What is Work?
advertisement

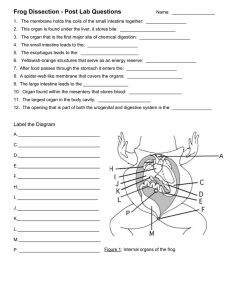
Levels of Organization Science Fair Checkpoint later this week! Create a Venn diagram Plants 2 Animals 2 2 Helping Questions: What are they made up of? How do they get food? How do they reproduce? How do they get rid of wastes? How do they respond and change? Matching • What are the differences between animals and plants throughout the levels? • What are the similarities between animals and plants throughout the levels? Cells • Definition – The basis unit of life composed of mainly water, but also contain other substances that are essential for life • Examples: Red blood cell, nerve cell • Organelles: Mitochondrion, Nucleus, Chloroplast, Cytoplasm, Vacuole, Cell Wall, Cell Membrane • Prokaryotes – genetic material is NOT surrounded by a membrane, most are unicellular • Eukaryotes – genetic material IS surrounded by a membrane, contain organelles. Eukaryotic cells are larger than prokaryotic cells Tissue • Definition – groups of similar types of cells that work together to carry out specific tasks • Main types in animals: 1. 2. 3. 4. Muscle Connective Nervous Epithelial (skin) • Main types in plants: 1. Dermal (prevents water loss) 2. Vascular (transports water) 3. Ground (provides storage & support, site of photosynthesis) Organs • Definition – groups of different tissues working together to perform a particular job. • Examples– esophagus, stomach, large intestine, small intestine, rectum, tongue, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, lungs, nose, mouth, bronchi, diaphragm, pharynx, trachea, heart, arteries, veins, skin, brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves Organ System • Definition – groups of different organs that work together to complete a series of tasks • Examples: o Respiratory o Skeletal o Circulatory o Muscular o Digestive o Nervous Organism • Definition – an individual form of life that is capable of growing, taking in nutrients, and usually reproducing (organ systems working together) • Unicellular Eukaryotes: o Amoeba o Algae o Athlete’s foot • Multicellular Eukaryotes: o Humans o Animals 1. Why do organisms require different levels of cellular organization? 2. What are the 5 levels of organization? 3. Do unicellular organisms have levels of organization? Explain your answer. Complete the worksheet • Cells R Us