f212 health and disease
advertisement

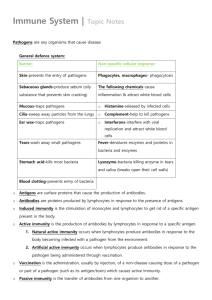
Health and Disease OCR AS Biology Unit 2 Module 2: Food and Health Learning Outcomes • Discuss what is meant by the terms health and disease • Define and discuss the meanings of the terms parasite and pathogen What is health? • “health is more than just the absence of disease” – What is meant by health? – What is meant by disease? • Health – absence of disease • Disease – disorder of a systems normal functions What is health? • You have been given 6 case studies • In your groups – discuss the health of each individual – Rank them from 1 – 6 • 1 healthiest • 6 unhealthiest – Remember you must be able to give reasons for your choices Definitions • Health – A state of complete physical, mental and social well-being, which is more than just the absence of disease. • Disease – A problem with mind or body leading to a departure from good health. Good Health • Free from disease • Able to carry out mental and physical tasks expected by society • Well fed, balanced diet • Housing and sanitation • Happy and positive outlook • Well integrated into society The Health Triangle • Physical health means the health of the body • Mental health means the health of the mind. • Social health means forming good relationships. The Health Triangle Physical Social Mental • If you take any of these away - the triangle collapses What is health? • In your groups – Go back to the original 6 case studies – Have your opinions changes – Rank them from 1 – 6 • 1 healthiest • 6 unhealthiest – Remember you must be able to give reasons for your choices Disease • There are nine broad overlapping categories of disease (see handout) • Diseases can also be grouped into – Single cause e.g. malaria – Multifactorial e.g. heart disease Disease • Acute – Sudden rapid changes and lasting for a short time • Chronic – Long term – debilitating – Develops slowly and persists pathogen • Infectious diseases are diseases caused by pathogens. • A pathogen – is defined as an organism which causes disease – Lives by taking nutrition from the host – May cause damage to the host • Disease transmission is the transfer of a pathogen from infected to uninfected people Parasite • A parasite is defined as – Organisms that live in or on another living things – Benefit at the hosts expense – Can be • Internal parasite e.g. tapeworm • External parasite e.g. head louse Infectious Disease • Organisms that can cause infectious disease include – – – – Bacteria e.g. cholera and TB Fungi e.g. athlete’s foot and ringworm Virus e.g. cold, influenza and AIDS Protoctista e.g. amoeboid dysentery, malaria Learning Outcomes • Describe the causes and means of transmission of malaria, AIDS/HIV and TB (symptoms not required) • Describe the global impact of malaria, AIDS/HIV and TB Infectious diseases • A pathogen can: – – – – Gain entry to the host Colonize the tissues of the host Resist the defences of the host Cause damage to host tissues Transmission • The most common forms of transmission are – By means of a vector – By physical contact – By droplet infection • Malaria and tuberculosis – Pathogens invade cells and spread through the tissues • HIV – Virus can lie dormant in T lymphocytes – Weakens the immune system to opportunistic infections (AIDS) Malaria • Causative organism – Protoctista – genus Plasmodium – P. falciparum is the most widespread • Methods of transmission – insect vector – Female Anopheles mosquito – See diagram • Global distribution – Widely distributed through the tropics and sub tropics – Annual incidence • 300 million – Annual mortality worldwide • 1.5 – 1.7 million Malaria • Global impact – Increasing drug resistance by Plasmodium – 40% of world’s population live in malarial areas – Difficulty in developing a vaccine – Increase in epidemics as environmental and climatic changes favour mosquitoes – Mosquitoes are developing resistance to insecticides • Control measures – Use sleeping nets to prevent mosquitoes biting at night – Use of drugs to fight of Plasmodium – Reduce mosquito populations • drain marshes and swamps • destroy mosquito larva – oil or insecticide on water, use carnivorous fish TB (tuberculosis) • Causative organism – Mycobacterium tuberculosis – Mycobacterium bovis • Methods of transmission – inhalation of droplets from infected person – via infected milk • Global distribution – Worldwide in developing countries and among migrants and inner cities in developed countries – 8.8 million new cases every year – 1.5 million deaths TB (tuberculosis) • Global impact – Some strains are resistant to drugs (1950’s) – AIDS pandemic – Poor housing and rising homelessness – Breakdown of TB control programmes • Control measures – Contact tracing, • through testing for bacteria and screening for symptoms – 2005 – BCG vaccine ruled ineffective – DOTS (directly observed short course treatment) – Long course of antibiotics HIV/AIDS • Causative organism – Human Immunodeficiency Virus • Methods of transmission – Body fluids, esp. semen, vaginal fluids and blood – Sexual