilization is different than pollination. 4. Seed: A seed contains the mature fertilized ovule (egg). It has an outer seed coat that protects the seed. Inside, a seed contains a plant embryo (baby plant) and food for its growth. Seeds come in a variety of shapes and sizes and they take various amounts of time to germinate. A seed can be a monocot or a dicot; depending on how many cotyledons it has. 5. Germination: Germination is the process by which the plant embryo (baby plant) within the seed grows and the seedling breaks through the seed coat. Germinate = sprout. Review Questions: What is the difference between pollination and fertilization? How are the life cycles of annual and perennial plants different? How do the seasons in the Northwest affect plant life cycles? Worksheet & Activity: On the overhead or chalkboard, create a follow-along drawing that demonstrates the life cycle of a flowering annual plant through the four seasons. Do the same for a perennial. Have students label their annual drawings: Spring germination/ summer pollination and fertilization/ fall seed dissemination/ winter death. Lesson 5. Plant Life Cycle Have students label their perennial drawings: Spring germination and regrowth/ summer pollination and fertilization/ fall seed dissemination/ winter dormancy. Vocab: Angiosperms are flowering plants. Pollination is when pollen lands on a flower’s stigma. Fertilization is when genetic material from pollen enters the egg and they fuse to create an embryo that will mature into a seed. Cotyledons are embryotic leaves that become the first leaves of a plant. Germination is when the seed sprouts. Annual is a plant that only lives one year. Perennial is a plant that lives many years. Photoperiod is the period of daylight in a day.