File
advertisement

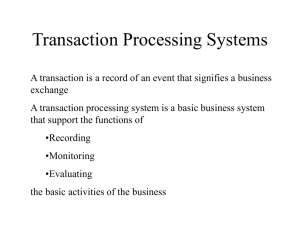
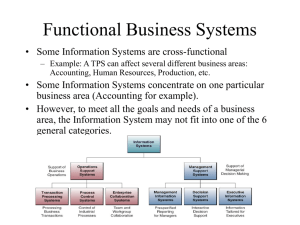
Information Systems & Enhancing Decision Making for the Digital Firm Rashedul Hasan Management Information Systems Chapter 13 Enhancing Decision Making for the Digital Firm DECISION MAKING AND DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS Business Decision Making and the Decision-Making Process Decision-Making Levels: • Senior management • Middle management and project teams • Operational management and project teams • Individual employees Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Types of Information Systems Figure 2-1 Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Different Kinds of Systems Three main categories of information systems serve different organizational levels: 1. Operational-level systems: support operational managers, keeping track of the elementary activities and transactions 2. Management-level systems: serve the monitoring, controlling, decision-making, and administrative activities 3. Strategic-level systems: help senior management tackle and address strategic issues Management Information Systems Chapter 13 Enhancing Decision Making for the Digital Firm DECISION MAKING AND DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS Information Requirements of Key Decision-Making Groups in a Firm Figure 13-2 Management Information Systems Chapter 13 Enhancing Decision Making for the Digital Firm DECISION MAKING AND DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS Types of Decisions Unstructured decisions: • Novel, non-routine decisions requiring judgment and insights • Examples: Approve capital budget; decide corporate objectives Management Information Systems Chapter 13 Enhancing Decision Making for the Digital Firm DECISION MAKING AND DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS Types of Decisions (Continued) Structured decisions: • Routine decisions with definite procedures • Examples: Restock inventory; determine special offers to customers Semi-structured decisions: • Only part of decision has clear-cut answers provided by accepted procedures • Examples: Allocate resources to managers; develop a marketing plan Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Major Types of Systems • Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) • Management Information Systems (MIS) • Decision-Support Systems (DSS) • Executive Support Systems (ESS) Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS The Four Major Types of Information Systems Figure 2-2 Management Information Systems Chapter 13 Enhancing Decision Making for the Digital Firm DECISION MAKING AND DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS Stages in Decision Making Figure 13-3 Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) • Basic business systems that serve the operational level • A computerized system that performs and records the daily routine transactions necessary to the conduct of the business Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS A Symbolic Representation for a Payroll TPS Figure 2-3 Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Typical Applications of TPS Figure 2-4 Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Management Information Systems (MIS) Management level • Inputs: High volume transaction level data • Processing: Simple models • Outputs: Summary reports • Users: Middle managers Example: Annual budgeting Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Management Information Systems (MIS) (continued) Figure 2-5 Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Management Information Systems (MIS) (continued) A sample MIS report Figure 2-6 Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Decision-Support Systems (DSS) Management level • Inputs: Transaction level data • Processing: Interactive • Outputs: Decision analysis • Users: Professionals, staff Example: Contract cost analysis Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Decision-Support Systems (DSS) (Continued) Voyage-estimating decision-support system Figure 2-7 Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SYSTEMS (ESS): • Inputs: Aggregate data • Processing: Interactive • Outputs: Projections • Users: Senior managers Example: 5 year operating plan Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Model of a Typical Executive Support System Figure 2-8 Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SYSTEMS (ESS) (Continued) • Top Level Management • Designed to the individual senior manager • Ties CEO to all levels • Very expensive to keep up • Extensive support staff Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Relationship of Systems to One Another Interrelationships among systems Figure 2-9 Management Information Systems Chapter 2 Information Systems in the Enterprise MAJOR TYPES OF SYSTEMS IN ORGANIZATIONS Relationship of Systems to One Another In contemporary digital firms, the different types of systems are closely linked to one another. This is the ideal. In traditional firms these systems tend to be isolated from one another, and information does not flow seamlessly from one end of the organization to the other. Efficiency and business value tend to suffer greatly in these traditional firms Management Information Systems Chapter 13 Enhancing Decision Making for the Digital Firm SYSTEMS FOR DECISION SUPPORT The Difference between MIS and DSS Management Information Systems: • Primarily address structured problems • Provides typically fixed, scheduled reports based on routine flows of data and assists in the general control of the business Management Information Systems Chapter 13 Enhancing Decision Making for the Digital Firm SYSTEMS FOR DECISION SUPPORT Decision Support Systems: • Support semistructured and unstructured problems • Greater emphasis on models, assumptions, ad-hoc queries, display graphics • Emphasizes change, flexibility, and a rapid response Management Information Systems Chapter 13 Enhancing Decision Making for the Digital Firm SYSTEMS FOR DECISION SUPPORT Types of Decision-Support Systems Model-driven DSS: • Primarily stand-alone systems • Use a strong theory or model to perform “what-if” and similar analyses Management Information Systems Chapter 13 Enhancing Decision Making for the Digital Firm SYSTEMS FOR DECISION SUPPORT Components of DSS • DSS database: A collection of current or historical data from a number of applications or groups • DSS software system: Contains the software tools for data analysis, with models, data mining, and other analytical tools • DSS user interface: Graphical, flexible interaction between users of the system and the DSS software tools Management Information Systems Chapter 13 Enhancing Decision Making for the Digital Firm SYSTEMS FOR DECISION SUPPORT Data-driven DSS: • Integrated with large pools of data in major enterprise systems and Web sites • Support decision making by enabling user to extract useful information • Data mining: Can obtain types of information such as associations, sequences, classifications, clusters, and forecasts Management Information Systems Chapter 13 Enhancing Decision Making for the Digital Firm SYSTEMS FOR DECISION SUPPORT Model: An abstract representation that illustrates the components or relationships of a phenomenon • Statistical models • Optimization models • Forecasting models • Sensitivity analysis (“what-if” models) Management Information Systems Chapter 13 Enhancing Decision Making for the Digital Firm SYSTEMS FOR DECISION SUPPORT Overview of a Decision-Support System Figure 13-4 Management Information Systems Chapter 13 Enhancing Decision Making for the Digital Firm SYSTEMS FOR DECISION SUPPORT Sensitivity Analysis Figure 13-5