intercourse, – shared needles, – child birth, breast feeding – Infected blood products • Global distribution – World wide – Highest prevalence in subSaharan Africa and Southeast Asia HIV/AIDS • Global impact – 39.5 million people living with HIV – 2006 • 4.9 million new cases • 2.9 million deaths from AIDS – Affects the affluent and the impoverished – TB is an associated opportunistic infection • Control measures – Use of condoms – Health education (safe sex) – Screening of blood donations – Heat treatment of blood products to kill viruses – Needle exchange schemes – Contact tracing Immunity Module 2: Food and Health Health and Disease Learning Outcomes • Define the terms immune response, antigen and antibody. • Describe the primary defences against pathogens and parasites (including skin and mucous membranes) and outline their importance. • Describe, with the aid of diagrams and photographs, the structure and mode of action of phagocytes. Definitions • Immune response – Specific response to a pathogen – Involves the action of lymphocytes and the production of antibodies • Antibodies – Protein molecules produced and released in response to a antigen • Antigen – Foreign molecule – protein or glycoprotein – Provokes an immune response Primary Defences • The body’s primary defences attempt to stop pathogens from entering body tissues • This includes – – – – The skin (epidermis) Mucous membranes Eyes protected with tears Ear canal lined with wax Epidermis • The outer layer of the epidermis is a layer of dead cells which contain the fibrous protein keratin. • These cells are produced in the process keratinisation – the cells dry out and the cytoplasm is replaced with keratin. • This layer of cells acts as a barrier Mucous membranes • Mucous membranes protect surfaces which are at risk of infection • Mucus is secreted by the epithelial linings of airways, digestive system and reproductive systems • In the airways ciliated cells move mucus up to the mouths where it can be swallowed • In the stomach, hydrochloric acid kills most pathogens that we ingest. Secondary Defences • Non-specific immune response – Phagocytes • Specific Immune response – B and T lymphocytes – Antibody production Phagocytosis • Phagocytes engulf and digest pathogenic cells • Neutrophils – found in the blood and body tissues – Collect at an area of infection • Macrophages – Travel in blood as monocytes – settle into the lymph nodes where they develop – Stimulates production of T lymphocytes Phagocyte - photographs Neutrophil Macrophage Macrophage engulfing tuberculosis bacterium Stages in phagocytosis • Pathogens are recognised by antigens on their surface • Phagocyte moves towards pathogen and receptors on the cell surface membrane attach to antigens on the pathogen • Phagocyte engulfs the pathogen creating a phagosome • Lysosomes fuse with the phagosome releasing digestive enzymes • End products absorbed into the cytoplasm. Phagocytosis Animations • http://www.microbelibrary.org/images /tterry/anim/phago053.html Stages of Phagocytosis Learning Outcomes • Describe the structure and mode of action of T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes, including the significance of cell signalling and the role of memory cells. • Describe, with the aid of diagrams, the structure of antibodies. • Outline the mode of action of antibodies, with reference to the neutralisation and agglutination of pathogens. Immune Response • Immune response is the activation of lymphocytes in the blood to help fight disease – T- Lymphocytes • Produced in bone marrow • Mature in the Thymus – B-Lymphocytes • Produced and matures in bone marrow Immune response • Pathogen enters body • Clonal selection – Antigens bind to complementary glycoproteins on B and T lymphocytes – This stimulate the immune response • Clonal expansion – B and T lymphocytes divide by mitosis T-lymphocytes • T lymphocytes divide into 3 types of cell – T helper cells (Th) • Release cytokines – stimulate B cells to develop – Stimulate phagocytosis (cell signalling) – T killer cells (Tk) • Attack and kill infected body cells – T memory cells (Tm) B lymphocytes • B lymphocytes develop into two types of cell – Plasma cells (P) • Flow in blood • Manufacture and release antibodies – B memory cells (Bm) • Immunological memory – Remain in blood for a number of years – Stimulate the production of plasma cells quickly upon reinfection by same pathogen. Cell signalling in immune response • Identification of pathogens • Sending distress signals • Antigen presentation • Instructions – Communication using cytokines Stages in immune response • Infection and reproduction of pathogen • Presentation of antigens • Clonal selection • Clonal expansion • Differentiation (proliferation) • Action – antibody production Antibodies • Proteins a.k.a. immunoglobulins • Specific shape complementary to that of an antigen • Antibody shape – 4 polypeptide chains held together by disulphide bridges – Variable region • 2 binding sites specific to an antigen – Hinge regions allow flexibility Antibody structure Mode of action