Unit 10 Chapter 39 Immunity from Disease

Unit 10
Chapter 39
Immunity from Disease
The Nature of Disease
Pathogens
Disease producing agents, such as, bacteria, viruses, protozoans, fungi & other parasites
Infectious disease
Any disease caused by the presence of pathogens in the body
The Nature of Disease
Koch’s postulates of 1884
(a procedure to establish the cause of a disease)
1) A pathogen must be found in the body of a sick organism
2) The pathogen must be isolated & grown in the lab to produce a culture
3) When the cultured pathogen is placed in a new host, it should cause the same disease
4) The pathogen should be isolated from the new host and shown to be the original pathogen
The Nature of Disease
Endemic disease
Disease that are constantly present in a population (ex: common cold)
Epidemic
When many people in a given area are affected with the same disease at about the same time (ex: influenza)
The Nature of Disease
Antibiotics
Substances produced by microorganisms that, in small amounts, will kill or inhibit the growth
& reproduction of other microorganisms
Ex: Penicillin, an antibiotic produced by a fungus, has been in use for over 50 years; many microorganisms are now resistant to penicillin
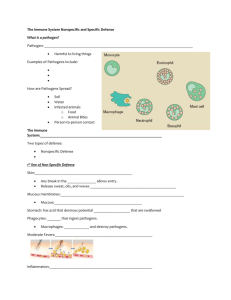
The Immune System
Innate Immunity
Your body’s own built-in defense system
First (& best) line of defense:
– Unbroken skin
– Body secretions, such as mucus, tears, sweat, & saliva
The Immune System
Second line of defense is inflammatory response:
Fever = increased body temperature slows or stops the growth of pathogens
Phagocytes = white blood cells, such as macrophages , that destroy pathogens
Interferon = proteins that protect cells from viruses
The Immune System
Third line of defense is cellular immunity:
Lymphocytes are types of white blood cells that defend the body against foreign substances
T cells are lymphocytes that defend against abnormal cells & pathogens inside livings cells
B cells are lymphocytes that provide immunity against antigens & pathogens in the body fluids
The Immune System
Lymph
Tissue fluid (to bathe, nourish cells) after it enters the lymph vessels that will return it to the blood
Lymph nodes
Glands that filter pathogens from the lymph before it returns to the bloodstream
The Immune System
Acquired Immunity
Defending against a specific pathogen by gradually building up a resistance to it.
Passive = acquired naturally when antibodies are transferred from mother to unborn child through the placenta
Active = acquired artificially when induced by vaccines
Nonspecific defense
Click on image to play video.
Cellular immunity
Click on image to play video.