Chapter 10
advertisement

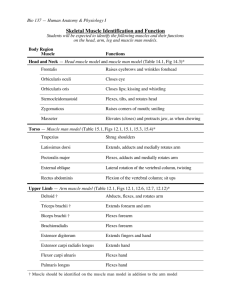
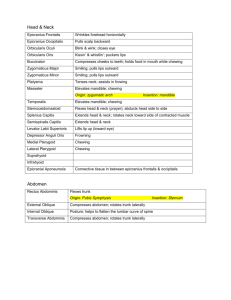
Chapter 10 Muscular System Three types of muscles 1) smooth muscles- involuntary muscles example: large and small intestines 2) Cardiac muscles- involuntary muscle example: heart 3) Skeletal muscles- voluntary muscles example: muscles attached to bones Function of Skeletal Muscles 1) Help maintain homeostasis 2) Produce body movements Skeletal Muscles There are more than 600 muscles in the body. 40 to 50 percent of our body is skeletal muscle. Connective tissue components Endomysium- covers specialized skeletal muscle fibers Perimysium- binding together fascicles Epimysium- sheath covering the muscle as a whole Three ways muscles are arranged 1) Size- small to large masses 2) Shape- broad, narrow, long, tapering, short, blunt, triangular, quadrilateral, irregular, flat sheets, or bulky masses 3) Arrangement- parallel to long axis, converge to a narrow attachment, oblique, pennate, bipennate, or curved Attachment of muscles 1) Origin- point of attachment that does not move when the muscle contracts 2) Insertion- point of attachment that moves when muscles contract Muscle actions 1) Prime movers (agonist)- muscle or group of muscles that directly performs a specific movement 2) Antagonist- muscle that, when contracting, directly oppose prime movers; relax while prime mover (agonist) is contracting to produce movement; provide precision and control during contraction of prime movers 3) synergists- muscles that contract at the same time as the prime movers; they facilitate prime mover actions to produce a more efficient movement 4) Fixator muscles- joint stabilizers Lever system Composed of 4 components 1) Rigid bar (bone) 2) Fulcrum (F) around which the rod moves (joint) 3) Load (L) that is moved 4) Pull (P) that produces movement (muscle contraction) Types of levers 1) First class leverfulcrum lies between pull and the load Not abundant in the human body; serve as levers of stability Types of levers 2) Second Class lever- Load lies between the fulcrum and the joint at which the pull is exerted Presence of these levers in the human body is a controversial issue Types of levers Third-class leversPull is exerted between the fulcrum and the load Permit rapid and extensive movement Most common type of lever found in the body Naming Muscles 1) Location, function, shape 2) Direction of fibers- named according to fiber orientation 3) Number of heads of divisions 4) Points of attachment- origin and insertion points 5) Relative size- small, medium, or large Read page 286 on hints on how to deduce muscle action Facial Muscles Occipitofrontals- Raises eyebrows, wrinkles forehead Orbicularis oculi- closes eyes Zygomaticus major- Laughing Orbicularis oris- Draws lips together Buccinator- Permits smiling (no Coach Bryant does not have this muscle) Muscles for Mastification Masseter- Closes jaw Temporalis- Closes jaw Muscles that move head Sternocleidomastoid- Flexes head, one muscle alone, rotates head toward opposite side Semispinalis capitis- Extends head; bends it laterally Splenius capitis- Extends head/ Bends and rotates head toward same side as contracting muscle Longissimus capitis- Extents head Muscles of the Thorax External intercostals- Elevate ribs Internal intercostals- Depress ribs Diaphragm- Enlarges thorax, causing inspiration Muscles of the Abdominal Wall External oblique- Compresses abdomen/ rotates trunk laterally Internal oblique- same as external oblique Transverse abdominis- same as external oblique Rectus abdominis- same as external oblique Muscles moving on Shoulder Girdle Trapezius- Raises or lowers shoulder and shrugs them Pectoralis minor- Pulls shoulder down and forward Serratus anterior- Pulls shoulder down and forward; abducts and rotates it upward Levator scapulae- Elevates and retracts scapula and abducts neck. Rhomboid major and minor- Retracts, rotates, fixes scapula Muscles moving upper arm Pectoralis major- Flexes upper arm, Adducts upper arm anteriorly Latissimus dorsi- Extends upper arm, Adducts upper arm posteriorly Deltoid- Abducts upper arm Coracobrachialis- Adduction Supraspinatus- Assist in abducting arm Teres minor- rotates arm outward Upper arm cont. Teres major- Assist in extension, adduction, and medial rotation of arm Infraspinatus- Rotates arm outward Subscapularis- medial rotation Muscles moving the Forearm Biceps brachii- flexes supinated forearm Brachialis- flexes pronated forearm Brachioradialis- flexes semipronated or semisupinated forearm Triceps brachii- Extends lower arm Pronator teres- Pronates and flexer forearm Pronator quadratus- Pronates forearm Supinator- Supinates forearm Muscles that move the hand Flexor carpi radialis- Flexes hand/forearm Flexor carpi ulnaris- Flexes hand/ adducts hand Extensor carpi radialis brevis- Extends hand Extensor carpi ulnaris- Extends hand/ Adducts hand Flexor digitorum- flexes fingers Extensor digitorum- extends fingers Muscles that move thigh Iliopsoas- Flexes thigh Rectus femoris- Flexes thigh/ extends lower leg Gluteal muscles (maximus- extends thigh/ medius- abducts thigh/ minimus- abducts thigh) Tensor fasciae latae- abducts thigh Adductor group- (brevis/longus/mangusadducts thigh) Gracilis- adducts tigh and flexes and adducts leg Muscles that move lower leg Quadriceps femoris group: Rectus femoris- Flexes thigh/ extends leg Vastus lateralis- Extends leg Vastus medialis- Extends leg Vastus intermedius- Extends leg Sartorius- Adducts and flexes leg Muscles moving lower leg cont. Hamstring group: Biceps femoris- Flexes leg Semitendinosus- Extends thigh Semimembranosus- Extends thigh Muscles move the foot Tibialis anterior- Flexes/ Inverts foot Gastrocnemius- Extends foot/ Flexes lower leg Soleus- Extends foot (planter flexion) Peroneus longus- extends foot Peroneus brevis- Flexes foot Peroneus tertius- Flexes foot Extensor digitorum longus- Dorsiflexion of foot/ extension of toes