of antibodies • Neutralisation – Antibodies bind to toxins neutralising their effects – Antibodies combine to viruses and prevent them from entering the cell. • Agglutination – Pathogen clump together • Too large to enter host cells • Helps phagocyte to engulf and digest pathogens Learning outcome • Compare and contrast the primary and secondary immune responses. Primary Immune response • Production of plasma cells • Antibodies produced to combat infection • Takes a few days for number of antibodies in blood to rise Secondary immune response • B memory cells circulate in blood • Rapidly produce plasma cells upon reinfection • Plasma cells produce antibodies • Rapid response Primary and secondary immune response Learning Outcomes • Compare and contrast active, passive, natural and artificial immunity. • Explain how vaccination can control disease. • Discuss the responses of governments and other organisations to the threat of new strains of influenza each year Immunity • Natural immunity – gained as part of normal life processes • Artificial immunity – Gained by deliberate exposure to antibodies or antigens • Active immunity – Results from stimulation of immune response • Passive immunity – Introduction of antibodies – Short lived Immunity Immunity Active Passive Natural Long term immunity Infected by the disease inducing an immune response Takes time Immediate protection Antibodies from mother -Across placenta -In colostrum (breast milk) Short term immunity Artificial Long term immunity Immunisation or vaccination Takes time Immediate protection Injected with antibodies e.g. tetanus injections Short term immunity Vaccination • Vaccine – – – – Preparation of antigen Injected or given by mouth Stimulates primary immune response Boosters given to stimulate secondary immune response Antigenic material • Living attenuated micro-organisms – Can not cause symptoms – Multiply – E.g. TB, poliomyelitis • Dead micro-organisms – Harmless but induce immunity – E.g. typhoid, cholera • Preparation of antigens – E.g. hepatitis B vaccine • Harmless toxin – E.g. tetanus vaccine Control of disease • Vaccinations can be used to control disease by providing immunity to all those at risk • Herd immunity – Use a vaccine to provide immunity to all of the population at risk • Ring immunity – Vaccinate everyone in surrounding area to prevent transmission of disease Influenza • Viral disease of the respiratory system • Associated with – – – – – Fever Sore throat Headache Muscle pains Weakness • Can lead to pneumonia • Can be fatal • New strains arise by mutations (some virulent) vaccination programmes • Epidemic – Disease suddenly spreads rapidly to infect many people • Pandemic – Large scale outbreak of a disease • Governments research and try to predict which strains of flu are going to appear each year Vaccination programmes in UK • All people aged over 65 • Young people with asthma • People who work in high-risk categories such as medical professionals • The strains of flu used in the immunisation programme change each year. Learning Outcomes • Outline possible new sources of medicines, with reference to microorganisms and plants and the need to maintain biodiversity. New Medicines • Why do we need new medicines – Pathogens become resistant to existing drugs e.g. antibiotics – New disease emerge – New vaccines needed e.g. HIV – Existing vaccines can be improved Discovery of New Medicines • By accident – E.g. Alexander Fleming and the discovery of penicillin • Traditional medicine • Anaesthetics • Observation of wildlife • Modern research Natural medicines • Discovery of natural drugs has concentrated on tropical plants due to the great diversity of species in tropical rainforests • Examples – Madagascan periwinkle – anticancer – Sweet wormwood – antimalarial • It is important that plant species do not become extinct before we can discover their value. Smoking and Disease Module 2: Food and Health Health and Disease Learning Outcome • Describe the effects of smoking on the mammalian gas exchange system, with reference to the symptoms of chronic bronchitis, emphysema (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) and lung cancer. Smoking - Intro • WHO considers smoking to be an epidemic • Cigarette smoke contains – Tar – a group of chemicals including carcinogens – Carbon monoxide – nicotine Reasons to give up smoking Short term effects of Tar • Tar settles in linings of airways and alveoli – Inceases diffusion distance of gases – Chemicals can cause an allergic reaction • Lumen of airway narrows restricting air flow. – Paralyses cilia – Mucus secreting cells enlarge – produce more mucus – Increase risk of infection Long term effects of tar • Smokers cough – – – – Irritation of airways Damages lining of airways and alveoli Lining replaced by scar tissue Smooth muscles thickens, lumen narrows and airflow is permanently restricted. Diseases linked with smoking • Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary disease – Combination of diseases that includes • Asthma • Chronic bronchitis • emphysema Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Chronic Bronchitis • Inflamed lining • Smooth muscle layer thickens • Goblet cells and mucus glands secrete more mucus • Damage to cilia • Symptoms – – – – Shortness of breath Wheezing Persistent cough Increase risk of lung infection Emphysema • Loss of elasticity of alveoli • Alveoli burst • Air spaces are larger reducing surface area for gas exchange • Symptoms – Shortness of breath – Difficulty exhaling – Blood less well oxygenated – fatigue Lung Cancer • Cigarette smoke contains carcinogenic compounds including benzopyrene – Carcinogens enter cells of lung tissue – Mutation affects the gene controlling cell division – Uncontrolled cell division leads to a tumour – Bronchi become blocked by cancerous growths Symptoms of lung cancer • persistent cough • Coughing up blood • Weight loss • Pain in chest Learning Outcomes • Describe the effects of nicotine and carbon monoxide in tobacco smoke on the cardiovascular system with reference to the course of events that lead to atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease and stroke. Nicotine and carbon monoxide • Nicotine and carbon monoxide pass from the lungs into the circulation • Changes occur that can lead to – Atherosclerosis – Coronary heart disease – stroke Nicotine • Addictive drug • stimulant • Releases adrenaline which increases heart rate and blood pressure • Stimulates decrease in blood flow to extremities • Increases chance of blood clots • Makes platelets sticky Carbon monoxide • Enters red blood cells and combines with haemoglobin to form carboxyhaemoglobin • Reduces oxygen carrying capacity of the blood • Damages linings of arteries Cardiovascular disease • Multifactorial – There is a number of risk factors – Of which smoking is just one • Degenerative disease of the heart and circulatory systems • 20% death worldwide • Up to 50% developed countries Atherosclerosis • Atherosclerosis – Accumulation of fatty material (atheroma) in artery walls, reducing flow of blood to the tissues – Reduces the size of the lumen – Reduces blood flow Definitions • Atheroma – Contains cholesterol, fibres, dead muscle cells and platelets • Plaques – Build up of atheroma – Make arteries less elastic and reduce the flow of blood atherosclerosis Stages in development of Atherosclerosis • Damage to endothelium of arteries • invasion of phagocytes to repair damage • Secretions from phagocytes stimulate growth of smooth muscle and the accumulation of cholesterol • Atheroma builds up • Atheroma forms plaque • Size of lumen reduced, Blood flow reduced Stages in atherosclerosis Thrombosis • Blood flow past the plaque is not smooth which increases the risk of blood clotting. • Thrombus – Blood clot in artery which stops flow – May dislodge and be carried in the blood Coronary heart Disease • Lumen of coronary arteries narrowed by plaque • Reduces the blood flow to heart muscles • 3 forms – Angina – Heart attack / myocardial infarction – Heart failure Stroke • Death of part of the brain • Can be sudden • Two causes – Thrombus • Blood clot blocks a narrow artery in the brain – Haemorrhage • an artery leading to the brain burst • Aneurysm = weakness in wall of artery Learning Outcomes • Evaluate the epidemiological and experimental evidence linking cigarette smoking to disease and early death. Epidemiology • The study of the distribution of diseases in order to find a means of preventing and controlling it. • Epidemiological studies – Identify links between disease and risk factors – Identifies which countries / age range / gender may be at greater risk. Epidemiological studies • Information gained can be used to: – – – – – Target funding Target research Target screening Target education and advice Predict future incidences of the disease Smoking and diseae • 1950’s doctors first noticed a correlation between lung cancer and smoking. • About half of smokers die of smoking related diseases • Smokers are three times more likely to die in middle age than non-smokers Linking smoking to lung cancer • if stop smoking the risk of lung cancer decreases • Smokers 18 times more likely to develop lung cancer than non smokers • 25% smokers die due to lung cancer Linking smoking to lung diseases • 98% emphysema sufferers are smokers • 20% smokers suffer emphysema • smokers twice as likely to die from pneumonia and influenza • COPD is rare in non smokers Linking smoking to CVD • This is less evident as CVD are multifactorial • However, substances in cigarette smoke can influence the cardiovascular system and likely to enhance atherosclerosis IMPORTANT POINT All conclusions drawn by epidemiological data show an association and not a causal link. Experimental Evidence - Dogs • Dogs exposed to unfiltered smoke developed changes similar to COPD and early signs of lung cancer. • Dogs smoking filtered cigarette smoke developed changes which can lead to lung cancer Experimental evidence - Tar • Chemical analysis of tar shows that it contains known carcinogens • When painted onto the bare skin in rats the tar caused cancer in the skin cells.