Taxonomy - Canton Local Schools
advertisement

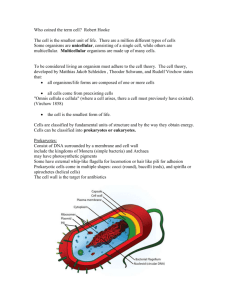
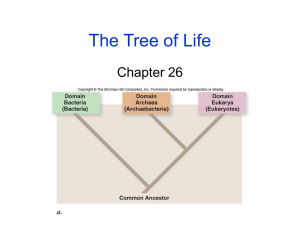
Taxonomy • Taxonomy- the practice and science of classification – Why do scientists classify organisms? • Used to organize living things into groups so that they are easier to study • Helps identify the relationship between organisms • Helps to avoid confusion in naming and identifying organisms • Taxon- divisions with subdivisions; from the most specific taxon (species) to the most general (kingdom) • Naming species – Species- group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring – Each species is identified by a binomial Latin name, which refers to both the genus and species, with genus capitalized and species in lower case. The whole thing is italicized or underlined • Human = Homo sapiens • Great White Shark = Carcharodon carcharias • Megalodon Shark = Carcharadon megalodon • Current classification system – Three Domains- all life dividing into 3 Domains 1. Bacteria- single- celled microorganisms; they are prokaryotes, which means they have no nucleus or organelles in their cells 2. Archaea- single celled microorganisms; also prokaryotes. When first discovered (1977), considered bacteria. After further research, they have no close relationship to bacteria 3. Eukarya- organism with eukaryotic cells (nucleus and other membrane bound organelles) • 6 kingdoms 1. Eubacteria- prokaryotes, unicellular; found in every habitat on earth 2. Archaebacteria- prokaryotes; unicellular; more closely related to eukaryotes than bacteria; many species found in ocean 3. Protista- simple eukaryotes; either uni or multicellular without specialized tissues 4. Fungi- eukaryotes; unicellular and multicellular; heterotrophic decomposers 5. Plantae- eukaryotes; multicellular; cell walls; autotrophic photosynthesizers 6. Animalia- eukaryotes; multicellular; no cell walls; heterotrophic consumers • How scientists classify organisms – Methods: organisms can be placed into certain taxonomical groups based on their… • Morphology and anatomical structure • Biochemical structure (RNA, DNA, Protein sequences) • How scientists classify organims – Phylogeny-evolutionary history of organism • Phylogenetics- study of evolutionary relatedness among various groups of organisms, which is discovered through molecular sequencing data and morphological data • Phylogenetic tree- diagram showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities that are known to have a common ancestor